Raw Milk Educational Materials and Videos
Read our raw milk Q&As for more information about the health risks of raw milk.
Educational Materials
Julie Riggs and her family live in a small town in Missouri. Her husband and daughter couldn’t tolerate cow’s milk, so the family decided to try raw goat’s milk from a local farmer. In this video, Julie describes what happened to her daughter and husband after they drank the raw milk.
Mary McGonigle-Martin, from California, is the kind of mom who does her homework. Searching for a healthier way to provide dairy for her 7-year-old son, she considered raw milk. In this video, Mary describes what happened after her son drank contaminated raw milk.
Kalee Prue is a health-conscious single mom from Connecticut, who enjoyed being active. Kalee is lactose intolerant and read that drinking raw milk would help her digest dairy better. A few days after finishing the raw milk, Kalee began to get sick. In this video, Kalee tells her story.
Dr. Adam Langer, CDC epidemiologist, discusses the dangers of consuming raw or nonpasteurized dairy products in this CDC podcast, “Raw or Nonpasteurized Products Can Make You Sick” (includes transcript).
- CDC Letter to Epidemiologists and Veterinarians: The Ongoing Public Health Hazards of Consuming Raw Milk [PDF – 5 pages]
Foodborne Outbreak Data

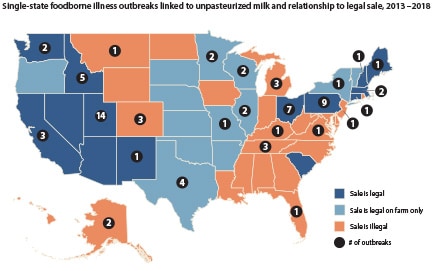
NORS Dashboard provides information on foodborne outbreaks reported to CDC since 1998. You can use it to search outbreak data and see results displayed on interactive maps, graphs, and charts. Conduct a search in NORS Dashboard.
Partner Resources
FDA
- The Dangers of Raw Milk: Unpasteurized Milk Can Pose a Serious Health Risk (Español)
- Video: The Dangers of Unpasteurized Milk
- Questions & Answers: Raw Milk
- Raw Milk Misconceptions and the Danger of Raw Milk Consumption
- Preventing Listeriosis in Pregnant Hispanic Women in the United States (Español)
- Food Safety for Moms-to-Be (Español)
- Food Safety for Moms-to-Be: Once Baby Arrives (Español)