5.5 Coding of Congenital Anomalies
On this Page
Expected time: 3 hours
Importance of Accuracy
It is critical to ensure that coding of the recorded diagnostic information is done correctly and accurately. Correct and accurate coding is:
- Central to the process of generating valid and reliable information within a congenital anomalies surveillance system
- Achieved by following a standardized coding system such as the ICD-10 or the more detailed ICD-10-RCPCH
Similarly, it is important to obtain the best possible clinical descriptions, so that a careful review and an accurate classification will result in assignment of the correct code(s) for the congenital anomaly. Precise clinical descriptions can improve the accuracy of disease classification and coding.
- Clinical descriptions are recorded on the data-collection tool or abstraction form during data collection.
- Photographs of external congenital anomalies can supplement the clinical description and help with proper and accurate coding.
Information should be coded and entered into an electronic system whenever possible, to allow for easy retrieval and analysis when needed for reporting purposes.
Activity 5.1
Ask participants to refer to Activity 5.1 in the Participant Workbook pdf icon[457 KB, 21 Pages, Print Only].
Have participants identify the diagnoses for each of the following congenital anomalies, and code each case. After enough time has been given to complete the activity, discuss responses aloud as a larger group.
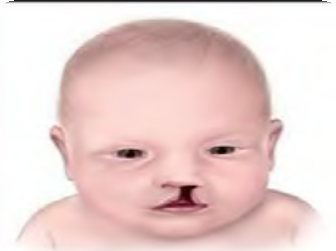
Baby 1
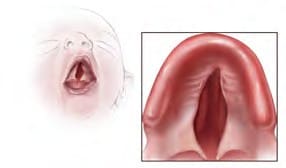
Baby 2
| Coding: ICD-10 or RCPCH | |
| Cleft palate | Q35.1, Q35.3, Q35.5, Q35.59, Q35.9, Q87.0 |
| Cleft lip | Q36.0, Q36.9, Q36.90, Q36.99 |
| Cleft palate with cleft lip | Q37.0, Q37.10, Q37.19, Q37.2, Q37.3, Q37.4, Q37.5, Q37.59, Q37.8, Q37.9, Q37.99 |
Responses:
- Baby 1: Unilateral cleft lip – Q36.90
- Baby 2: Cleft palate – Q35.5
Types of hypospadias
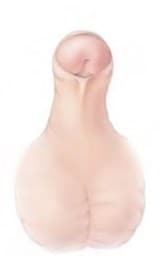
Subcoronal
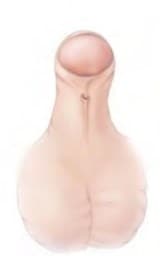
Midshaft
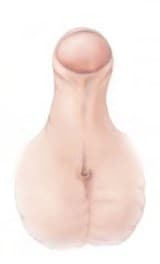
Penoscrotal
| Coding: ICD-10 or RCPCH | |
| Q54.0 | Hypospadias, balanic, Coronal, Glanular |
| Q54.1 | Hypospadias, penile |
| Q54.2 | Hypospadias, penoscrotal |
| Q54.3 | Hypospadias, perineal |
| Q54.8 | Other hypospadias |
| Q54.9 | Hypospadias, unspecified |
Responses:
- Subcoronal: Hypospadias, penile – Q54.1
- Midshaft: Hypospadias, penile – Q54.1
- Penoscrotal: Hypospdias, penoscrotal – Q54.2
Response: The correct diagnosis is craniorachischisis. The ICD-10-RCPCH code is Q00.1. Craniorachischisis refers to the presence of anencephaly with a contiguous spine defect without meninges covering the neural tissue (rachischisis). It may be limited to the cervical region or affect the entire spine.
Response: In cases in which anencephaly and spina bifida are present, but are not contiguous, both should be coded; however, when the malformations are counted, only anencephaly should be counted.
Ask participants
Activity 5.2
Ask participants to refer to Activity 5.2 in the Participant Workbook pdf icon[457 KB, 21 Pages, Print Only].
Review the photos in the activity and describe the cases on your answer sheet. For each description you wrote, write down the ICD-10 or ICD-10-RCPCH code and check your answers.
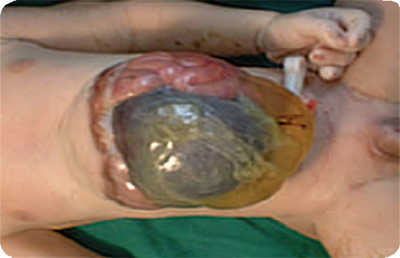
Omphalocele Q79.2
Large abdominal midline defect.
Some organs outside abdomen throughout the overstretched umbilical cord, the umbilical cord membrane covers the leaked intestine.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
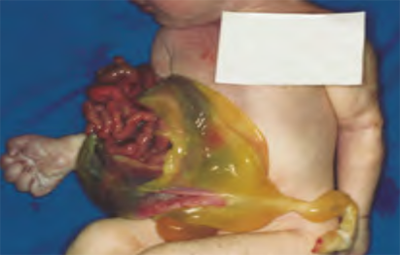
Omphalocele Q79.2
Very large abdominal midline defect.
Greater part of intestine outside abdomen through the overstretched umbilical cord (terminal part visible at lower left).
The translucent membrane is ruptured and covers only part of the herniated abdominal content.
Make sure you document the size (in cm).
Source: Birth defects surveillance: atlas of selected congenital anomalies (5)

Gastroschisis Q79.3
Small anterior abdominal defect on the right of the umbilical cord.
Most of small intestine outside of the abdomen through the abdominal opening.
The intestine outside of the body is not covered by any membrane.
Source: Birth defects surveillance: atlas of selected congenital anomalies (5)
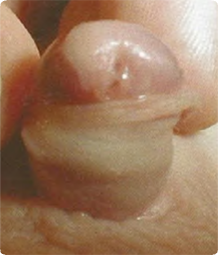
Glan(d)ular first degree hypospadias Q54.0
The external urethral meatus is not at the tip of the penis as it should be, but is on the ventral part of the glans.
Chordee not present (descended testes?)
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
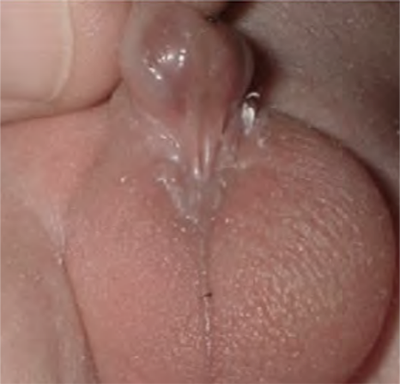
Glan(d)ular first degree hypospadias Q54.0
The external urethral meatus is not at the tip of penis but below the bases of the shat, just between the scrotal sacs.
Descended testes.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
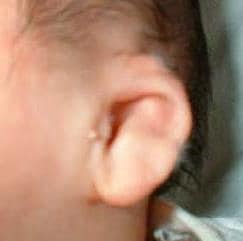
Microtia type II Q17.22
The left external ear is smaller than normal, the shape is simplified and some anatomical components are missing or abnormal. Upper portion of helix is missing.
Preauricular tags or pits present. Make sure you document the size (in cm).
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)

Microtia type III Q17.23
The right external ear is replaced by vertical rudiments of soft tissue (peanut shape) that do not conform to recognized ear components.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
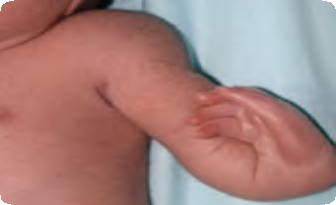
Transverse intercalary upper limb defect (true phocomelia) Q71.1
Bilateral and nearly symmetric defects of upper limbs.
Both defects are characterized by almost complete absence of arm and forearm, the hands are present but malformed with missing fingers.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
Radial (preaxial) deficiency Q71.4
Limb deficiency involving left forearm and hand.
The forearm is shorter than normal, with radial deviation of the hand.
The hand shows only four fingers and the thumb is missing (replaced by the second finger).
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
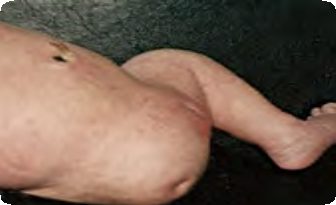
Transverse lower limb deficiency Q72.0
Complete absence of right lower limb.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)

Down syndrome Q90.9
Distinctive facial traits: upslanting palpebral fissures (Q10.3), flat nasal bridge (Q30.8).
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
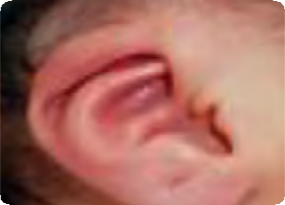
Misshapen ear Q17.3
Overfolded helix right ear. Make sure you measure the ear length (in cm).
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)

Congenital deformity of foot Q66.8
Wide gap between 1st and 2nd toe of left foot. Sandal gap.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
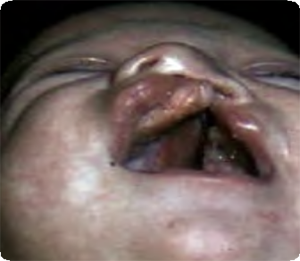
Cleft lip and palate unilateral Q37.10
Unilateral left clefting involving lip, nose, and palate.
Total schisis of lip, deformed nose, cleft palate (hard and soft).
No pits of lower lip.
Source: Birth defects surveillance: atlas of selected congenital anomalies (5)
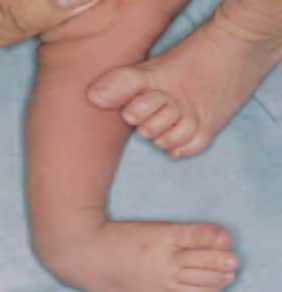
Talipes equinovarus Q66.0
Rigid (non-reducible) deformity involving right foot.
Plantar flexion (talus pointing down), deviation of heel (calcaneus) and forefoot (inward), foot rests on outer side (upward rotation).
Source: Birth defects surveillance: atlas of selected congenital anomalies (5)
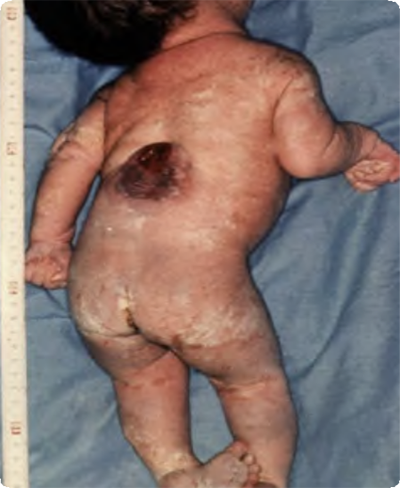
Thoracic spina bifida with hydrocephalus Q 05.1
Talipes equinovarus Q66.0
Midline spinal defect, lower thorax.
Rounded mass of degenerated spinal cord not covered by membrane. Possible hydrocephalus (head circumference 39 cm), bilateral talipes equinovarus.
Source: Birth defects surveillance: atlas of selected congenital anomalies (5)
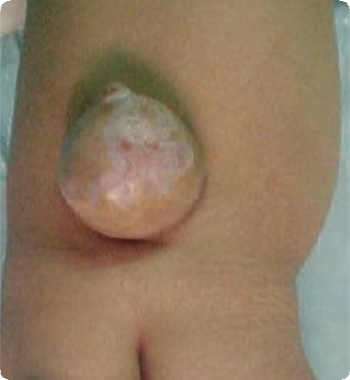
Lumbar spina bifida without hydrocephalus Q05.7
Midline spinal defect, lumbar region.
Rounded mass covered by partially atrophic skin.
Hydrocephalus not mentioned (talipes equinovarus present/ absent, bilateral/unilateral).
Note: Spina bifida without mention of hydrocephalus does not have a specific code. We should assume that there is not hydrocephalus. The code should be changed if hydrocephalus is discovered later.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
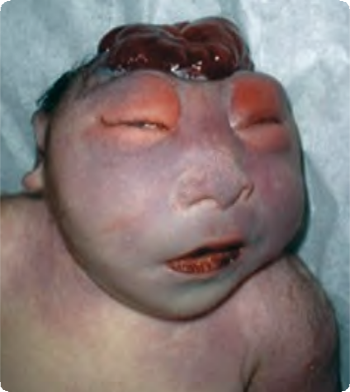
Mero-anencephaly (incomplete) Q00.01
Defect of cranial vault, partially degenerated brain tissue visible within the cranial bone defect. Severe swelling of palpebrae, large nose.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
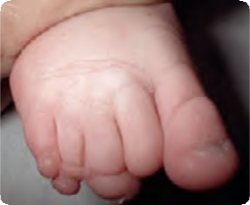
Partial absence of toes (terminal transverse deficiency) Q72.30
Ring constriction Q84.81
Constriction band Q79.80
Deficiency involving all digits of right foot, with absence of terminal parts of digits. Nubbins present.
Ring constriction and fibrotic band noted on 3rd, 4th and 5th digits.
(To be confirmed by X-rays)
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
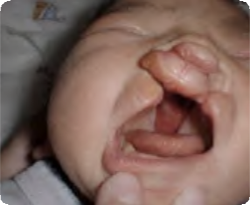
Bilateral cleft lip Q36.0
Severe defect of upper lip.
Bilateral schisis of upper lip with midline part of the lip present.
No lower lip pits.
Cleft palate.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
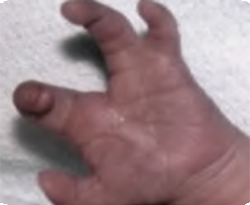
Absent third finger Q71.30
Limb deficiency involving left hand.
Absent 3rd, 4th and 5th fingers, partially fused at the first phalanx level.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
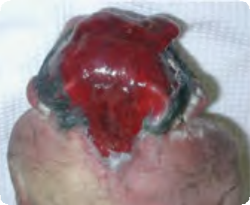
Craniorachischisis Q00.1
Severe defect of cranial vault, parietal and occipital region and cervical spine: partially degenerated brain tissue outside the cranial and cervical spinal defect.
Source: Reproduced with permission of Estudio Colaborativo Latino Americano de Malformaciones Congénitas (ECLAMC)
Activity 5.3
Ask participants to refer to Activity 5.3 in the Participant Workbookpdf icon pdf icon[457 KB, 21 Pages, Print Only].
Assign an ICD-10-RCPCH code or codes, based on the available clinical description of the different fetuses or infants with congenital anomalies.
Response:
- In this case, “LS” is used to abbreviate “lumbosacral”. Although the description might suggest two anomalies (spina bifida and hydrocephalus), hydrocephalus is common among children with spina bifida and it is considered a consequence of spina bifida, the primary major congenital anomaly in this case. There are specific codes for “spina bifida with hydrocephalus” in the ICD-10.
- The ICD-10 code for lumbosacral spina bifida with hydrocephalus is Q05.2.
Note: This case would not be included in analyses of hydrocephalus as a primary anomaly.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “frontal encephalocele” is Q01.0.
- The ICD-10 code for “clubbing of left foot” is Q66.8.
Response:
- It is not specified whether the soft palate, hard palate or both are affected, and no information is provided regarding the laterality (sidedness) of the cleft lip. The ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code for “cleft lip and palate” is Q37.99 (Cleft palate with cleft lip, unspecified).
- The ICD-10 code for “omphalocele” is Q79.2.
Note: For cleft palate, it is uncommon to have the detailed description available (whether the soft or hard palate is affected), unless the description is provided as a result of a surgical repair.
Response:
- Since “amniotic band” is present on the face, this is the most likely cause of the facial cleft. Facial cleft is different from cleft lip.
- The ICD-10 code for “facial cleft” is Q18.8 (Other specified congenital malformations of face and neck).
- If the surveillance programme is focusing on recording cases with cleft lip and cleft palate, then it is not necessary to code this anomaly, and the case can be excluded from surveillance. However, if one would like to include all types of congenital anomalies and assign a code, then the code for cases with known or probable amniotic band/constriction band presence is Q79.80 (Congenital constriction bands), which is the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation of ICD-10 code Q79.8 (Other congenital malformations of musculoskeletal system).
Note: ICBDSR recommends using Q79.80 to identify the presence of an amniotic band. Cases with amniotic bands should be coded using the codes for the specific congenital anomalies as well as the Q79.80 amniotic band code. This anomaly will be excluded from analysis of cleft lip and palate. It is on the exclusion list as noted in WHO/CDC/ICBDSR Birth defects surveillance: a manual for programme managers (4).
Response:
- The abbreviation “NOS” stands for “not otherwise specified”.
- The ICD-10 code for “encephalocele in the parietal area” is Q01.8 (Encephalocele of other sites) or the more specific ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q01.80 (Parietal encephalocele).
- The ICD-10 code for “cleft palate NOS” is Q35.9 (Cleft palate, unspecified) or the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q35.99 (Cleft palate, unspecified).
- The ICD-10 code for “fused toes” is Q70.2.
Note: Although “NOS” is a valid term in the ICD-10, it should be used only when there is no possibility of obtaining a better description for a specific congenital anomaly. For cleft palate, it is uncommon to have the detailed description available (whether the soft or hard palate is affected), unless the description is provided as a result of a surgical repair.
Response:
- The abbreviation “NOS” stands for “not otherwise specified”.
- The ICD-10 code for “anencephaly” is Q00.0.
- The ICD-10 code for “heart defect NOS” is Q24.9.
- The ICD-10 code for “spinal anomalies NOS” is Other congenital malformations of spine – Q76.4.
- The ICD-10 code for “lower extremity abnormal development” is Q74.9 (Unspecified congenital malformation of limbs).
Note: Although “NOS” is a valid term in the ICD-10, it should be used only when there is no possibility of obtaining a better description for a specific congenital anomaly.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “hypospadias, penoscrotal” is Q54.2.
- The ICD-10 code for “unilateral absent middle phalanx on foot” is Q72.3 (Congenital absence of foot and toe(s)) or the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q72.30 (Congenital absence of toe(s)).
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “transposition of the great arteries with intact ventricular septum (D-TGA)” is Q20.3 (Discordant ventriculoarterial connection). Transposition of great vessels complete is listed under this code.
- The ICD-10 code for “bilateral cleft lip and palate” is Q37.8 (Unspecified cleft palate with cleft lip, bilateral).
Note: For cleft palate, it is uncommon to have the detailed description available (whether the soft or hard palate is affected), unless the description is provided as a result of a surgical repair.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “occipital encephalocele” is Q01.2.
- The ICD-10 code for “subcoronal hypospadias” is Q54.1.
- The ICD-10 code for “bilateral club feet is Q66.8 (Clubfoot NOS).
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “cleft palate” is Q35.9 (Cleft palate, unspecified).
- The ICD-10 code for “missing middle phalanx on finger” is Q71.3 (Congenital absence of hand and finger(s)) or the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q71.30 (Congenital absence of finger(s)).
- The ICD-10 code for “hydronephrosis” is Q62.0 (Congenital hydronephrosis).
The other malformations listed are considered minor anomalies. Coding them is optional. If coded:
- The ICD-10 code for “micrognathia” is Q75.8 or K07.00 (although not in chapter Q).
- The ICD-10 code for “low set ears” is Q17.4.
- The ICD-10 code for “posteriorly rotated ears” is Q17.4.
- The ICD-10 code for “excess nuchal skin posteriorly” is Q18.3.
- The ICD-10 code for “bilateral 5th finger clinodactyly” is Q68.1 or the more specific ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q68.10.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “craniorachischisis” is Q00.1.
Response:
- The abbreviation “NOS” means “not otherwise specified”.
- The ICD-10 code for “cleft lip NOS” is Q36.9.
- The ICD-10 code for “spina bifida NOS” is Q05.9.
- Ear tags are considered minor anomalies; therefore, coding them is optional. If coded, the ICD-10 code for “ear tags” is Q17.0 (Preauricular appendage or tag).
Note: Although “NOS” is a valid term in the ICD-10, it should be used only when there is no possibility of obtaining a better description for a specific congenital anomaly.
Response:
- The abbreviation “NOS” means “not otherwise specified”.
- The ICD-10 code for “anencephaly” is Q00.0.
- The ICD-10 code for “absence of digits NOS” is Q73.8 or the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q73.80 (Absent digits, unspecified).
- The ICD-10 code for “malformed feet NOS” is Q66.9 (Congenital deformity of feet, unspecified).
Note: Although “NOS” is a valid term in the ICD-10, it should be used only when there is no possibility of obtaining a better description for a specific congenital anomaly.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “myelomeningocele” is Q05.6 (Thoracic spina bifida without hydrocephalus). T3–T4 indicates the level of lesion in the thoracic region (the spine is open at the T3–T4 vertebrae).
The other malformations listed are considered minor anomalies. Coding them is optional. If coded:
- The ICD-10 code for “epicanthal folds” is Q10.3.
- The ICD-10 code for “high arch palate” is Q38.50.
- The ICD-10 code for “hypoplastic nipples” is Q83.8.
Note: Since it is not mentioned or specified whether hydrocephalus is present or not, it is an assumption of “spina bifida without hydrocephalus”. It is possible to use the ICD-10 code Q05.9 (Spina bifida, unspecified) but by using this code, the specificity for lesion level would not be captured. It is recommended that the congenital anomalies surveillance programme includes information in its protocol on how to code spina bifida when hydrocephalus is not mentioned or described in the medical records.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “hypoplastic left heart syndrome” is Q23.4.
- “Spina bifida occulta” (Q76.0) is considered a minor anomaly.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “unilateral (right side) cleft lip with cleft hard palate” is Q37.1 or the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q37.10 (Cleft hard palate with cleft lip, specified as unilateral).
- The ICD-10 code for “bilateral talipes equinovarus” is Q66.0.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “left radial hypoplasia” is Q71.4.
- The ICD-10 code for “transposition of the great arteries” is Q20.3 (Discordant ventriculoarterial connection).
- The ICD-10 code for “secundum ASD” is Q21.1.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “gastroschisis” is Q79.3.
- The ICD-10 code for “large hiatal hernia” is Q40.1 (Congenital hiatus hernia).
- The ICD-10 code for “malrotated bowel” is Q43.9.
Response:
- ASD (atrial septal defect) is not part of tetralogy of Fallot, so needs to be coded separately. The ICD-10 code for “ASD” is Q21.1.
- The ICD-10 code for “tetralogy of Fallot” is Q21.3.
- The ICD-10 code for “urethral meatus opens in the shaft of the penis” is Q54.1 (Hypospadias, penile).
Note: Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a single entity consisting of four heart malformations: overriding aorta, pulmonary valve stenosis, ventricular septal defect (VSD) and right ventricular hypertrophy.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “holoprosencephaly” is Q04.2.
- The ICD-10 code for “cleft lip bilateral” is Q36.0.
Note: Cleft lip is included but this case would not be counted in studies of clefts.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “gastroschisis” is Q79.3.
- The ICD-10 code for “split hand” is Q71.6.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “absent right foot” is Q72.3 (Congenital absence of foot and toe(s)). This code includes the “3 toes missing on left foot” diagnosis. However, using the more specific ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation, the code for the missing toes would be Q72.30, which could be added as an additional code since the toes are missing on the left foot, keeping the ICD-10 code Q72.3 for the missing right foot.
Although, the clinical description “hypoplasia of femur and tibia right leg” may sound like one anomaly affecting the right leg, there are different codes for femoral and tibial hypoplasia.
- The ICD-10 code for “hypoplasia of femur” is Q72.4.
- The ICD-10 code for “hypoplasia of tibia” is Q72.5.
- The ICD-10 code for “club right hand” is Q71.4.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “spina bifida, cervical without hydrocephalus” is Q05.5.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “cleft soft palate” is Q35.3.
- The ICD-10 code for “tetralogy of Fallot” is Q21.3.
- The ICD-10 code for “spina bifida sacral” is Q05.3 (Sacral spina bifida with hydrocephalus).
- The ICD-10 code for “oligodactyly on foot” is Q72.3 (Congenital absence of foot and toes) or the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q72.30 (Congenital absence or hypoplasia of toe(s) with remainder of foot intact).
Note: Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a single entity consisting of four heart malformations: overriding aorta, pulmonary valve stenosis, VSD and right ventricular hypertrophy
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “ulnar hypoplasia, right” is Q71.5.
- The ICD-10 code for “tibial hypoplasia, right” is Q72.5.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “Pierre Robin sequence” is the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q87.08.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “anencephaly” is Q00.0 (Anencephaly).
- The “gross abnormalities” description is vague, and coding is optional. If coded, the ICD-10 code is Q89.9 (Congenital malformation, unspecified).
- Although, the description may suggest two anomalies (cleft lip and cleft palate), there is a specific ICD-10 code to assign to cleft palate with bilateral cleft lip. Because the type of cleft palate is not specified, the ICD-10 code is Q37.8 (Unspecified cleft palate with bilateral cleft lip).
Note: Avoid using the Q89.9 ICD-10 code if possible because it does not provide any specificity, and it has very minimal value in congenital anomalies surveillance.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “iniencephaly” is Q00.2.
- The ICD-10 code for “complete amelia of upper limb” is Q71.0.
Response:
- The ICD-10 code for “achondroplasia” would be Q77.4. However, the diagnosis is not definite. Generalized limb shortening including skeletal dysplasias are on the exclusion list in WHO/CDC/ICBDSR Birth defects surveillance: a manual for programme managers (4).
Response:
- There are two ICD-10 codes to be assigned. One is for “amelia of upper limbs”: Q71.0 (Congenital complete absence of upper limb(s), amelia); the other is for “amelia of lower limbs”: Q72.0 (Congenital complete absence of lower limb(s), amelia).
- World Health Organization. Congenital anomalies. Fact sheet No 370. October 2012 (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs370/en/index.htmlexternal icon , accessed 29 April 2015).
- Resolution WHA63.17. Birth defects. In: Sixty-third World Health Assembly, Geneva,17–21 May 2010. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010 (http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA63/A63_R17-en.pdfexternal icon, accessed 29 April 2015).
- International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, 10th revision. Geneva: World Health organization; 2015 (http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2015/enexternal icon , accessed 24 February 2015).
- World Health Organization, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), International Clearinghouse for Birth Defects Surveillance and Research (ICBDSR). Birth defects surveillance: a manual for programme managers. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014 (https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefectscount/documents/bd-surveillance-manual.pdf, accessed 10 February 2015).
- World Health Organization, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC), International Clearinghouse for Birth Defects Surveillance and Research (ICBDSR). Birth defects surveillance: atlas of selected congenital anomalies. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014 (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/127941/1/9789241564762_eng.pdf?ua=1pdf iconexternal icon , accessed 10 February 2015).
- CDC Foundation. What is public health? (http://www.cdcfoundation.org/content/what-public-healthexternal icon , accessed 24 February 2015).