HIV and Women: HIV Risk Behaviors

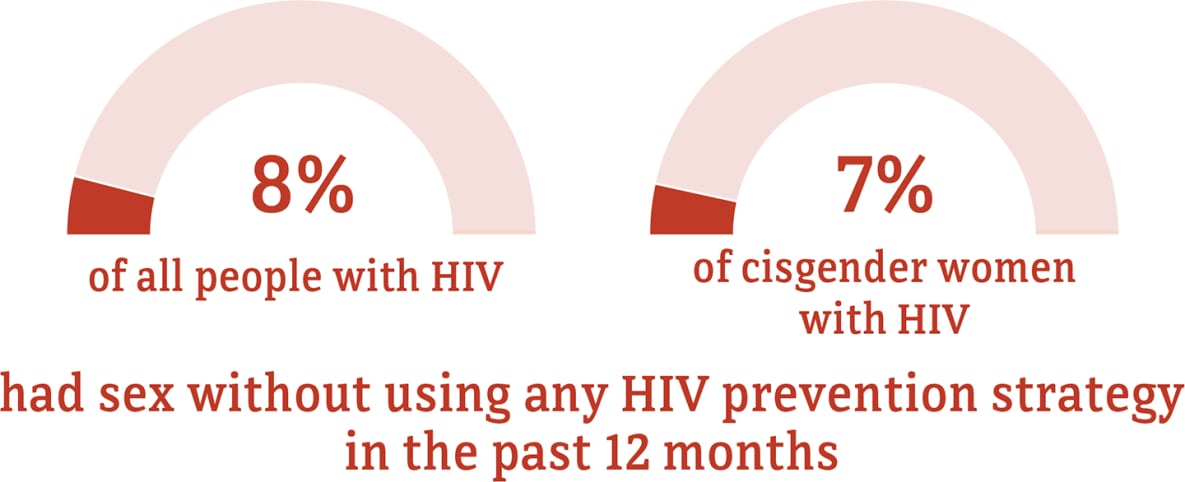
Data for transgender women are not included because the numbers are too small to report.
* The term cisgender women refers to people assigned female at birth who identify as female.
† Had sex while not virally suppressed with a partner whose HIV status was negative or unknown, a condom was not used, and the partner was not taking PrEP.
Visit the terminology section for terms and definitions.
Source: CDC. Behavioral and Clinical Characteristics of Persons with Diagnosed HIV Infection—Medical Monitoring Project, United States, 2020 Cycle (June 2020–May 2021). HIV Surveillance Special Report 2022;29.
Download and Share This Infographic
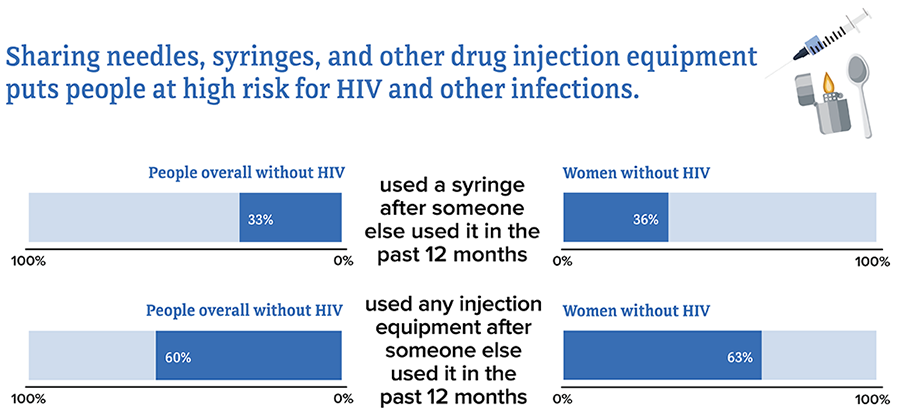
* Based on current gender identity.
Source: CDC. HIV infection risk, prevention, and testing behaviors among persons who inject drugs—National HIV Behavioral Surveillance: injection drug use, 23 U.S. Cities, 2018 [PDF – 2 MB]. HIV Surveillance Special Report 2020; 24.
Cisgender: A person whose sex assigned at birth is the same as their gender identity or expression.
Gender expression: A person’s outward presentation of their gender (for example, how they dress).
Gender identity: A person’s internal understanding of their own gender.
Transgender: A person whose gender identity or expression is different from their sex assigned at birth.
- CDC. Behavioral and clinical characteristics of persons with diagnosed HIV infection—Medical Monitoring Project, United States, 2020 cycle (June 2020–May 2021). HIV Surveillance Special Report 2022;29.
- CDC. Diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Report 2021;32.
- CDC. Estimated HIV incidence and prevalence in the United States, 2015-2019 [PDF – 3 MB]. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2021;26(1).
- CDC. HIV infection risk, prevention, and testing behaviors among heterosexually active adults at increased risk for HIV infection–National HIV Behavioral Surveillance – 23 U.S. Cities, 2019 [PDF – 3 MB]. HIV Surveillance Special Report 2021; 26.
- CDC. HIV infection risk, prevention, and testing behaviors among persons who inject drugs–National HIV Behavioral Surveillance: injection drug use – 23 U.S. Cities, 2018 [PDF – 2 MB]. HIV Surveillance Special Report 2020; 24.
- CDC. Monitoring selected national HIV prevention and care objectives by using HIV surveillance data—United States and 6 dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2021;26(2).