HIV and Women: Viral Suppression and Barriers to Care
Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state and local jurisdictions. While 2020 data on HIV diagnoses and prevention and care outcomes are available, we are not updating this web content with data from these reports.
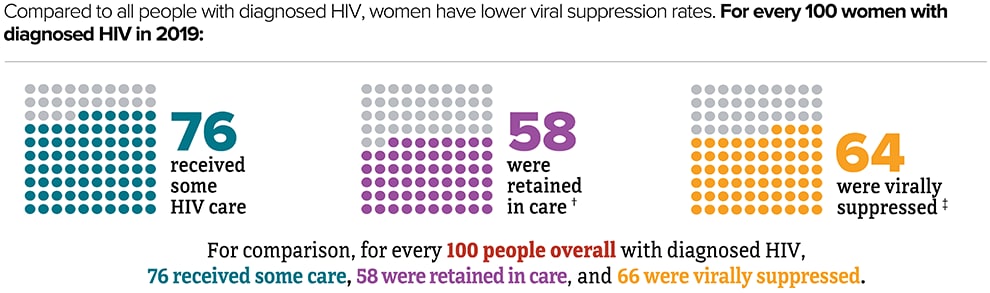
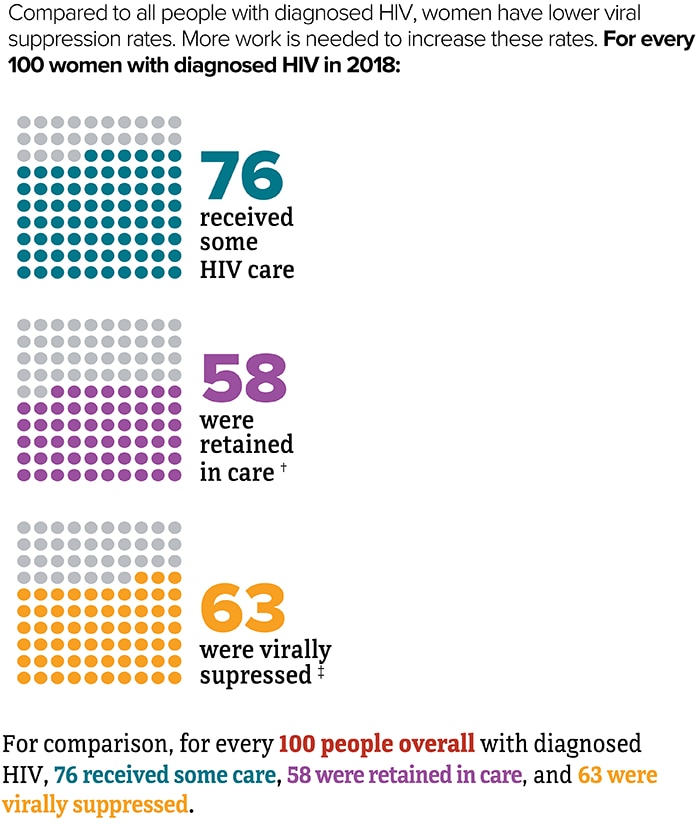
Viral suppression is one of the six Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S. indicators. Viral suppression refers to the percentage of people with diagnosed HIV who have less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.

Download and Share This Infographic
* Based on sex assigned at birth.
† Had 2 viral load or CD4 tests at least 3 months apart in a year.
‡ Based on most recent viral load test.
Source: CDC. Monitoring selected national HIV prevention and care objectives by using HIV surveillance data United States and 6 dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2021;26(2).
Although many people taking HIV medicine are virally suppressed, some people with HIV are currently not virally suppressed or do not maintain viral suppression over time. Some challenges with achieving and maintaining viral suppression include missing multiple doses of HIV treatment, missing medical appointments, or needing other important health care services.

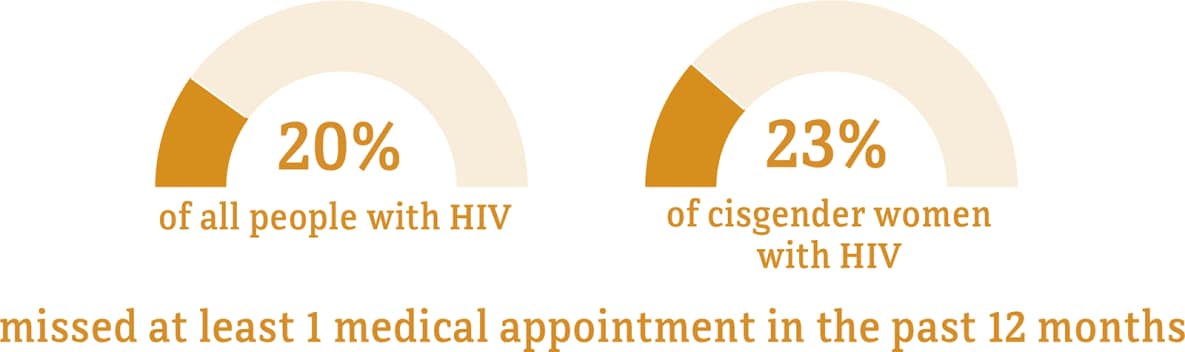
Data for transgender women are not included because the numbers are too small to report.
* The term cisgender women refers to people assigned female at birth who identify as female.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
Visit the terminology section for terms and definitions.
Source: CDC. Medical Monitoring Project.

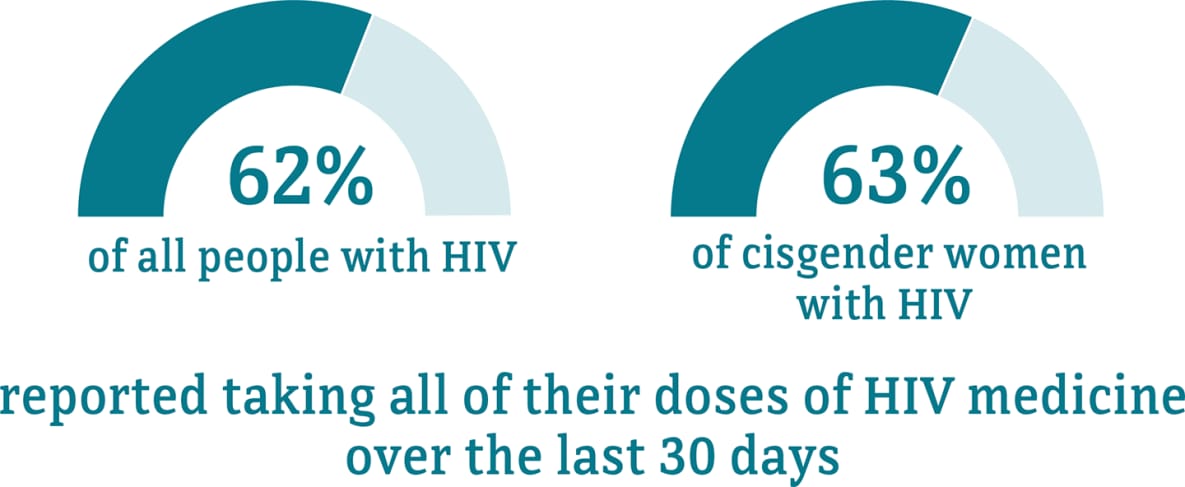
Data for transgender women are not included because the numbers are too small to report.
* The term cisgender women refers to people assigned female at birth who identify as female.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
Visit the terminology section for terms and definitions.
Source: CDC. Medical Monitoring Project.
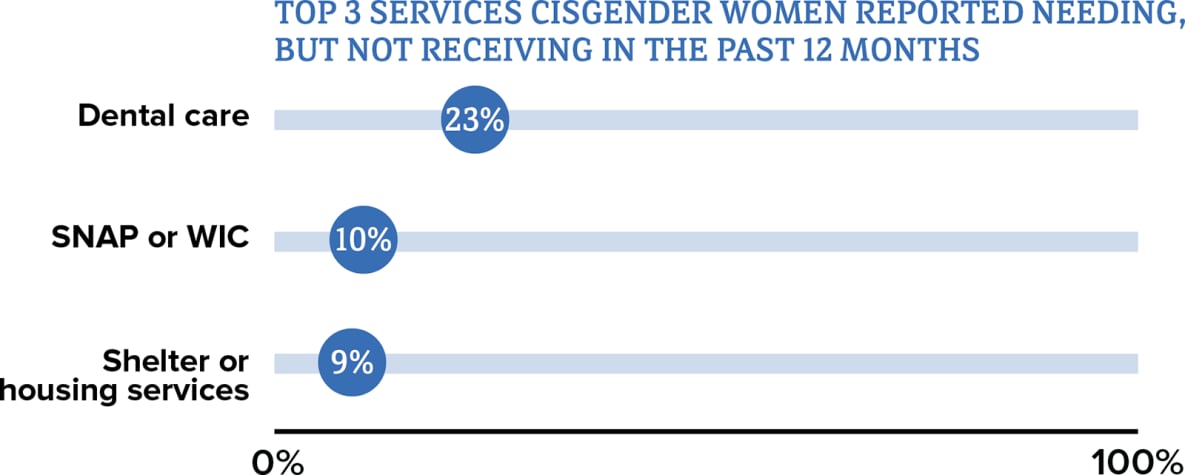

Abbreviations: SNAP = Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program; WIC = Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children.
Data for transgender women are not included because the numbers are too small to report.
* The term cisgender women refers to people assigned female at birth who identify as female.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
‡ HIV ancillary services, such as case management and mental health services, are services that support retention in HIV care.
Visit the terminology section for terms and definitions.
Source: CDC. Medical Monitoring Project.

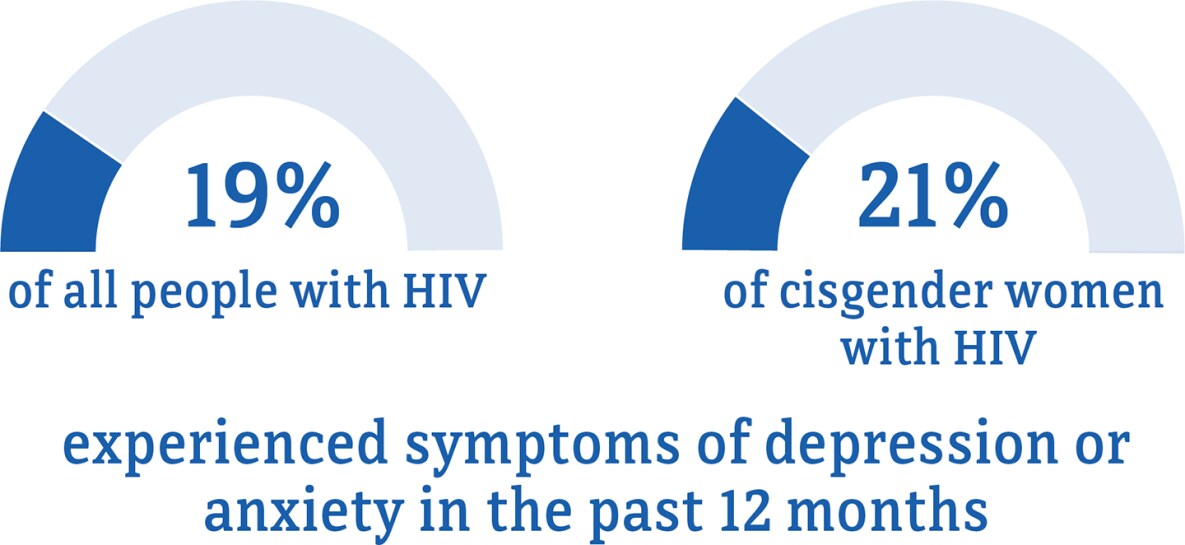
Data for transgender women are not included because the numbers are too small to report.
* The term cisgender women refers to people assigned female at birth who identify as female.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
Visit the terminology section for terms and definitions.
Source: CDC. Medical Monitoring Project.
Social and economic issues—such as stigma and homelessness—have also prevented some women from getting the HIV care and treatment they need.

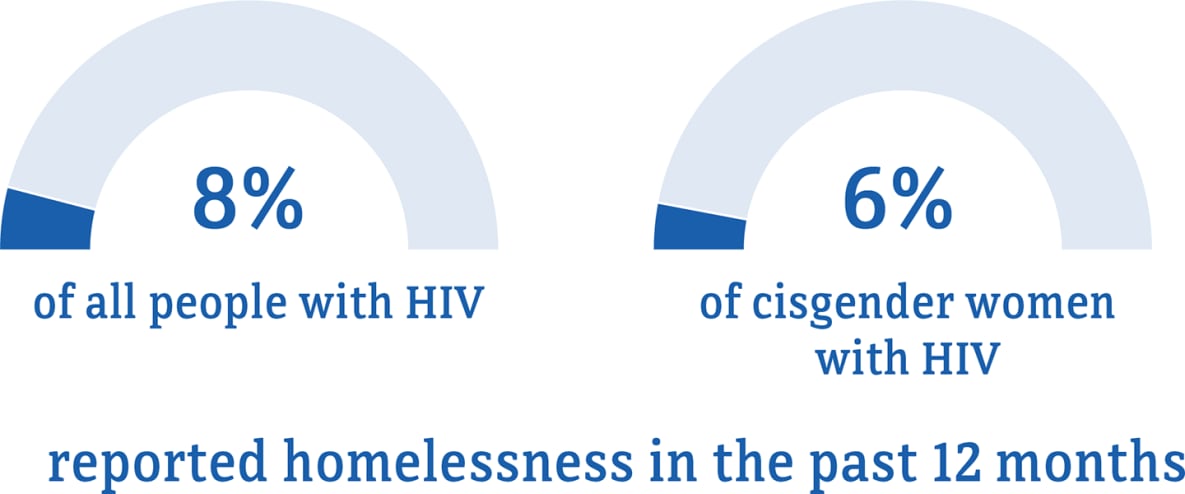
Data for transgender women are not included because the numbers are too small to report.
* The term cisgender women refers to people assigned female at birth who identify as female.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
Visit the terminology section for terms and definitions.
Source: CDC. Medical Monitoring Project.
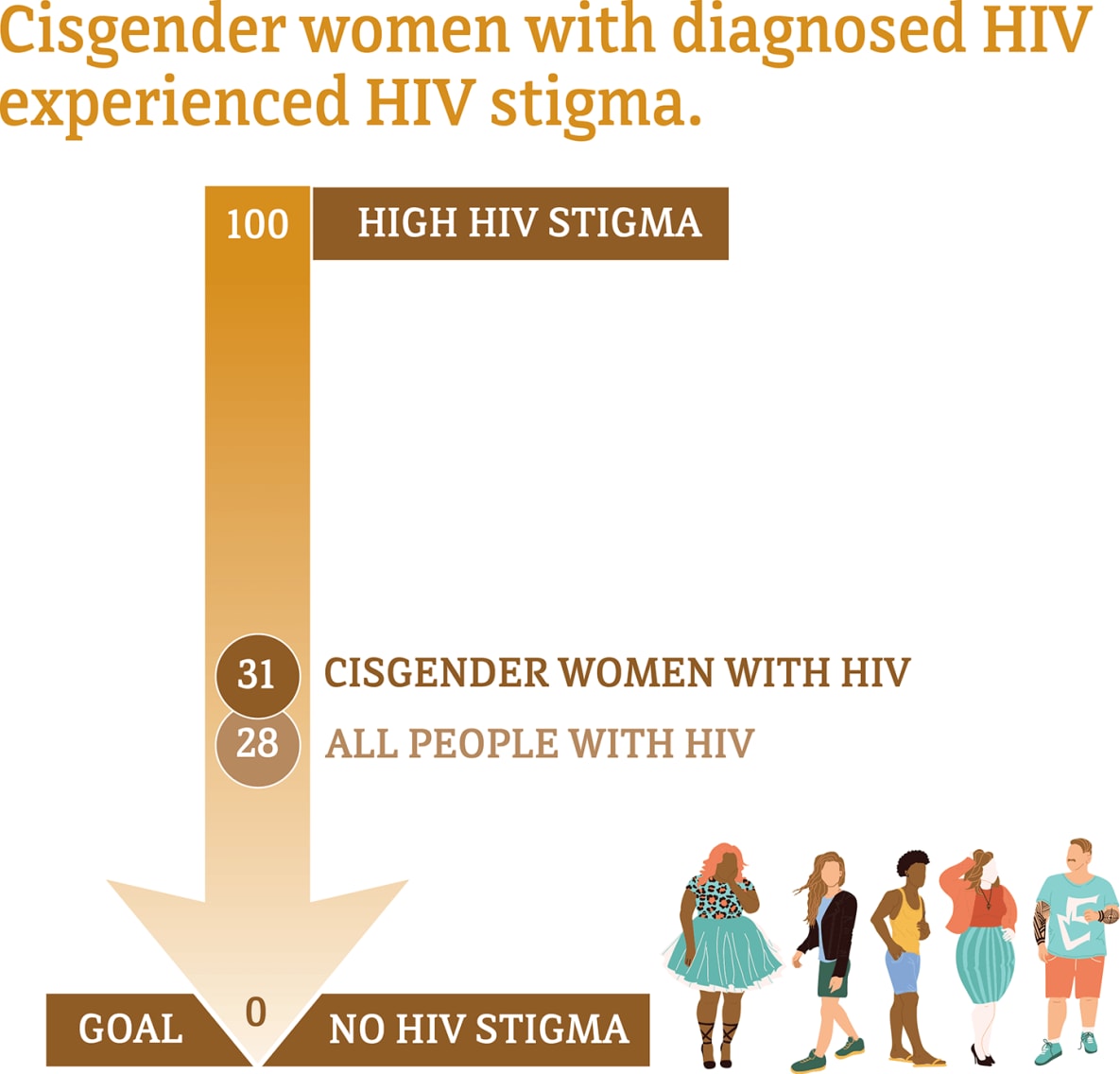
Data for transgender women are not included because the numbers are too small to report.
Median HIV stigma scores are presented based on a ten-item scale ranging from 0 (no stigma) to 100 (high stigma) that measures personalized stigma during the past 12 months, current disclosure concerns, current negative self-image, and current perceived public attitudes about people with HIV.
* The term cisgender women refers to people assigned female at birth who identify as female.
† Among people aged 18 and older.
Visit the terminology section for terms and definitions.
Source: CDC. Medical Monitoring Project.
Cisgender: A person whose sex assigned at birth is the same as their gender identity or expression.
Gender expression: A person’s outward presentation of their gender (for example, how they dress).
Gender identity: A person’s internal understanding of their own gender.
Transgender: A person whose gender identity or expression is different from their sex assigned at birth.
- CDC. Behavioral and clinical characteristics of persons with diagnosed HIV infection—Medical Monitoring Project, United States, 2020 cycle (June 2020–May 2021). HIV Surveillance Special Report 2022;29.
- CDC. Diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Report 2021;32.
- CDC. Estimated HIV incidence and prevalence in the United States, 2015-2019 [PDF – 3 MB]. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2021;26(1).
- CDC. HIV infection risk, prevention, and testing behaviors among heterosexually active adults at increased risk for HIV infection–National HIV Behavioral Surveillance – 23 U.S. Cities, 2019 [PDF – 3 MB]. HIV Surveillance Special Report 2021; 26.
- CDC. HIV infection risk, prevention, and testing behaviors among persons who inject drugs–National HIV Behavioral Surveillance: injection drug use – 23 U.S. Cities, 2018 [PDF – 2 MB]. HIV Surveillance Special Report 2020; 24.
- CDC. Monitoring selected national HIV prevention and care objectives by using HIV surveillance data—United States and 6 dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2021;26(2).