Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP)
The Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP) was established in 1986 to monitor antimicrobial resistance (AR) trends in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the US. GISP is a collaborative project among selected sexually transmitted disease (STD) clinics and their state or local public health authorities, and regional laboratories participating in the Antibiotic Resistance Laboratory Network (ARLN), and CDC.
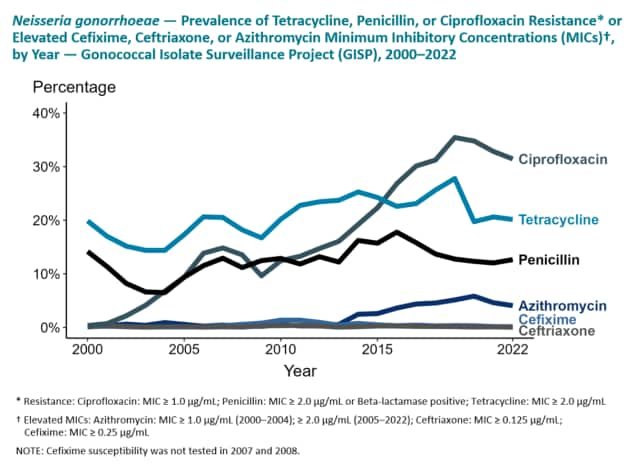
GISP collects N. gonorrhoeae specimens from the first 25 men diagnosed with urethral gonorrhea attending participating STD clinics in selected US cities each month. Participating ARLN regional laboratories test the specimens for resistance to the following antibiotics: azithromycin, cefixime, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, penicillin, and tetracycline. These are antibiotics which either are currently or were previously used for gonorrhea treatment. The ability of the bacteria to resist the effect of the antibiotics in the laboratory is measured, and the results are interpreted according to criteria recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. The results of these tests are then transmitted to CDC where they are collated and analyzed. GISP provides susceptibility trends data used to directly informing gonorrhea treatment recommendations.
GISP, the main surveillance system in the US for monitoring resistant gonorrhea, has expanded in recent years to help improve the ability to detect changes in susceptibility patterns in extragenital anatomic sites of infection and in females. In 2017, GISP expanded in a subset of STD clinics to conduct N. gonorrhoeae surveillance in non-urethral specimens (i.e., pharynx, rectum, and endocervix). The Enhanced Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Program (eGISP) was established to help understand if the pharynx and/or rectum may be anatomic niches that select for or foster resistance and to evaluate if antibiotic susceptibility patterns may vary between men and women.
In 2021, a new molecular testing component was added to eGISP to include the evaluation of known resistance-associated genetic markers. This molecular surveillance project was added to improve the identification of resistant gonorrhea in a culture-independent manner. Culture remains the best way to detect strains with reduced susceptibility to antibiotics used to treat gonorrhea, but molecular surveillance has the potential to increase the availability of resistant gonorrhea detection in the US, especially in locations without culture capacity.
- The Impact of Rapid Drug Susceptibility Tests on Gonorrhea Burden and the Life Span of Antibiotic Treatments: A Modeling Study Among Men Who Have Sex With Men in the United States. Am J Epidemiol. 2024 Jan 8; 193(1):17-25. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwad175.
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Urogenital and Extragenital Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolates Among Men Who Have Sex With Men: Strengthening the US Response to Resistant Gonorrhea and Enhanced Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project, 2018 to 2019. Sex Transm Dis 2021; 48(12S Suppl 2): S111-S117. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001548.
- Management of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States: Summary of Evidence From the Development of the 2020 Gonorrhea Treatment Recommendations and the 2021 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Sexually Transmitted Infection Treatment Guidelines. Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 74, Issue Supplement_2, 15 April 2022, Pages S95–S111, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac043
- Estimates of the Prevalence and Incidence of Chlamydia and Gonorrhea Among US Men and Women, 2018. Sex Transm Dis. 2021 Apr 1;48(4):222-231. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001382. PMID: 33492094.
- Genomic Analysis of the Predominant Strains and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants Within 1479 Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolates From the US Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project in 2018. Sex Transm Dis. 2021 Aug 1;48(8S):S78-S87. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001471. PMID: 33993166; PMCID: PMC8284387
- Update to CDC’s Treatment Guidelines for Gonococcal Infection, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Dec 18;69(50):1911-1916. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6950a6.
- Notes from the Field: First Case in the United States of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Harboring Emerging Mosaic penA60 Allele, Conferring Reduced Susceptibility to Cefixime and Ceftriaxone. MMWR Mortal Wkly Rep 2020; 69(49): 1876-1877. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6949a5.
- CDC Drug Resistant Gonorrhea
- Strengthening the United States Response to Resistant Gonorrhea: Rising to Meet the Programmatic Public Health Challenges of Emerging Neisseria gonorrhoeae Antimicrobial Resistance
- Antibiotic Resistance Laboratory Network
- Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases
- CDC & FDA Antibiotic Resistance Isolate Bank
- For questions about the Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project, please email:
Healthcare providers and health departments can report suspected gonorrhea cephalosporin treatment failure or any N. gonorrhoeae specimen with decreased cephalosporin susceptibility through the Suspected Gonorrhea Treatment Failure Consultation Form.
For questions about reporting a suspected treatment failure or resistant case, please email: GCFAILURE@cdc.gov