HIV and Hispanic/Latino People: Risk Behaviors
The risk of getting or transmitting HIV varies widely depending on the type of exposure or behavior. Most commonly, people get or transmit HIV through anal or vaginal sex, or sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment—for example, cookers.

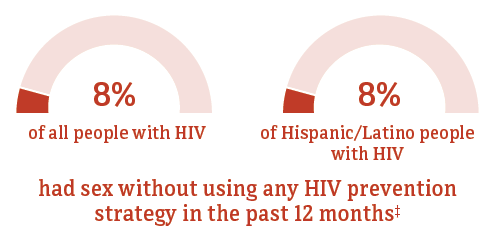
* Hispanic/Latino people can be of any race.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
‡ Had sex while not virally suppressed with a partner whose HIV status was negative or unknown, a condom was not used, and the partner was not taking PrEP.
Source: CDC. Medical Monitoring Project.

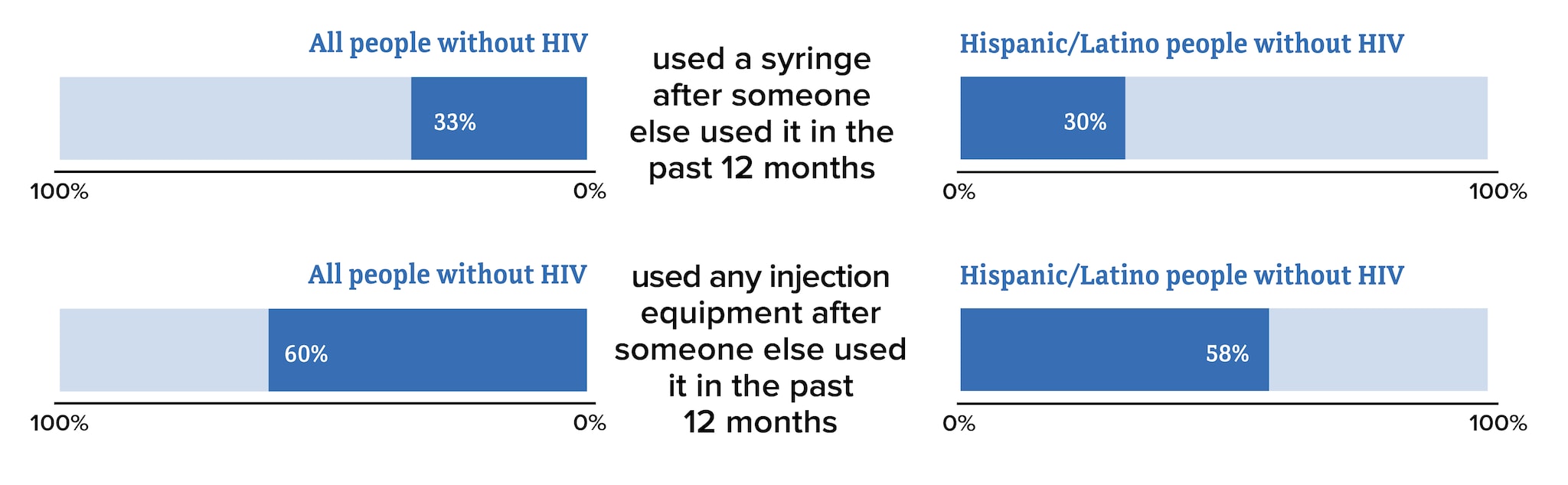
* Hispanic/Latino people can be of any race.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
Source: CDC. HIV infection risk, prevention, and testing behaviors among persons who inject drugs—National HIV Behavioral Surveillance: injection drug use, 23 U.S. Cities, 2018. HIV Surveillance Special Report 2020;24.
- CDC. Behavioral and clinical characteristics of persons with diagnosed HIV infection—Medical Monitoring Project, United States, 2020 cycle (June 2020–May 2021). HIV Surveillance Special Report 2022;29.
- CDC. Diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Report 2021;32.
- CDC. Estimated HIV incidence and prevalence in the United States, 2015–2019. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2021;26(1).
- CDC. Monitoring selected national HIV prevention and care objectives by using HIV surveillance data—United States and 6 dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2021;26(2).
- del Rio C. Latinos and HIV care in the Southeastern United States: New challenges complicating longstanding problems. Clin Infect Dis 2011;53(5):488-9. PubMed abstract.