FAQs: Antimicrobial Resistance (AR) Option
General Submission Requirements
The first step is to ensure your facility meets the requirements for NHSN AR Option participation: 1) has an Admission Discharge Transfer (ADT) system and an electronic Laboratory Information System (LIS) or electronic access to the required data elements and 2) ability to package the data into standardized Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) format for upload into NHSN.
The NHSN AR Option does not allow manual entry due to the amount of data submitted each month. Facilities use a vendor system to package and submit the AR data via CDA. As of May 2023, all vendors that submit data to the NHSN AR Option are required to pass Synthetic Data Set (SDS) validation. The AR SDS Validation website lists vendors that have an NHSN-validated AR reporting solution.
Your facility may already use one of these vendors to submit other types of data to NHSN, so you should check with your vendor to see if 1) your facility has the capability to submit these data already using your current vendor or 2) your current vendor offers this capability with an “add on” feature. Some facilities leverage internal information technology (IT)/informatics resources to report these data via a “homegrown” system. NHSN does not recommend this option for most facilities because it requires specialized knowledge of coding and data aggregation. Please note: facilities that create their AR CDA files in-house using their own “homegrown” IT or informatics resources must also pass AR SDS Validation.
You can find the details on what data are required to be reported on our NHSN AUR Module webpage within the AUR Protocol.
If your facility would like to begin submitting Antimicrobial Use (AU) and AR data for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Promoting Interoperability Program, please see the additional guidance document [PDF – 1MB].
If your facility is interested/considering taking up this work internally rather than using a vendor, you’ll find the AU and AR CDA toolkits, which contain the sample CDA files, link to the CDA Implementation Guide, helpful hints, etc., on the CDA Submission Support Portal website.
It depends. If the off-site laboratory is sending susceptibility results back to your facility and your facility has electronic access to the required data elements, then yes, your facility may still be able to submit AR data. Please work with your software vendor to determine if your antimicrobial susceptibility data are in a format conducive to electronic reporting. Facilities should not employ manual means of data collection to report AR Option data to NHSN.
Yes, you will need SAMS credentials to submit and/or view AR data. If you are new to NHSN, a user with administrative rights at your facility, such as the Facility Administrator, must first add you to your NHSN facility following the steps in Q4 in the General Submission Requirements section. After being invited to NHSN, review and accept the NHSN Rules of Behavior and complete the SAMS enrollment process [PDF – 542 KB]. All NHSN users must follow these steps before using the NHSN application. While waiting for your SAMS credentials, you can complete the trainings in the AUR Educational Roadmap. After you receive your SAMS credentials, you’ll be able to log into your NHSN facility. You can find more information about SAMS on the About SAMS webpage.
A user with administrative rights, such as the Facility Administrator, must follow these steps to add users to the NHSN AR Option:
- From the NHSN Homepage, navigate to Users on the left-hand side menu.
- Determine whether the user is new or existing within your NHSN facility.
- For people not already registered as users within your NHSN facility, select Add User. Complete all fields marked with a red asterisk (*) and click Save. Consider whether you should designate this new user as an AU Option and/or AR Option contact. The NHSN AUR Team uses this information to target notifications for AUR-related content like AUR data quality outreach.
- For existing users, select Find User, locate the user, and click their name. Scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Edit, then click Edit Rights.
- On the next screen, assign user rights. At a minimum, users need rights to the Patient Safety Component as well as patient identifiers to view and submit AR data. If the user will submit AR data, NHSN recommends Administrator-level user rights. You can use the Custom Rights option to limit user rights to just AR data and no other patient safety modules. Be careful when assigning Custom Rights, as certain settings will prevent users from accessing AR data. When assigning Custom Rights, users also need rights to the Patient Safety Annual Facility Survey to view Standardized Resistant Infection Ratio (SRIR) and Pathogen-specific Standardized Infection Ratio (pSIR) reports, as the SRIRs and pSIRs use variables from the Patient Safety Annual Facility Survey for risk-adjustment. Once all rights have been correctly assigned, click Save.
For complete details and instructions, please refer to the NHSN AUR User Rights document [PDF – 350 KB].
NHSN requires a Monthly Reporting Plan for every month that you plan to submit AR data.
- From the NHSN Homepage, select “Reporting Plan” from the left side menu.
- Click Add and select “Monthly Reporting Plan” for the Reporting Plan Type to add a new Monthly Reporting Plan, or click Find to find an existing plan.
- Select the month and year for the AR data submission.
- If editing an existing plan, first scroll down to the bottom of the page and click “Edit”. Then scroll to the “Antimicrobial Use and Resistance Module” section of the plan.
- See example screenshot and details below for guidance in selecting the Locations on Monthly Reporting Plan:
- Select Facility-wide Inpatient (FacWideIN) and check the AR box to submit AR Option data for inpatient locations. Do not list individual inpatient locations in the AR Option plan.
- If applicable, select an allowed outpatient location type (specifically Emergency Department [ED], Pediatric ED, and 24-hour Observation Area) and check the AR box to submit for that specific outpatient location. List the outpatient locations as separate lines in the Monthly Reporting Plan.
- Click Save at the bottom of the screen.
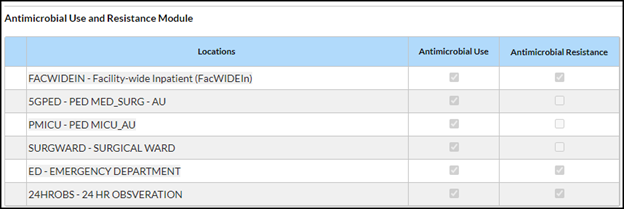
Note: You do not have to check the AU boxes unless you also plan to submit AU Option data.
Please note that the AUR Measure of the CMS Promoting Interoperability Program is attestation-based, so CDC will not share AUR data with CMS, even if it is included in the Monthly Reporting Plan. View the complete list of data required for each CMS Quality Reporting Program [PDF – 1 MB].
Yes. Facilities can submit AR Option data separately without submitting AU Option data. To get credit for participation in the CMS Promoting Interoperability Program, CMS requires facilities to submit data for AR and/or AU Options. Refer to CDC’s PI Program Guidance for NHSN Facilities [PDF – 356 KB] for more information.
An AR Event contains isolate-level antimicrobial susceptibility results for a specific organism. An isolate is defined as a population of a single organism observed in a culture obtained from a patient specimen. The isolate must meet the four criteria below:
- Must be collected while the patient was in an eligible location (any inpatient location or ED, pediatric ED, or 24-hour observation area).
- Must be collected from an eligible specimen type: blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound or musculoskeletal.
- Must be an eligible organism (see Q9 in the General Submission Requirements section).
- If a bacterial organism isolated, it must have had antimicrobial susceptibility testing performed for at least one drug. If the organism is Candida, no susceptibility testing is required for the isolate to be eligible for reporting.
Note: your facility should report all eligible isolates that meet the reporting guidelines outlined in the NHSN AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1 MB] to NHSN regardless of the antimicrobial resistance of the isolated organism. This means that even isolates that are susceptible to all required antimicrobials are eligible to be reported to the AR Option.
NHSN strongly encourages reporting specimens from all NHSN-defined inpatient locations (including inpatient procedural areas like operating rooms) and three select outpatient locations (ED, Pediatric ED, and 24-hour Observation Area) at each facility.
A high-level list can be found in the AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1MB]. Facilities and vendors should refer to the AR Option Pathogen Roll-up Workbook found in the Antimicrobial Resistance Toolkit for organisms eligible for AR Option reporting and the complete list of their associated SNOMED codes. All organisms in the Workbook are eligible for reporting. Refer to the AR Option Pathogen Roll-up Reference Guide, also found in the AR Toolkit, for guidance using the workbook and determining which SNOMED codes are accepted into NHSN.
The NHSN Alerts tell you that you haven’t yet submitted data for something listed in your Monthly Reporting Plan. The Missing Event alert specifically tells you that you have reported AR Option summary data for those location/month(s), but you have not yet reported AR Events. Missing AR Event alerts will appear within the AUR alerts section on the Missing Events tab of the alert screen as shown in the screenshot below:
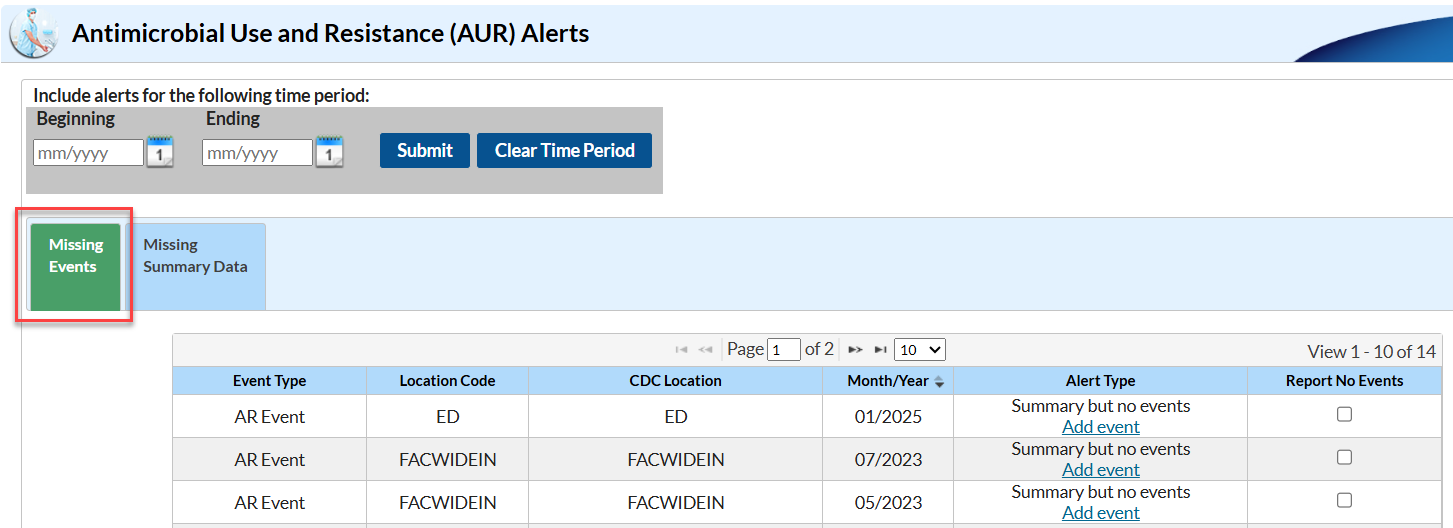
To clear the Missing Event alerts, you will need to submit the AR Event CDA files for the month(s) listed on your alerts screen. If you thought you had already uploaded these data, there is a good chance an error occurred during the original upload process and these specific files failed to import. During the re-submission process, make sure you pay special attention to any errors that may show up on the PDF submission report. Once you have uploaded these data, be sure to generate new datasets.
It would be rare, but not unheard of, to have zero AR Events to report for a given month based on the criteria for determining whether something is an AR Event. For example, any urine specimen in which E. coli was cultured would be eligible to be reported regardless of the susceptibility of that organism to the drugs tested by the lab. However, if there were zero specimens collected with eligible organisms for these months, you can click the “Report No Events” box for the month(s) in question on the Alerts screen. View our guide for more information on how to report no events [PDF – 395 KB].
If you do not yet have AR Event reporting from your vendor software set up, we request that instead of clicking the “Report No Events” box, you remove the AR Option check boxes on your Monthly Reporting Plan for the time being. Clicking the “Report No Events” box, tells NHSN that your facility identified no specimens that met the criteria for an AR Event (in other words, a “true zero”). It would not be appropriate to “Report No Events” because you were not able to report AR Events from your vendor software. See Q5 in the General Submission Requirements section for how to edit the Monthly Reporting Plan.
The Missing Summary Data alert specifically tells you that you have not yet reported AR summary records for those location(s)/month(s) listed in your Monthly Reporting Plan. Missing AR Summary alerts will appear within the AUR alerts section on the Missing Summary tab of the alert screen as shown in the screenshot below:
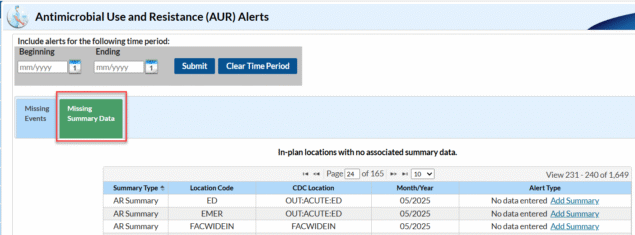
To clear the Missing Summary Data alerts, you will need to submit the AR summary records (also known as the “denominator” data) for the month(s) listed on your alerts screen. If you thought you had already uploaded these data, there is a good chance an error occurred during the original upload process and these specific files failed to import or these summary files were not included in your original zip file submission. During the re-submission process, make sure you pay special attention to any errors that may show up on the PDF submission report. Once you have uploaded these data, be sure to generate new datasets.
For the AUR Module, the number of admissions is defined as the aggregate number of admissions to any of the inpatient locations within the facility (facility-wide inpatient) starting on the first day of each calendar month through the last day of the calendar month. An admission is counted when the patient arrives in an NHSN designated inpatient location regardless of patient status (for example, inpatient, observation). Further, an admission to an inpatient unit is counted even if the patient is discharged that same calendar day. Additionally, a patient transfer from an inpatient to an outpatient ED, pediatric ED or 24-hour observation location then back to an inpatient location is counted as two separate admissions. Note: the admissions definition used in the AUR Module is different than the definition used in the NHSN MDRO/CDI Module.
Within the AR Event file, the date of admission is the calendar date that the patient physically locates to an inpatient location. If the specimen was collected in an outpatient location (for example, Emergency Department), use the admission status variable as a guide. If the admission status variable is “True” (Yes), then use the date the patient was admitted to the inpatient location for this field. If the admission status variable is “False” (No), then use the encounter date (the date the patient arrived in the first outpatient location) for this field.
Yes. NHSN’s updated Agreement to Participate and Consent allows the NHSN Team to share specific information with State & Local Health Departments, Veterans Affairs (VA), and Department of Defense (DoD) for prevention purposes such as the NHSN OrgIDs and names of facilities submitting AU and/or AR data into NHSN. Please send your request to NHSN@cdc.gov.
For state, local, and territorial health departments that require this information on an ongoing basis, we suggest setting up a Data Use Agreement (DUA) with the CDC, which allows you to gain access to NHSN data from the facilities in your jurisdiction. Facilities in your jurisdiction are automatically added to a Group through the DUA process and health departments do not have to wait for facilities to accept Confer Rights Template. You can find more information about the DUA process on the DUA page.
Yes, eligible hospitals and critical access hospitals (CAHs) participating in the Medicare Promoting Interoperability Program must be in active engagement with NHSN to report into the NHSN AUR Module.
For the reporting period in 2025, the Promoting Interoperability AUR Surveillance measure has been split into two measures: AU Surveillance and AR Surveillance. Eligible hospitals and CAHs must be in active engagement with the CDC’s NHSN for submitting AU and/or AR data during the self-selected 180-day EHR reporting period and receive a report from NHSN indicating successful submission of AU and/or AR data or claim an applicable exclusion(s). Further, to meet the CMS Promoting Interoperability Program requirement, facilities must use CEHRT updated to meet 2015 Edition Cures Update criteria, including criteria at 45 CFR 170.315 (f)(6).
Refer to NHSN’s CMS Reporting web page for more information.
Specimen Sources
Your facility can report all specimen sources included in the “Specimen Source 2025” tab of the Information Data Model (IDM) spreadsheet with an “X” in the “Valueset: ARSpecimenSource” column to the AR Option. The Specimen Source tab in the IDM provides further breakdown of the specimen sources into the specific categories outlined in the AR Option Protocol:
- Specimen category = Non-invasive
- AR_LRI Specimen = Lower Respiratory
- AR_Urine Specimen = Urine
- AR_ Skin, Soft Tissue, Wound, Musculoskeletal Specimen = Skin, Soft Tissue, Wound and Musculoskeletal
- Specimen category = Invasive
- AR_Blood Specimen = Blood
- AR_CSF Specimen = Cerebrospinal Fluid
The IDM is found within the AR Toolkit located on the CDA Submission Support Portal website.
The full list of accepted terms is in the “Specimen Source 2025” tab of the Vendor IDM workbook within the AR CDA Toolkit posted on the CDA Toolkits webpage. When determining if a given specimen is eligible in the newly added specimen category the first step is to assess whether the specimen belongs to skin, soft tissue, musculoskeletal, or wound. The next step is to determine the body site. If there’s no information in the specimen label about which tissue it is, refer to the body site. If the site is on the four limbs, then yes, it is most likely eligible to be reported. If it’s not on the limbs or the site is unclear, the specimen is not eligible for reporting.
When determining whether swabs are available, if the only information on the sample is the body site, then the specimen is only eligible when the body site is on the four limbs.
Terms with “subcutaneous/intramuscular” are eligible under the musculoskeletal group so you’d map that term to the closest term on our list.
If it is clear the tissue/fluid/etc. specimen is from skin, joint, muscle, bone, or wound, then include it. If it’s unclear whether the tissue/fluid/etc. specimen is from skin, joint, muscle, bone, or wound then use the site of where the specimen was collected. If the tissue/fluid/etc. specimen was collected from one of the four limbs, then the specimen is eligible.
The full list of accepted terms is in the “Specimen Source 2025” tab of the Vendor IDM workbook within the AR CDA Toolkit posted on the CDA Toolkits webpage. Below are some example mappings based on questions we’ve received in the NHSN@cdc.gov mailbox.
- If the specimen is labeled as a muscle, then yes, it is eligible. If it is unclear whether it’s a muscle, then it’s not eligible.
- Nares swab is not an eligible specimen. Similarly, nares-axilla-groin is also not an eligible specimen.
- Oral mucosa is not an eligible AR specimen.
- When mapping abscess terms, understand that SNOMED does not have a term for “abscess from bone.” In these cases, please use “Specimen from bone” which is SNOMED code 430268003. If you do not have information on where the abscess is located, it should not be mapped as we don’t want to introduce noise into the AR Option data. On the other hand, “Specimen from wound abscess” can be reported.
- Map the generic term “Synovial fluid specimen” as “Joint fluid specimen” which is SNOMED code 431361003. The other more specific synovial fluid specimens (for example, elbow joint synovial fluid, knee joint synovial fluid) have eligible terms on the Specimen Source 2025 tab.
The new specimens (skin, soft tissue, wound and musculoskeletal) are considered a single bucket in the non-invasive category. The specimen should be submitted using the specific SNOMED specimen code found in the “Specimen Source 2025” tab of the vendor IDM.
Here’s the logic to be applied:
- New specimens are all part of one group (similar to lower respiratory)
- New group is considered non-invasive which means the 1 per month de-duplication rule will apply
- For non-invasive source isolate selection, select isolates based on the order specified: 1) lower respiratory, 2) urine, 3) skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal.
- If two or more isolates are identified from skin, soft tissue, wound and/or musculoskeletal on the same day, use the Figure 3 flow chart in the NHSN AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1 MB] to assess which isolate has higher amount of drug resistance based on the number of antimicrobials testing first “NS”, if equal amount of “NS” then move to the amount of “R”, then “I”, then “S-DD” then “S”. If it cannot be determined which is most resistant, then report the isolate that was the first entered into the LIS.
Data Import
NHSN recommends that facilities submit both AR Summary and AR Event data files to NHSN for a given calendar month within 30 days following the completion of the month to make the data most actionable by your facility. Facilities should wait at least seven calendar days following the end of the month before submitting AR Event data to ensure the lab completed all susceptibility testing and reported results to the electronic health record (EHR).
Facilities participating in AUR reporting to get credit for the Medicare Promoting Interoperability Program must upload data for the calendar year no later than January 31 of the following year in order to have all submissions included in the annual report summarizing AUR submission status.
Yes, you can submit AU and AR CDA files together in the same zip file. For manual upload, all the CDA files in a zip file must be from one facility. For DIRECT submission, the zip file can contain CDA files for multiple facilities. For both manual and DIRECT submission, the zip file can contain up to 1,000 CDA files or a maximum of 2 MB, whichever comes first. Keep in mind, the larger the zip file, the longer it takes to upload when manually logged into NHSN.
Note: NHSN only accepts alphanumeric characters, hyphens, and underscores in CDA and zip file names. NHSN does not accept other special characters.
Sometimes, when you are uploading many AR files, some files will successfully upload, and others will not. Below is a screenshot of what it looks like when you submit files together and you have some records pass and others fail. Note that both the Error Report and Submit buttons are enabled:
If you click on the Events tab in the Validation Results table, you can see the files that passed and failed validation by looking in the Status column. In this instance, 13 records were submitted. Four passed validation and nine failed. When you click the Submit button, only the four files that successfully passed validation will upload into NHSN. Clicking the submit button generates a PDF report, which shows the file(s) that successfully imported and the file(s) that did not pass validation and did not import (see example screenshot below).
Please view and save the PDF report for your records each time you import data into the AR Option. The above example of the PDF report shows you which files passed validation and which files failed validation. For each file that failed, the reasons for failure are included in the section below the record information. The NHSN Help Desk requires information from the PDF report to assist users with inquiries related to data import errors.
Retrospective data submission is always encouraged! Your facility can submit AR Option data as far back as January 2012, if you have existing Monthly Reporting Plans during that time, or January of the previous calendar year (if no Monthly Reporting Plans previously existed).
Below are two scenarios to help explain this:
- Existing reporting plans: Facility A has existing NHSN Monthly Reporting Plans going back to January 2019. They can edit the Monthly Reporting Plan to add AUR Module locations to submit retrospective AR Option data back to January 2019.
- No existing reporting plans: Facility B just started submitting data to NHSN and does not have any Monthly Reporting Plans in NHSN (meaning they didn’t even have reporting plans for HAI data). They can add Monthly Reporting Plans going back to the January of the year they enrolled in NHSN or back to the January of one calendar year in the past, whichever comes first.
- If Facility B enrolled in January 2024 and its currently December 2024, they can add Monthly Reporting Plans and submit AR Option data back to January 2024.
- If Facility B enrolled in December 2023 and its currently January 2025, they can add Monthly Reporting Plans and submit AR Option data back to January 2024.
Import Errors
The NHSN AR Option requires users to upload CDA files in a zip file. Try zipping the file(s) and resubmitting. Note that each zip file can contain up to 1,000 CDA files or a maximum of 2 MB, whichever comes first.
If you receive this error for specimens collected in an inpatient location, it means that you have not included FacWideIN for this month and year in the Antimicrobial Resistance portion of your Monthly Reporting Plan. If you receive this error for specimens collected in a 24-hour Observation Unit, ED or Pediatric ED then you have not included that location for that month and year in the Antimicrobial Resistance portion of your Monthly Reporting Plan. Therefore, you’ll need to add the location(s) (either FacWideIN or the specific outpatient location[s]) to the Antimicrobial Resistance portion of your Monthly Reporting Plan for every month you plan to submit AR data. NHSN will not accept any data that is out of plan.
To edit your Monthly Reporting Plan, follow the steps in Q5 in the General Submission Requirements section. After you have edited your Monthly Reporting Plan to include the AR data you are wanting to upload, NHSN should accept the CDA file for that month, year, and location.
If you have verified FacWideIN or the specific 24-hour Observation Unit, ED, or Pediatric ED is on your Monthly Reporting Plan and you’re still receiving this error during upload, incorrect location information in your CDA file could be the cause. See the question below for details on location errors.
The location in the CDA file must be the exact match of the “Your Code” value, “NHSN HL7 code” and location type of the values in the NHSN Location Manager (see screenshot below). This error message is telling you that the location name used in your CDA file does not match a location currently mapped in your NHSN facility.
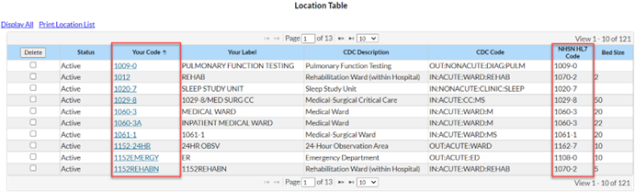
We recommend meeting with your NHSN Facility Administrator to have them export the location list out of NHSN (Facility > Locations > Export Location List) so you can compare what’s in NHSN to what’s in your vendor system. Decide the best way to rectify the differences (update NHSN or update the vendor software) with your Infection Control/Infection Prevention department. Once you’ve matched the locations across both systems, re-export your AR CDA files and import them into NHSN.
Based on the organism reported, the NHSN application requires you to include specific drug susceptibility tests in the CDA file. The list of drug susceptibility tests for each organism is called the drug panel, and the number of drug tests included in each panel varies. The organism and corresponding drug panel can be found in Appendix F of the AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1 MB]. These panels are reviewed by the NHSN AUR Team annually and drug tests are added and removed yearly as needed. Work with your vendor to ensure the CDA file includes all required drug tests. The CDA file must include all drug tests in the specific panel regardless of whether the lab tested them. Further, each drug test must be listed only once. If the lab conducted more than one susceptibility test for a given drug, please use the same day de-duplication rules in the NHSN AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1 MB] to report a single result.
This error means you’ve included a drug test in your AR Event file that is not required for the year the specimen was collected. Based on the organism reported, the NHSN application requires you to include specific drug susceptibility tests in the CDA file. The list of drug susceptibility tests for each organism is called the drug panel and the number of drug tests included in each panel varies. The organism and corresponding drug panel can be found in Appendix F of the AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1 MB]. These panels are reviewed by the NHSN AUR Team annually and drug tests are added and removed yearly as needed. Work with your vendor to match the NHSN AUR Protocol [PDF – 1 MB] requirements with the data being included in the CDA files.
This error is generated when the zip file contains an AR Event for the same patient and organism from an invasive source (blood or CSF) within 14 days. A new AR Event for a given patient and organism from an invasive source can only be submitted if the specimen collection date is more than 14 days after the specimen collection date of the event already stored in NHSN. Work with your software vendor to ensure the de-duplication rules are being applied correctly.
This error is generated when the zip file contains an AR Event for the same patient and organism from a non-invasive specimen source (urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound and musculoskeletal) in a single calendar month. Each month, only 1 non-invasive isolate is allowed per patient and organism. Work with your software vendor to ensure the de-duplication rules are being applied correctly.
This error message indicates that you are uploading a CDA file that was previously uploaded into NHSN with that same setID (unique identifier for a CDA file). If you are trying to update an existing record in NHSN with new information, first try re-exporting the file(s) from your vendor software to update the version number. If, after re-exporting the files from your vendor software, you’re still getting that error during upload, you’ll need to manually delete the existing record first. Follow the steps in Q1 in the Data Deletion section to manually delete the month(s). Once you’ve deleted the records, try the upload again.
There are a few reasons the “Rhapsody error” message appears. In all cases, we recommend waiting a few hours or trying the next day to complete your upload. If the original error was generated because of internal NHSN issues, the files should upload when you try again the following day. If the original error was due to an issue in your file(s), you’ll continue to see the “Rhapsody error” when you try to upload them. If possible, you can separate the files into smaller zip files and try the upload again to isolate which file(s) may be causing the issue. For assistance in troubleshooting, please send your file to NHSNCDA@cdc.gov for further investigation.
Data Deletion
There are two options for correcting AR Summary files:
- Manually delete and re-upload a new file
- Use Succession Management within vendor software
Manual Deletion: To manually delete the record, log into NHSN, select ‘Summary Data’ from the navigation menu on the left side and then select ‘Delete AUR Data’. Use the Summary Data Type drop down menu to select ‘Antimicrobial Resistance Data.’ Select the Location Code (for example, FACWIDEIN, Emergency Department), and use the Month and Year drop down menus to select the month/year you’d like to delete from NHSN. Then click the ‘Delete’ button to delete the record. See the screen shot below for reference.

Succession Management: Your vendor software may be able to automatically update AR summary files in NHSN using succession management. Many vendors have implemented this feature by allowing users to simply export a new version of the file but be sure to work with your vendor to determine if this approach is appropriate for you. Please note that succession management does not allow you to delete a record without overwriting it with a new record for that location/month.
There are two options:
- Manually delete and re-upload a new file.
- Use Succession Management within vendor software to replace the existing file.
Manual Deletion:
- Log into NHSN, select ‘Event’ from the navigation menu on the left side and then select Find.
- Use the Event Type drop down menu to select ‘AR – Antimicrobial Resistance’ and optionally input any other identifying information. Select Find.

3. Locate the AR Event you want to delete on the Event List table. Check the box in the Delete column next to the AR Event. Click the ‘Delete’ button at the top of the column to delete the event. You can select additional check boxes if you’d like to delete more than one event.

Succession Management: Your vendor software may be able to automatically update AR Event files in NHSN using succession management. Many vendors have implemented this feature by allowing users to simply export a new version of the file but be sure to work with your vendor to determine if this approach is appropriate for you.
Important Note: Succession management does not allow you to delete a record without overwriting it with a new record for that patient. If you need to simply delete an AR Event that was erroneously submitted, please follow the manual deletion steps above.
No. Succession management will only overwrite or replace an existing record with a new record. If you need to completely delete an AR Event or AR Summary record without replacing it with an updated version, you’ll need to follow the steps in Q1 and Q2 above to manually delete the record.
Duplicate Rules
The 14-day duplicate rule for invasive specimens (blood & CSF) does extend across calendar months. Even across calendar months there should be 14 days with no positive culture result from the laboratory for the patient and specific organism SNOMED code before your facility can report another invasive source AR Event in NHSN for the same patient and specific organism SNOMED code. See the below example to visualize the 14-day duplicate rule for invasive sources:
| Date | Lab Result | Reported to NHSN? | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 15 | Staph aureus isolated from blood culture | Yes | Patient’s first blood culture of admission; Staph aureus is isolated; AR Event reported |
| January 28 | Staph aureus isolated from blood culture | No | <14 days since last positive culture (Jan 15) of Staph aureus |
| February 3 | Staph aureus isolated from CSF culture | No | <14 days since last positive culture (Jan 28) of Staph aureus |
| February 20 | Staph aureus isolated from blood culture | Yes | >14 days since last positive culture (Feb 3) of Staph aureus; AR Event reported |
However, the 1 per month duplicate rule for non-invasive specimens (urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal) does not extend across calendar months. For urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal specimen isolates, report the first non-invasive source AR Event per month. Report no more than 1 non-invasive specimen per patient per organism to NHSN per calendar month. See the below example to visualize the 1 per month duplicate rule for non-invasive sources:
| Date | Lab Result | Reported to NHSN? | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 1 | Staph aureus isolated from urine | Yes | Patient’s first non-invasive specimen of the month; Staph aureus is isolated; AR Event reported |
| January 20 | Staph aureus isolated from wound | No | Still same month (Jan) as the non-invasive specimen Staph aureus reported to NHSN |
| January 31 | Staph aureus isolated from lower respiratory culture | No | Still same month (Jan) as the non-invasive specimen Staph aureus reported to NHSN |
| February 3 | Staph aureus isolated from urine | Yes | Patient’s first non-invasive specimen of new month (Feb); Staph aureus is isolated; AR Event reported |
Both the 14-day duplicate rule for invasive specimens (blood & CSF) and 1 per month duplicate rule for non-invasive specimens (urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal) extend across patient admissions. See the examples below for clarification.
Invasive specimen (blood & CSF) example of the 14-day rule for a specific organism from a single patient across admissions:
| Date | Lab Result | Reported to NHSN? | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| July 1 | Escherichia coli isolated from blood culture in Medical Ward | Yes | Patient’s first blood culture of inpatient admission; Escherichia coli is isolated; Report AR Event into NHSN. |
| July 4 | Patient discharged from facility | ||
| July 7 | Escherichia coli isolated from blood culture in Emergency Department | No | It has been less than 14 days since the last positive culture (July 1) from the patient isolating E. coli. |
| July 17 | Escherichia coli isolated from blood culture in Medical Ward | No | It has been less than 14 days since the last positive culture (July 7) from the patient isolating E. coli. |
Non-invasive specimen (urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal) example of the 1 per month rule for a specific organism from a single patient across admissions:
| Date | Lab Result | Reported to NHSN? | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| July 1 | Escherichia coli isolated from soft tissue in Medical Ward | Yes | Patient’s first soft tissue specimen of inpatient admission; Escherichia coli is isolated; Report AR Event into NHSN. |
| July 15 | Patient discharged from facility | ||
| July 31 | Escherichia coli isolated from soft tissue in Emergency Department | No | Still same month (July) as the non-invasive specimen E. coli reported to NHSN |
| August 3 | Escherichia coli isolated from soft tissue in Medical Ward | Yes | Patient’s first non-invasive specimen of new month (Aug); E. coli is isolated; AR Event reported |
No. The 14-day duplicate rule for invasive specimens (blood & CSF) & 1-per-month duplicate rule for non-invasive specimens (urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal) apply only to specimens collected in the reporting facility. Do not include specimens obtained while the patient was at another healthcare facility in the 14-day (blood & CSF) or 1 per month (urine, lower respiratory, skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal) calculations.
No. The duplicate rules are specific to a single pathogen. If the laboratory identifies another pathogen, regardless of the specimen source or the date the previous pathogen was identified, this is not considered a duplicate event. The subsequent pathogens should be reported as AR Events.
See the example below for clarification.
| Date | Lab Result | Reported to NHSN? | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| July 1 | Escherichia coli isolated from blood culture in Medical Ward | Yes | Patient’s first blood culture of inpatient admission; Escherichia coli is isolated; Report AR Event into NHSN. |
| July 3 | Escherichia coli isolated from blood culture in Medical Ward | No | It has been less than 14 days since the last positive culture (July 1) from the patient isolating E. coli. |
| July 3 | Staph aureus isolated from blood culture in Medical Ward | Yes | Patient’s first blood culture of Staph aureus is isolated; Report AR Event into NHSN. |
Laboratory Testing Results
No. You should report only final or corrected susceptibility testing results to NHSN. Do not report preliminary laboratory results for NHSN AR Option reporting. Facilities should wait at least seven calendar days following the end of the month before submitting data to ensure the lab completed all susceptibility testing and reported final results back to the EHR.
Facilities cannot report a pathogen that was not fully identified as the intention for the AR Option reporting is to be completely electronic and not require manual review/manipulation of the data. Review the AR Option Pathogen Roll-up Workbook within the AR CDA Toolkit to see the full list of eligible pathogen SNOMED codes.
Yes, facilities can still participate if they are still able to send the final interpretation provided by the lab for the given drug. NHSN requires the specific test result interpretations for MIC, E-Test, and KB are included in the AR Event CDA file. However, if your facility cannot send test-specific data, report these tests as “Not Tested” in the CDA file.
Data suppression prevents complete antimicrobial susceptibility data from being reported to the AR Option. We have observed that there are two types of suppression. The first is that the testing instrument suppresses the results for organism-drug combinations that are not supposed to be reported for microbiology purposes, such as ampicillin for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The second is data suppression for the purpose of antimicrobial stewardship; for example, suppressing carbapenems for E. coli isolates that are susceptible to first, second, or third generation cephalosporins to reduce the use of carbapenems.
For the first purpose, we would recommend keeping those results suppressed and not submitting them to NHSN. For the organism-drug combinations that are suppressed for purpose #2, generally we would recommend that, if feasible, allow labs to release complete antimicrobial susceptibility test results to the EHR and perform data suppression at the EHR level (as opposed to suppression at the susceptibility testing instrument or laboratory information system level). This way, complete data will still be available in the EHR and theoretically should be available for data extraction and submission for surveillance purposes. You might need to work with your microbiology lab to identify which combinations belong to which purpose.
However, if your facility cannot obtain and/or send suppressed data to the NHSN AR Option, NHSN will accept the data your facility is able to provide. Please be sure that your vendor is using ‘Not Tested’ for the unavailable tests/drugs. The NHSN application will not accept AR Event CDA files that do not contain all the required drugs for a given organism.
Yes. Isolates are eligible for reporting to the AR Option regardless of the susceptibility results.
Yes. Bacterial isolates where the laboratory did not test for all NHSN-required antimicrobials but did test for at least one non-required antimicrobial are eligible for NHSN AR Option reporting. For example, if your laboratory tested a Staph aureus isolate for the non-required drug oritavancin, but not for any NHSN-required antimicrobials, that isolate would still be considered eligible for reporting to the AR Option. In this case, your facility would report “Not Tested” for the required antimicrobials.
If it’s a bacterial isolate, your facility must perform at least one antimicrobial test for an isolate to be eligible for inclusion in the AR Option. However, as of January 2025, if it’s a fungal isolate, no antimicrobial susceptibility testing is required.
No. Do not report additional drugs to NHSN. NHSN will only accept the drugs listed in the specific organism’s drug panel.
NHSN requires that Staph aureus isolate CDA files include the PBP2a and PCR mec-gene test variables. However, facilities unable to electronically obtain the results of the PBP2a-agglutination and/or PCR mec-gene tests for Staph aureus may report “Unknown” for these specific tests in the AR Event CDA file.
Report the final interpretation provided by the laboratory. If your laboratory provides no final interpretation, then report the most resistant interpretation (Not Susceptible [NS] > Resistant [R] > Intermediate [I] > Susceptible-Dose Dependent [S-DD] > Susceptible [S] > Not Tested [NA]). For example, if your laboratory performs two E-Tests for the same drug on the same isolate and one produces “Intermediate” (“I”) and the other produces “Susceptible” (“S”), report “Intermediate” (“I”) as the final interpretation for that specific drug susceptibility.
Report the final interpretation provided by the laboratory. If your laboratory provides no final interpretation, then report the most resistant specific test interpretation as the final interpretation (NS > R > I > S-DD > S > NA). For example, if drug susceptibility results produced MIC = “Resistant” (“R”) and E-Test = “Intermediate” (“I”) but your laboratory provides no final interpretation, report “Resistant” (“R”) as the final interpretation for that specific drug susceptibility.
Report the isolate with the most resistant final interpretation (NS > R > I > S-DD > S > NA). If your laboratory does not provide a final interpretation, report the isolate with the higher amount of drug resistance based on the number of antimicrobials testing first “Not Susceptible” (“NS”), if equal amount of “NS” then move to the amount of “Resistant” (“R”), then “I”, then “S-DD”, then “S”. If it cannot be determined which isolate is the most resistant, report the isolate that was the first entered into the LIS.
For example, suppose the laboratory isolated Staph aureus from two blood specimens collected from the same patient on the same calendar day and provided no final interpretation. The first isolate tested resistant to three of the eight antimicrobials tested and the second isolate tested resistant to four of the eight antimicrobials tested. Report the second isolate to NHSN since it showed the higher amount of resistance.
If the LIS does not differentiate between Penicillin G and Penicillin V, list susceptibility results under Penicillin G and report Penicillin V as not tested.
If the LIS produces meningitis and non-meningitis breakpoint results, rely on the specimen source to determine which susceptibility results to report. If the specimen source is CSF, report the meningitis breakpoint susceptibility. If the specimen source is blood, urine, or lower respiratory, report the non-meningitis breakpoint susceptibility.
AR Summary Data
Report combined denominator data for all inpatient locations within the facility (FacWideIN) monthly. This includes patient days (the number of patients present in the facility at the same time on each day of the month, summed across all days in the month) and admissions (the number of admissions to an inpatient location in the facility each month). A patient is counted in the patient days and admissions count for the facility if they are physically located in an NHSN-defined inpatient location regardless of patient status (for example, inpatient, observation). Further, a patient admitted to an inpatient unit is counted as an admission even if they were discharged that same calendar day. Additionally, a patient transfer from an inpatient to an outpatient ED, pediatric ED, or 24-hour observation location then back to an inpatient location is counted as two separate admissions. Neither the FacWideIN patient days nor admissions denominators should include the counts from outpatient locations (ED, pediatric ED, and 24-hour observation area).
Facilities should also report AR Option denominator data from the outpatient locations included in their AR Option reporting plan (ED, pediatric ED, and 24-hr observation area). The number of outpatient encounters for the month for that location is included in each individual outpatient location AR Summary file. Each patient visit to the outpatient location counts as a single encounter.
- If the patient’s stay continues into subsequent calendar days, that patient should still only be counted as one encounter.
- If the patient transfers from one outpatient location to another within the same facility, that patient should be counted as one encounter for the first outpatient location and should not be counted as an encounter for the receiving location (specifically, a patient should not contribute two encounters when transferring between outpatient locations in the same facility).
- If the patient is discharged or leaves then returns to that outpatient unit during the same calendar day, that patient should be counted as two encounters.
- If the patient transfers from outpatient to inpatient, then to outpatient, the second outpatient stay (assuming it’s in an eligible location) would be considered a new encounter because there was time spent in an inpatient location.
- If the patient’s stay in the facility crosses calendar months, the patient will contribute an encounter to the first month the patient was in an outpatient location.
The day a patient enters the door to a facility or a location is the date of their admission to that facility or location regardless of patient status (for example, inpatient, observation). If the patient remains in an inpatient location and the facility does not discharge the patient, then that stay is all part of the same admission, no matter how long. A stay that continues across multiple calendar months, assuming the patient remains in an inpatient location the entire stay, is still only one admission counted in the month the patient was originally admitted.
If the patient discharges and then returns on a separate calendar day, then count the patient as a new admission with a new admission date. If the patient discharges and then returns on the same calendar day, then do not count the patient as another admission.
Patient Days and Admissions are not reported for outpatient locations for the AR Option. These location types report outpatient encounters only. Additionally, outpatient locations are not included in the FacWideIN patient day and admission counts.
AR Option Analysis
You can view AR Option data using the NHSN Analysis function. You can find specific details on the AR Option analysis in the AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 3 MB] or in the Analysis Resources section of the NHSN AUR Module webpage. Additionally, NHSN developed short analysis Quick Reference Guides to assist with viewing, modifying, and interpreting the AR Option event and summary data:
AR Option Analysis Cheat Sheet [PDF – 172 KB]
SRIR & pSIR
- Standardized Resistant Infection Ratio (SRIR) [PDF – 739 KB]
- Pathogen-specific Standardized Infection Ratio (pSIR) [PDF – 695 KB]
Incidence & Prevalence
- Hospital-onset Antimicrobial Resistance Incidence Rate Table [PDF – 597 KB]
- Community-onset Antimicrobial Resistance Prevalence Rate Table [PDF – 677 KB]
- Outpatient Antimicrobial Resistance Prevalence Rate Table [PDF – 564 KB]
- Hospital-onset Positive Culture Incidence by Organism Rate Table [PDF – 602 KB]
- Community-onset Positive Culture Prevalence by Organism Rate Table [PDF – 696 KB]
- Outpatient Positive Culture Prevalence by Organism Rate Table [PDF – 575 KB]
Antibiogram
Drug-resistant Organisms
- Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms Line List [PDF – 365 KB]
- Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms Frequency Table [PDF – 309 KB]
- Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms Rate Table [PDF – 293 KB]
Other Report Types
- Antimicrobial Resistance Event Line List [PDF – 376 KB]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Bar Chart [PDF – 361 KB]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Denominator Line List [PDF – 394 KB]
Remember to generate data sets within your NHSN facility before running your analysis reports so the data set includes any newly uploaded data. See question below for information on generating data sets.
Newly uploaded data do not appear in the analysis reports until you generate new data sets within NHSN. Your data set is a snapshot of the data currently in your NHSN facility during the time period specified when you click the “Generate New Data Sets” button. Always generate new data sets after uploading data into NHSN. See the Generating Datasets Guide [PDF – 359 KB] for more information.
Note: Each NHSN user has their own data sets. You may not see the same data as your coworkers if you generated data sets at different times or with different parameters.
AR Events include all events reported into the AR Option regardless of susceptibility results (specifically, a positive culture). Reports for AR Organisms allow you to analyze AR Events from your facility (or group) in which a specific antimicrobial resistant organism (or “phenotype”) was identified. CDC has defined many AR Option phenotypes of epidemiologic importance. Criteria and definitions for the pre-defined phenotypes can be found in Appendix I of the AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 3 MB].
The Antimicrobial Resistance Event Line List report is an organized, detailed list of each record a facility reports into NHSN. You may have to modify the report by filtering by month, pathogen, specimen, or other variable as the default settings may produce a report that is too lengthy to be useful and/or displayed. Users can review the report to verify the data imported successfully and can also be helpful for data validation.
Below is an example AR Event Line List report showing fictitious data and a description of how to read this report:

The Laboratory isolated Stenotrophomonas maltophilia from a patient’s cerebrospinal fluid collected in the MSICU on October 14, 2021. This isolate was resistant to cefiderocol, ceftazidime, chloramphenicol, levofloxacin, and minocycline. The laboratory did not test for sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim. (Please note that data on this report are fictitious and for example only.)
You can find more information about the AR Event Line List in the Antimicrobial Resistance Event Line List quick reference guide [PDF – 323 KB].
The AR Summary line list is a report summarizing denominator data reported into NHSN for FacWideIN and the individual outpatient locations. For FacWideIN, this includes data on patient days and admissions whereas outpatient encounters are reported for the outpatient locations. By default, this report also includes the “Report No AR Events” variable. Information on how to modify the AR Summary Line List, for example filtering by month or changing the variables displayed, is available in our AR Denominator Line List [PDF – 394 KB] quick reference guide. NHSN has also developed a guide for more information on how to report no AR events [PDF – 394 KB]. Below is an example AR Summary Line List report showing fictitious data and a description of how to read this report:

Please note that data on this report are fictitious and for example only.
This report includes the default variables included in the AR summary line list report. The first line shows that in January 2021 for FacWideIN, there were 5,241 patient days and 264 admissions. The second line shows in July 2021 for EMER, there were 375 patient encounters. The third line shows in July 2021 for FacWideIN, there were 2,350 patient days and 460 admissions reported. In January 2021, the Report No AR Event variable = N, indicating that there are AR Events reported for that calendar month. However, in both rows for July 2021, the Report No AR Event variable = Y, indicating that there were no AR Events to be reported for that calendar month and the facility checked the “Report No Events” boxes for both FacWideIN and EMER.
NHSN provides guidance on recommended AR validation [PDF – 400 KB]. This guidance is helpful for all facilities including those implementing AR Option reporting, those that have undergone a vendor system change, and those that have been reporting for years.
Suppression can lead to significant biases in the antimicrobial resistance data available for surveillance or infection control. Facilities should make every effort to report all antimicrobial resistance data that meet the NHSN protocol requirements, regardless of whether those data are suppressed from clinical end users. Refer to Q4 in the Laboratory Testing Results section for more information. Review of AR Option data, including the steps outlined in the AR Validation guidance [PDF – 400 KB], can be an important step in ensuring data reported to NHSN are complete and accurate.
The NHSN facility-wide antibiogram shows the organisms from the specimens reported into the AR Option for a specified time period of interest. NHSN calculates the percent of isolates that were susceptible (%S) and percent of isolates that were tested (%Tested) for all organism-antimicrobial pairings using the following formulas:
%S = ×100
%Tested = ×100
The numerator of the %S formula only includes susceptible (S) values. The denominator includes susceptible (S), susceptible-dose dependent (S-DD), intermediate (I), resistant (R), and non-susceptible (NS) values.
The percent susceptible is only calculated when 30 or more isolates were tested for a drug.
The percent tested is calculated when at least 1 isolate has been reported.
No, if your lab uses CLSI M39 guidance, the antibiograms will be different. While the NHSN AR Option Protocol and the CLSI M39 guidance differ in deduplication rules, the results should be similar. Further, both can be used to guide the selection of empirical antimicrobial therapy. When a longer period of the analysis is applied the NHSN-CLSI difference is likely to be larger but not be huge. If you see a large difference, we recommend reviewing and validating the data [PDF – 1MB].
Also, NHSN users should keep in mind that prior to 2025, NHSN AR Option surveillance did not include specimen sources other than blood, CSF, lower respiratory tract, or urine. Other specimen types, such as wound cultures, can be included in your lab produced M39 antibiogram. As a result, only specimen-specific antibiograms can be compared, and use of NHSN AR Option surveillance data as guidance for empirical antimicrobial therapy is limited to infections of specific infection sites (bacteremia, pneumonia, central nervous system infections, or UTI).
Beginning in 2025, NHSN AR Option surveillance added isolates from skin, soft tissue, wound and musculoskeletal so the isolates included in the facility-produced M39 antibiogram should be much closer to what’s reported in NHSN.
The facility-wide antibiogram table displays the calculated percent susceptible (%S) for each organism-antimicrobial combination for the time period of interest. Users can modify the antibiogram table to further customize this output. Additional information on the antibiogram is available in the antibiogram quick reference guide [PDF – 1MB].
Below is an example of a facility-wide antibiogram showing fictitious data and a description of how to read it:
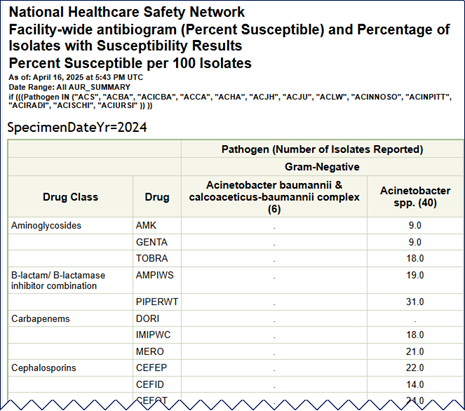
Please note that data on this report are fictitious and for example only.
The column headers list the organism category and specific pathogen while the rows represent each antimicrobial test, sorted by drug class. In this example, there were 40 isolates identified as Acinetobacter species. Since there were more than 30 isolates reported, NHSN generates the susceptibility percentages. The first row in that column shows 9% of the Acinetobacter spp. isolates tested were susceptible to amikacin (AMK).
There were only 6 isolates identified as Acinetobacter baumannii or Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex. Because there were less than 30 isolates reported, the susceptibility information is withheld and represented with “.” in the cell. Additionally, specific organism/drug combinations for which there were less than 30 isolates tested will also show as “.”.
Cells shaded in grey represent non-valid organism/drug combinations. When reviewing the antibiogram, keep in mind that some organisms may be grouped with others in their genus (for example, Acinetobacter spp.) and also be separated in a column of their own (Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex). For the full drug name, see the List of Antimicrobial Agents Eligible for AUR Module [XLS – 482 KB] spreadsheet, which is found in the Supporting Materials section of the AUR Module webpage.
Yes, if you customize an antibiogram report and plan to run the same analysis again, you can save your modifications as a template for future use. Once you’ve made your modifications, follow the steps below to save them as a custom report template:
- Click Save on the bottom right-hand side of the modifications screen.
- Change the report name and title on the “Specify a name for your Analysis Report” pop-up screen.
- Click Save to save your modified report as a custom analysis report.
Your report will save to the “Custom Reports” folder under your Antimicrobial Resistance Data folder.
Please note that your modifications will be saved as a template. The custom report will not save the results. Specifically, if new data are uploaded and new data sets are generated, the custom antibiogram output would include the new data (assuming they meet the modification criteria).
To make modifications to your custom report, click the report and select the “Modify Report” option.

Low percent tested values in your NHSN-produced antibiogram may be due to one or more the following reasons:
- The antimicrobial agent is only tested against that reportable organism by request, or
- Your facility implements data suppression practices for antimicrobial stewardship purposes, such as selective or cascade reporting, which may involve suppressing antimicrobial susceptibility testing results of select drug(s) from clinician’s view. If you notice your percent tested is low for a routinely tested drugs, we recommend reaching out to your micro lab and/or IT team to learn more about whether your facility implements data suppression practices. If data suppression is being applied, work with your lab and IT team to find ways to extract complete data for surveillance purposes.
For more information, refer “Minimizing Bias & Bypassing Suppression” under the AR Option section in the AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1 MB].
NHSN automatically calculates AR Event onset categorization based on the number of hospital days between the date the patient is admitted to the facility and the specimen collection date. Facility admission date is considered Day 1.
- ≤ 3 days = community-onset (CO)
- ≥ 4 days = healthcare facility-onset (HO)
The table and graphic below indicate the onset of an AR Event collected on specific hospital days.
| Specimen collected on hospital day: | AR Event onset: |
|---|---|
| ED encounter | CO |
| Day 1 (admission) | CO |
| Day 2 | CO |
| Day 3 | CO |
| Day 4 | HO |
| Day 5+ | HO |

Please note: any specimen collected in an outpatient location will be categorized as community-onset (CO).
The AR Option Incidence and Prevalence reports utilize AR Event data and AR Summary data to calculate the incidence and prevalence rates for specific pathogens (or pathogen groups) and AR phenotypes [PDF – 1MB]. We use the term incidence for our hospital-onset AR Events. We use the term prevalence for our community-onset AR Events. Rates are provided for each individual specimen type and for all specimen types combined. Additionally, we have AR Option incidence and prevalence quick reference guides and training videos can be found under: NHSN AUR Training.
Incidence Rate =
Community-onset Prevalence Rate =
Outpatient Prevalence Rate =
No, AR Option reporting is separate and independent of events reported through the MDRO/CDI Module. The AR Option and the MDRO/CDI Module use different definitions for event and summary data. For example, the two modules include different specimen sources and different de-duplication rules. Additionally, while the patient days definition used in the AR Option is the same as the definition used in the MDRO/CDI Module, the admissions definition used in the AR Option is different than the definition used in the MDRO/CDI Module.
Standardized Resistant Infection Ratio (SRIR) and Pathogen-specific Standardized Infection Ratio (pSIR)
The SRIR and pSIR are risk-adjusted metrics developed by CDC to analyze antimicrobial resistance and infections associated with specific pathogens. NHSN calculates the SRIR by dividing observed resistant infections by predicted resistant infections. NHSN calculated the pSIR by dividing observed infections of specific pathogens by predicted infections of specific pathogens. More information on how NHSN calculates the SRIR and pSIR can be found in the NHSN AUR Module Protocol [PDF – 1 MB] and the NHSN SRIR/pSIR Guide [PDF – 1 MB]. Additionally, we have SRIR/pSIR quick reference guides and training videos can be found under: NHSN AUR Training.
SRIR =
pSIR =
No. You cannot generate a SRIR or pSIR by month or location. SRIRs and pSIRs are only available by quarter, half year, year, or cumulative time periods. SRIRs and pSIRs are calculated for facility-wide inpatient locations.
You can generate 2019 baseline SRIRs/pSIRs for data for specimen collection dates January 1, 2019 and forward.
You can generate pSIRs for the following pathogens:
- Enterobacterales, which includes Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Enterobacter spp.
- Enterococcus: includes all Enterococcus spp.
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
You can generate SRIRs for the following AR Option phenotypes:
| Phenotype Name | Phenotype Definition |
| Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales | Any Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Enterobacter spp. that has tested resistant (R) to at least one of the following: imipenem, meropenem, doripenem, ertapenem, meropenem/vaborbactam, or imipenem/relebactam |
| Extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales | Any Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Enterobacter spp. that has tested resistant (R) to at least one of the following: cefepime, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ceftazidime-avibactam, or ceftolozane-tazobactam |
| Fluoroquinolone-resistant Enterobacterales | Any Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Enterobacter spp. that has tested resistant (R) to at least one of the following: ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, or moxifloxacin |
| Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus | Any Enterococcus spp. that has tested resistant (R) to vancomycin |
| Fluoroquinolone-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa that has tested resistant (R) to at least one of the following: ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin |
| Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa that has tested either intermediate (I) or resistant (R) to at least one drug in at least three of the following six categories:
1. Extended-spectrum cephalosporin (cefepime, ceftazidime, ceftazidime-avibactam, ceftolozane-tazobactam) 2. Fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) 3. Aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin, tobramycin) 4. Carbapenems (imipenem, meropenem, doripenem, imipenem/relebactam) 5. Piperacillin/tazobactam 6. Cefiderocol |
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | Staphylococcus aureus that has tested resistant (R) to at least one of the following: oxacillin or cefoxitin |
The SRIR report includes a set of tables that display the SRIR by AR phenotype (hospital-onset AR Events that meet NHSN-specific resistance definitions) and specimen source (blood, lower respiratory tract, and urine). SRIRs are not available for the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal specimen sources. The pSIR report includes a set of tables that display the pSIR by pathogen or pathogen group, regardless of susceptibility results, by specimen source (blood, lower respiratory tract, and urine). pSIRs are not available for the CSF, skin, soft tissue, wound, and musculoskeletal specimen sources.
Only hospital-onset events are included in the numerator for both SRIRs and pSIRs. The prevalence rate of community-onset events is included in the calculation of predicted resistant infections for most SRIR models.
When the SRIR equals 0, this indicates the facility reported HO isolates for the organism of interest from the given specimen source, but none were found to meet resistance criteria.
When the pSIR equals 0, this indicates the facility reported at least one isolate from the specimen source of interest (for any HO organism), but the organism of interest was not isolated from any of those specimens.
The SRIR will be missing when no HO isolates of the organism of interest were reported from the given specimen source during the time period, or an HO organism of interest was reported for the specimen source but <0.3 events were predicted. NHSN does not generate a SRIR when the number of predicted infections is less than 0.3 to enforce a minimum precision criterion and avoid statistically imprecise SRIRs, which typically have extreme values.
The pSIR will be missing when no positive culture grew reportable AR organisms from the given specimen source during the time period, or an HO organism of interest was reported for the specimen source but <0.3 events were predicted. NHSN does not generate a pSIR when the number of predicted infections is less than 0.3 to enforce a minimum precision criterion and avoid statistically imprecise pSIRs, which typically have extreme values.
If your facility answered ‘N’ to the NHSN Annual Hospital Survey question, “Has the laboratory implemented revised breakpoints recommended by CLSI?” for cephalosporin and monobactam breakpoints for Enterobacterales in 2010 or carbapenem breakpoints for Enterobacterales in 2010, then the predicted values and SRIRs for extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales and/or carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, respectively, will be suppressed for that year.

