FluView Summary ending on February 20, 2021

Note: CDC is tracking the COVID-19 pandemic in a weekly publication called COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review.
All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.
A description of the CDC influenza surveillance system, including methodology and detailed descriptions of each data component is available on the surveillance methods page.
Additional information on the current and previous influenza seasons for each surveillance component are available on FluView Interactive.
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Seasonal influenza activity in the United States remains lower than usual for this time of year.
Viruses
Severe Disease
All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.
A description of the CDC influenza surveillance system, including methodology and detailed descriptions of each data component is available on the surveillance methods page.
Additional information on the current and previous influenza seasons for each surveillance component are available on FluView Interactive.
Key Points
- Flu activity is unusually low at this time but may increase in the coming months.
- An annual flu vaccine is the best way to protect against flu and its potentially serious complications.
- If you haven’t gotten your flu vaccine yet, get vaccinated now.
- There are also flu antiviral drugs that can be used to treat flu illness.
U.S. Virologic Surveillance:
Clinical Laboratories
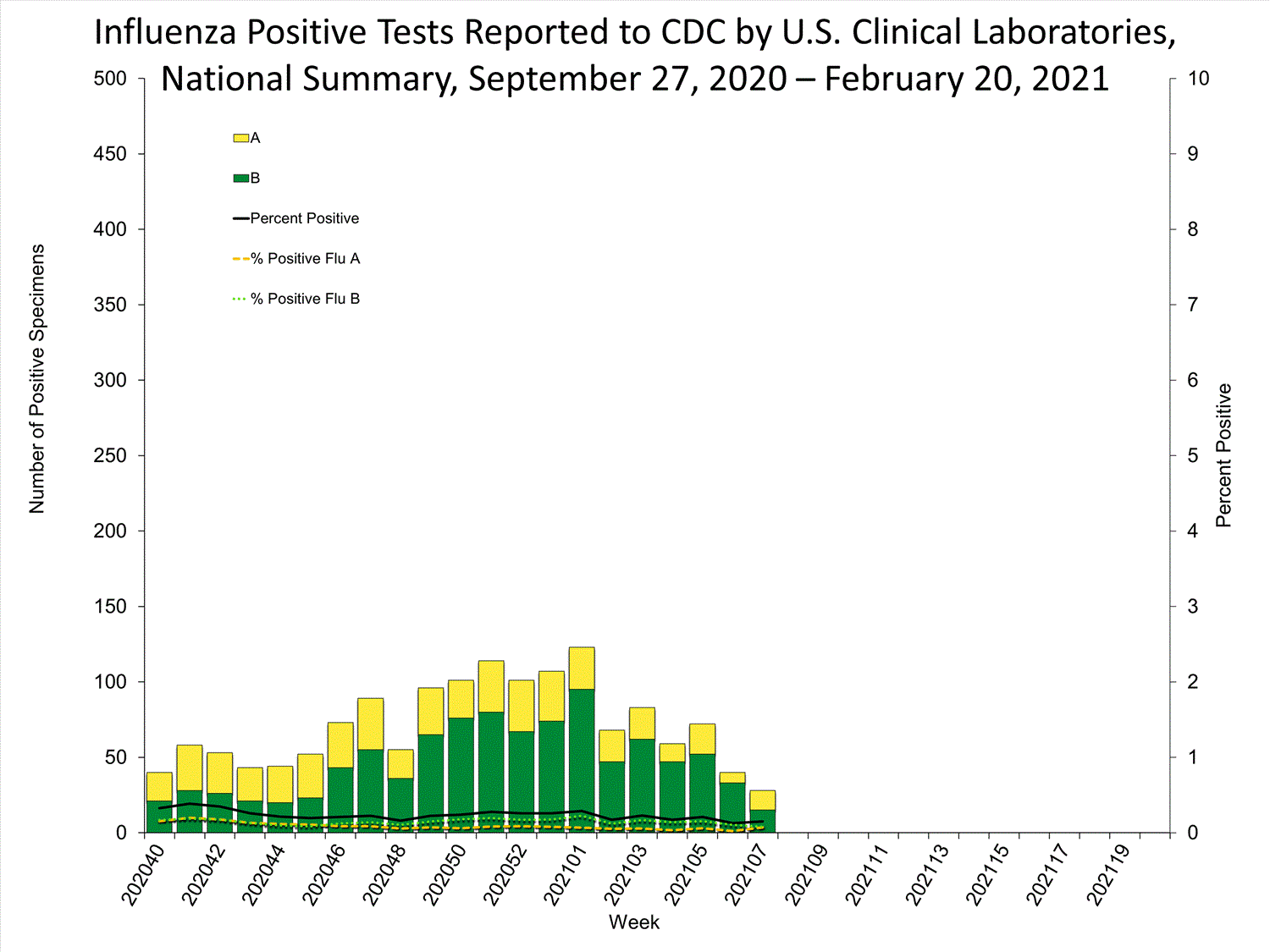
The results of tests performed by clinical laboratories nationwide are summarized below. Data from clinical laboratories (the percentage of specimens tested that are positive for influenza) are used to monitor whether influenza activity is increasing or decreasing.
| Week 7 | Data Cumulative since September 27, 2020 (Week 40) |
|
|---|---|---|
| No. of specimens tested | 18,740 | 659,131 |
| No. of positive specimens (%) | 28 (0.1%) | 1,499 (0.2%) |
| Positive specimens by type | ||
| Influenza A | 13 (46.4%) | 513 (34.2%) |
| Influenza B | 15 (53.6%) | 986 (65.8%) |
Public Health Laboratories
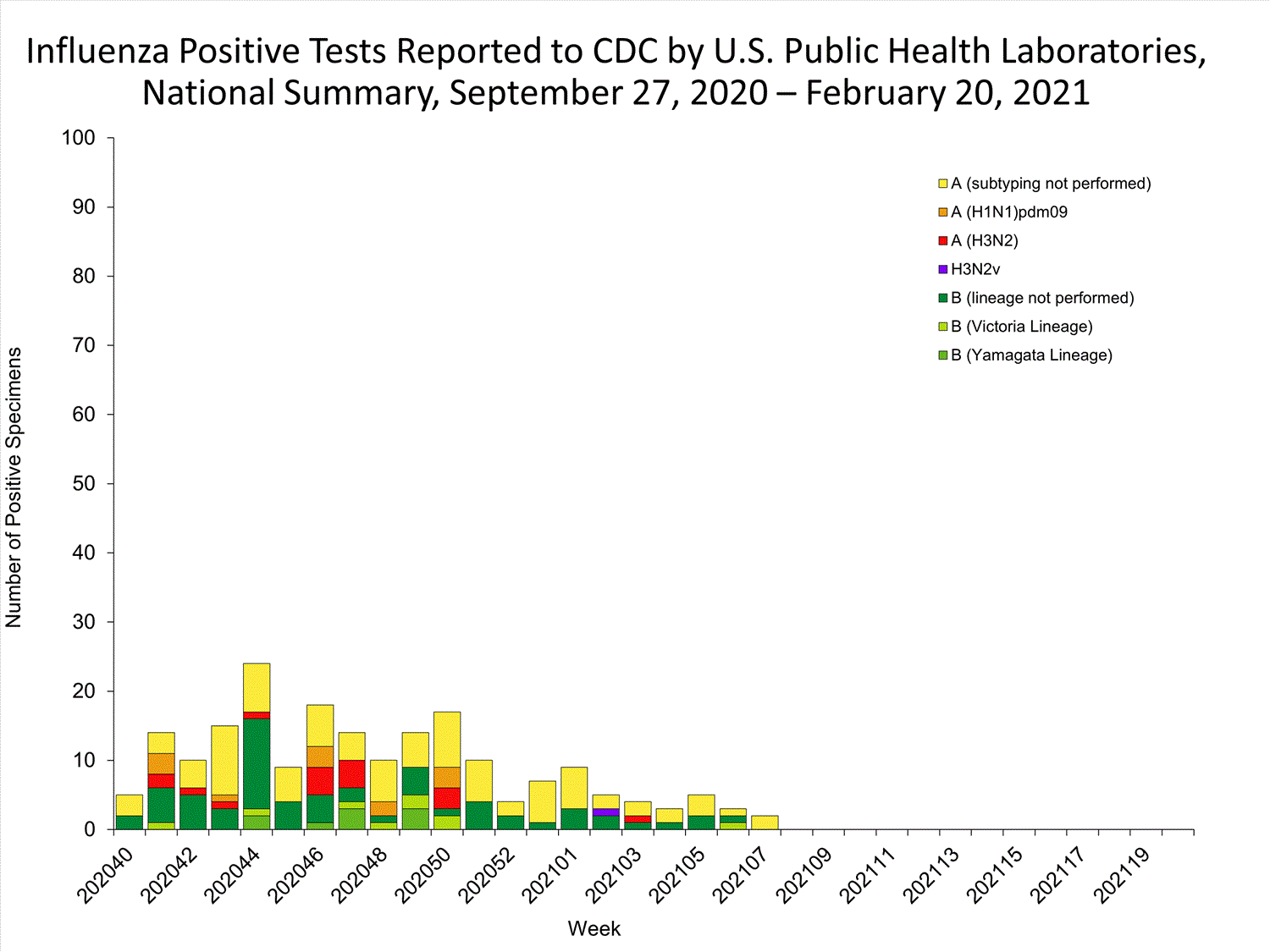
The results of tests performed by public health laboratories nationwide are summarized below. Data from public health laboratories are used to monitor the proportion of circulating viruses that belong to each influenza subtype/lineage.
| Week 7 | Data Cumulative since September 27, 2020 (Week 40) |
|
|---|---|---|
| No. of specimens tested | 12,280 | 321,844 |
| No. of positive specimens | 2 | 202 |
| Positive specimens by type/subtype | ||
| Influenza A | 2 (100%) | 123 (60.9%) |
| (H1N1)pdm09 | 0 (0%) | 12 (40.0%) |
| H3N2 | 0 (0%) | 17 (56.7%) |
| H3N2v | 0 (0%) | 1 (3.3%) |
| Subtyping not performed | 2 | 93 |
| Influenza B | 0 (0%) | 79 (39.1%) |
| Yamagata lineage | 0 (0%) | 9 (50.0%) |
| Victoria lineage | 0 (0%) | 9 (50.0%) |
| Lineage not performed | 0 | 61 |
While influenza B/Victoria viruses predominated earlier in the season, during recent weeks, influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses have been reported more frequently than B/Victoria viruses nationally and in all surveillance regions. For the season, A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses are the predominant virus nationally. Regional and state level data about circulating influenza viruses can be found on FluView Interactive.
The predominant virus also varies by age group. Nationally, for the season overall, influenza B viruses are the most commonly reported influenza viruses among persons 5-24 years, while influenza A viruses are the most commonly reported influenza viruses among persons 0-4 years and 25 years and older. In the most recent three weeks, influenza A viruses are the most commonly reported influenza viruses in all age groups.
Additional virologic surveillance information for current and past seasons:
Surveillance Methods | FluView Interactive: National, Regional, and State Data or Age Data
Novel Influenza A Virus
One human infection with a novel influenza A virus was reported by Wisconsin. This person was infected with an influenza A(H3N2) variant (A(H3N2)v) virus. The patient is a child < 18 years of age, was not hospitalized, and has completely recovered from their illness. Investigation into the source of the infection revealed that the child lives on a farm with swine present. This is the first influenza A(H3N2)v virus infection detected in the United States in 2021.
Early identification and investigation of human infections with novel influenza A viruses are critical so that the risk of infection can be more fully understood and appropriate public health measures can be taken. Additional information on influenza in swine, variant influenza infection in humans, and strategies to interact safely with swine can be found at http://www.cdc.gov/flu/swineflu/index.htm
Additional information regarding human infections with novel influenza A viruses can be found at http://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/fluview/Novel_Influenza.html.
Influenza Virus Characterization
CDC performs genetic and antigenic characterization of U.S. viruses submitted from state and local health laboratories using Right Size Roadmap submission guidance. These data are used to compare how similar the currently circulating influenza viruses are to the reference viruses representing viruses contained in the current influenza vaccines and to monitor evolutionary changes that continually occur in influenza viruses circulating in humans. CDC also tests susceptibility of influenza viruses to antiviral medications, including the neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir, zanamivir, and peramivir) and the PA endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir.
Virus characterization data will be updated weekly starting later this season when a sufficient number of specimens have been tested.
CDC genetically characterized 2,463 influenza viruses collected in the U.S. from September 29, 2019, to April 4, 2020.
| Virus Subtype or Lineage | Genetic Characterization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. of Subtype/Lineage Tested |
Clade | Number (% of subtype/lineage tested) |
Subclade | Number (% of subtype/lineage tested) |
|
| A/H1 | 896 | ||||
| 6B.1A | 896 (100%) | ||||
| A/H3 | 510 | ||||
| 3C.2a | 480 (94.1%) | 2a1 | 480 (94.1%) | ||
| 2a2 | 0 | ||||
| 2a3 | 0 | ||||
| 2a4 | 0 | ||||
| 3C.3a | 31 (5.9%) | 3a | 31 (5.9%) | ||
| B/Victoria | 965 | ||||
| V1A | 965 (100%) | V1A | 0 | ||
| V1A.1 | 60 (6.2%) | ||||
| V1A.3 | 905 (93.8%) | ||||
| B/Yamagata | 92 | ||||
| Y3 | 92 (100%) | ||||
CDC antigenically characterizes a subset of influenza viruses by hemagglutination inhibition (HI) or neutralization based Focus Reduction assays (FRA). Antigenic drift is evaluated by comparing antigenic properties of cell-propagated reference viruses representing currently recommended vaccine components with those of cell-propagated circulating viruses. CDC antigenically characterized 547 influenza viruses collected in the United States from September 29, 2019, to April 4, 2020. These data are not used to make calculations about vaccine effectiveness (VE). CDC conducts VE studies each year to measure the benefits of flu vaccines in people.
Influenza A Viruses
- A (H1N1)pdm09: 212 A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses were antigenically characterized by HI with ferret antisera, and 175 (82.5%) were antigenically similar (reacting at titers that were within 4-fold of the homologous virus titer) to cell-propagated A/Brisbane/02/2018-like reference viruses representing the A(H1N1)pdm09 component for the 2019-20 Northern Hemisphere influenza vaccines. The decrease in the percent of A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses similar to A/Brisbane/02/2018 is due to some of the recent viruses selected for testing having a single amino acid change that is antigenically distinguishable in antigenic assays using ferret sera. Similar viruses were observed last season as well and these represented a small proportion of virus circulating. We have observed an increase in the proportion of H1N1pdm09 viruses with this change late in the US season.
- A (H3N2): 86 A(H3N2) viruses were antigenically characterized by FRA with ferret antisera, and 40 (46.5%) were antigenically similar to cell-propagated A/Kansas/14/2017-like reference viruses representing the A(H3N2) component for the 2019-20 Northern Hemisphere influenza vaccines.
Influenza B Viruses
- B/Victoria: 201 B/Victoria lineage viruses, including viruses from both co-circulating sub-clades, were antigenically characterized by HI with ferret antisera, and 120 (59.7%) were antigenically similar to cell-propagated B/Colorado/06/2017-like reference viruses representing the B/Victoria component for the 2019-20 Northern Hemisphere influenza vaccines.
- B/Yamagata: 48 B/Yamagata lineage viruses were antigenically characterized by HI with ferret antisera, and all 48 (100%) were antigenically similar to cell-propagated B/Phuket/3073/2013-like reference viruses representing the B/Yamagata component for the 2019-20 Northern Hemisphere influenza vaccines.
CDC also assesses susceptibility of influenza viruses to the antiviral medications including the neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir, zanamivir, and peramivir) and the PA endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir using next generation sequence analysis supplemented by laboratory assays. Viruses collected in the United States since September 29, 2019, were tested for antiviral susceptibility as follows:
| Antiviral Medication | Total Viruses* |
A/H1 | A/H3 | B/Victoria | B/Yamagata | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuraminidase Inhibitors |
|||||||
| Oseltamivir | Viruses Tested |
2,433 | 885 | 502 | 954 | 92 | |
| Reduced Inhibition |
1 (0.04%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | 1 (0.1%) | (0.0%) | ||
| Highly Reduced Inhibition |
4 (0.2%) | 4 (0.5%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | ||
| Peramivir | Viruses Tested |
2,433 | 885 | 502 | 954 | 92 | |
| Reduced Inhibition |
(0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | ||
| Highly Reduced Inhibition |
5 (0.2%) | 4 (0.5%) | (0.0%) | 1 (0.1%) | (0.0%) | ||
| Zanamivir | Viruses Tested |
2,433 | 885 | 502 | 954 | 92 | |
| Reduced Inhibition |
2 (0.1%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | 2 (0.2%) | (0.0%) | ||
| Highly Reduced Inhibition |
(0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | ||
| PA Endonuclease Inhibitor | Baloxavir | Viruses Tested |
2,541 | 884 | 584 | 978 | 95 |
| Reduced Susceptibility |
(0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | ||
* Six influenza viruses showed reduced or highly reduced inhibition by at least one neuraminidase inhibitor. Four A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses showed highly reduced inhibition to oseltamivir and peramivir while showing normal inhibition to zanamivir. In addition, one B/Victoria virus showed highly reduced inhibition to peramivir and reduced inhibition to oseltamivir and zanamivir, while another influenza B/Victoria virus showed reduced inhibition to zanamivir.
A total of 556 additional viruses (211 A(H1N1)pdm09, 32 A(H3N2), and 313 B) collected in Alabama, Alaska, Florida, Illinois, Iowa, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Michigan, Nevada, New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Virginia and Wisconsin were analyzed for resistance to neuraminidase inhibitors by pyrosequencing assay. Three (1.4%) of the 211 A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses tested had the H275Y amino acid substitution in the neuraminidase and showed highly reduced inhibition by oseltamivir and peramivir. No molecular markers associated with reduced or highly reduced inhibition by neuraminidase inhibitors were detected in A(H3N2) and type B viruses tested.
Outpatient Illness Surveillance
Please note, the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) monitors outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI), not laboratory-confirmed influenza, and will capture visits due to other respiratory pathogens, such as SARS-CoV-2, that present with similar symptoms. In addition, healthcare-seeking behaviors have changed dramatically during the COVID-19 pandemic. Many people are accessing the healthcare system in alternative settings, which may or may not be captured as a part of ILINet. Therefore, ILI data, including ILI activity levels, should be interpreted with extreme caution. It is particularly important at this time to evaluate syndromic surveillance data, including that from ILINet, in the context of other sources of surveillance data to obtain a complete and accurate picture of both influenza and COVID-19 activity. CDC is tracking the COVID-19 pandemic in a weekly publication called COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review.
ILINet
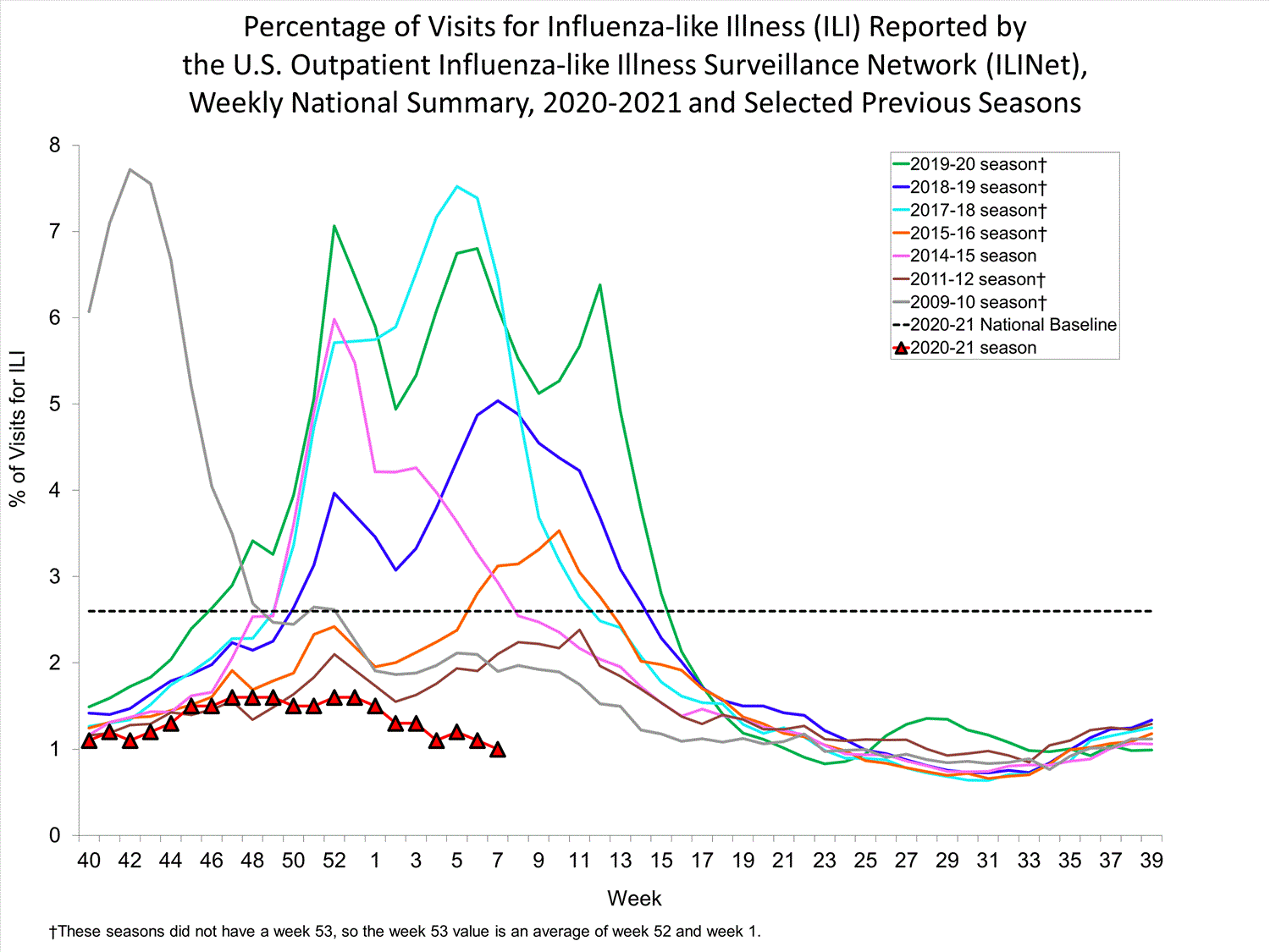
Nationwide during week 7, 1.0% of patient visits reported through ILINet were due to ILI. This percentage is below the national baseline of 2.6%.
During week 7, compared with week 6, the percentage of visits for ILI increased for one region (Region 6), decreased for two regions (Regions 2 and 4), and remained stable (change of ≤ 0.1%) in the remaining seven regions. All regions reported percentages of outpatient visits for ILI below their region-specific baselines.
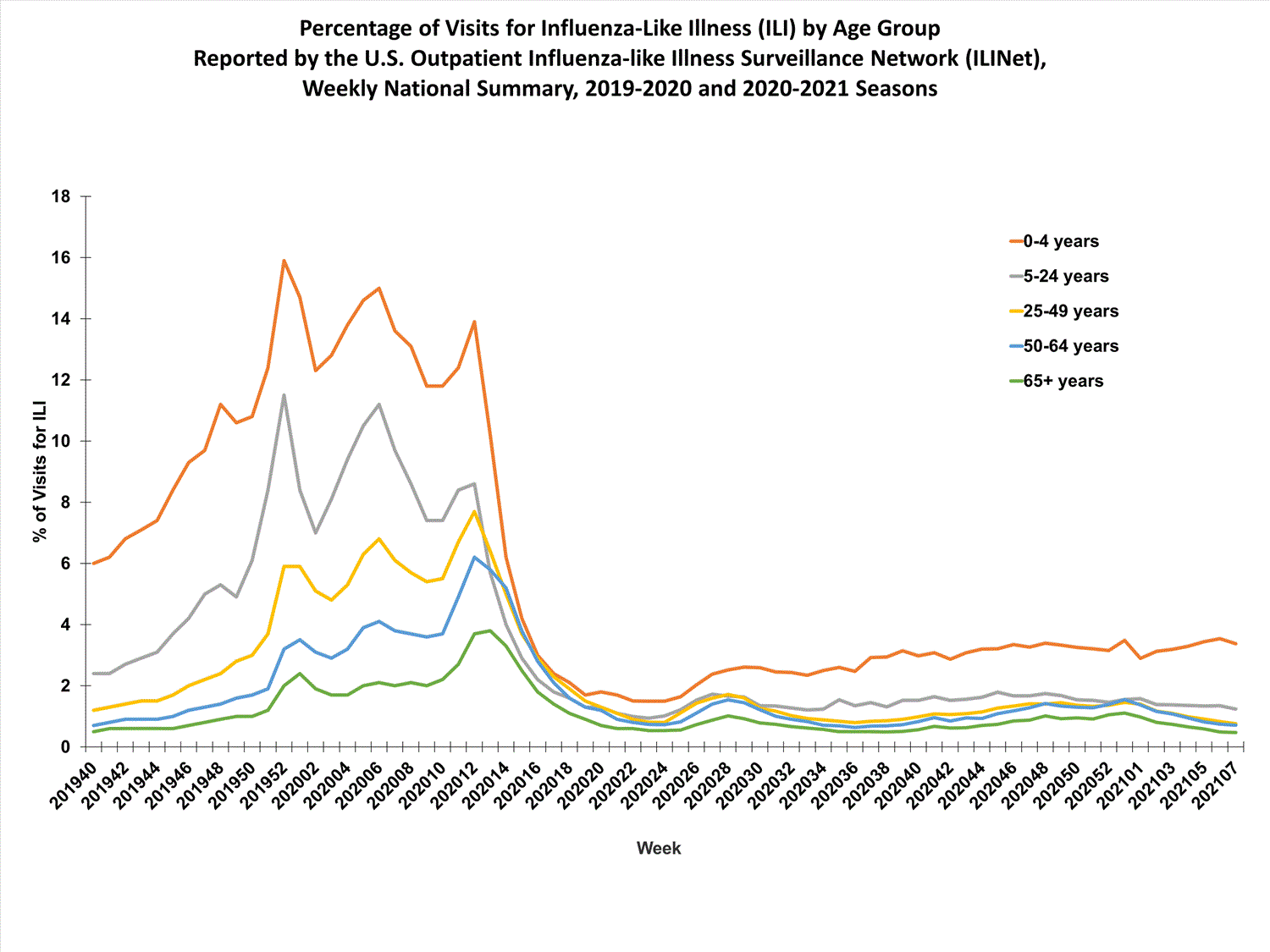
ILI Visits by Age Group
About 65% of ILINet providers provide both the number of patient visits for ILI and the total number of patient visits for the week broken out by age group. Data from this subset of providers are used to calculate the percentages of patient visits for ILI by age group. The percentages of visits for ILI reported in ILINet in week 7 remained stable (change of ≤0.1%) for all age groups (0–4 years, 5–24 years, 25–49 years, 50–64 years, and 65 years and older) compared with week 6. However, during the past six weeks there has been a slightly increasing trend among those 0–4 years and a slightly decreasing trend among the remaining age groups.
ILI Activity Map
Data collected in ILINet are used to produce a measure of ILI activity* by state/jurisdiction and Core Based Statistical Areas (CBSA).
| Activity Level | Number of Jurisdictions | Number of CBSAs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 7
(Week ending |
Week 6
(Week ending |
Week 7
(Week ending |
Week 6
(Week ending |
|
| Very High | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| High | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Low | 0 | 0 | 10 | 15 |
| Minimal | 54 | 55 | 582 | 594 |
| Insufficient Data | 1 | 0 | 336 | 318 |
*Data collected in ILINet may disproportionally represent certain populations within a jurisdiction or CBSA, and therefore, may not accurately depict the full picture of influenza activity for the entire jurisdiction or CBSA. Differences in the data presented here by CDC and independently by some health departments likely represent differing levels of data completeness with data presented by the health department likely being the more complete.
Additional information about medically attended visits for ILI for current and past seasons:
Surveillance Methods | FluView Interactive: National, Regional, and State Data or ILI Activity Map
Geographic Spread of Influenza as Assessed by State and Territorial Epidemiologists
The geographic spread of influenza as reported by state and territorial epidemiologists indicates geographic spread of influenza viruses but does not measure the severity of influenza activity. Due to the impact of COVID-19 on ILI surveillance, and the fact that the state and territorial epidemiologists report relies heavily on ILI activity, reporting for this system will be suspended for the 2020-21 influenza season. Data from previous seasons is available on FluView Interactive.
Additional geographic spread surveillance information for current and past seasons:
Surveillance Methods | FluView Interactive
Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations:
The Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET) conducts population-based surveillance for laboratory-confirmed influenza-related hospitalizations in select counties in 14 states and represents approximately 9% of the U.S. population.
Between October 1, 2020, and February 20, 2021, FluSurv-Net sites in 14 states reported 183 laboratory confirmed influenza hospitalizations for an overall cumulative hospitalization rate of 0.6 per 100,000 population. This is much lower than average for this point in the season and lower than rates for any season since routine data collection began in 2005, including the low severity 2011-12 season. During the 2011-12 season, the rate was 2.2 times higher at this time in the season. Hospitalization rates stratified by age will be presented once case counts increase to a level that produces stable rates by age.
The highest rate of hospitalization is among adults aged ≥ 65, followed by children aged 0-4 years and adults aged 50-64 years.
| Age Group | 2019-2020 Season Cumulative Rate per 100,000 Population |
|---|---|
| Overall | 68.2 |
| 0-4 years | 94.1 |
| 5-17 years | 24.6 |
| 18-49 years | 35.6 |
| 50-64 years | 90.2 |
| 65+ years | 179.7 |
Among 3,433 hospitalized adults with information on underlying medical conditions, 92.3% had at least one reported underlying medical condition, the most commonly reported were cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorder, obesity, and chronic lung disease. Among 569 hospitalized children with information on underlying medical conditions, 48.5% had at least one underlying medical condition; the most commonly reported was asthma. Among 600 hospitalized women of childbearing age (15-44 years) with information on pregnancy status, 27.2% were pregnant.
Additional hospitalization surveillance information for current and past seasons and additional age groups:
Surveillance Methods | FluView Interactive: Rates by Age or Patient Characteristics
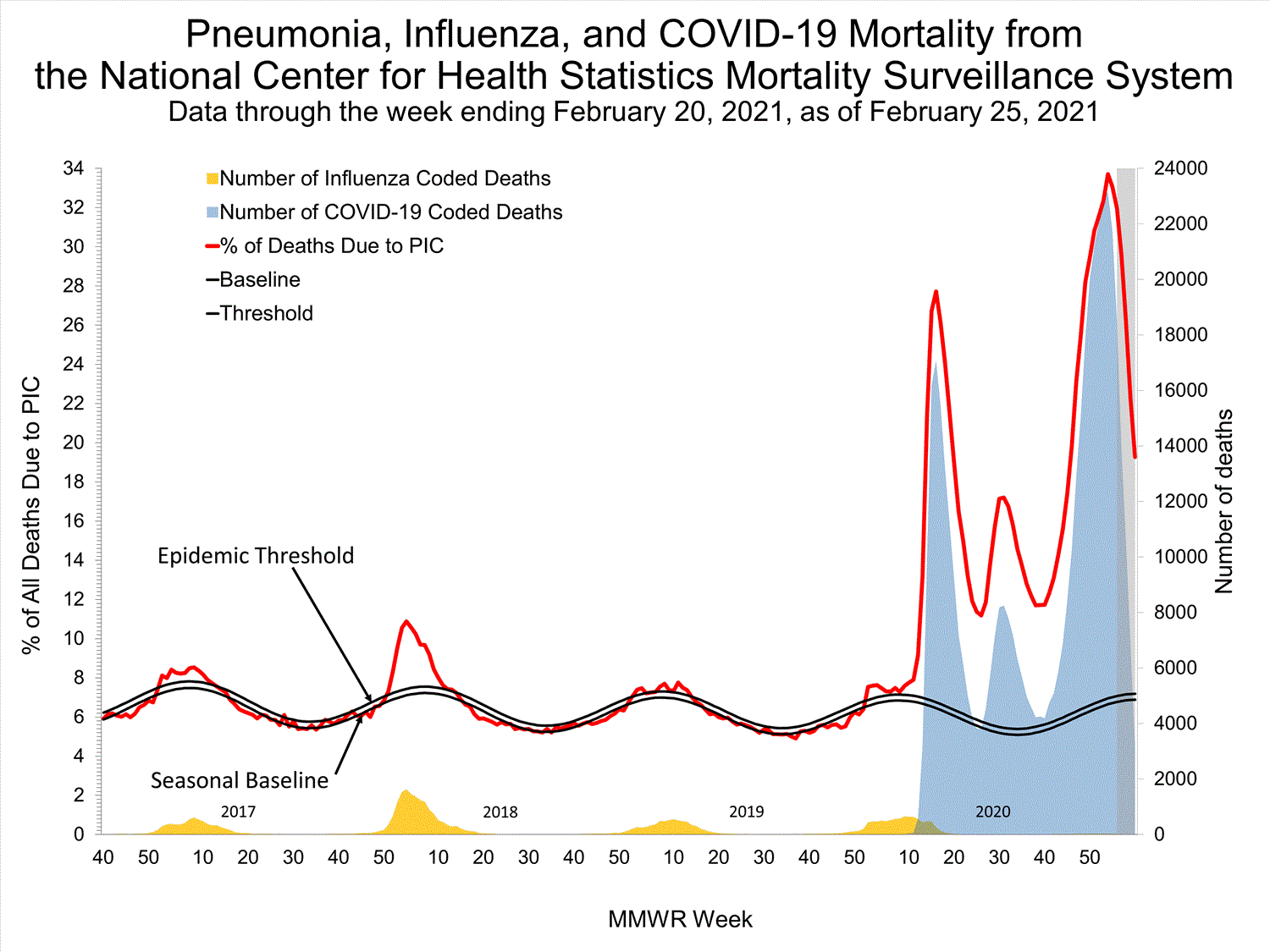
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Mortality Surveillance
Based on NCHS mortality surveillance data available on February 25, 2021, 19.3% of the deaths that occurred during the week ending February 20, 2021 (week 7), were due to pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19 (PIC). This percentage is above the epidemic threshold of 7.2% for week 7. Among the 3,972 PIC deaths reported for this week (week 7), 3,130 had COVID-19 listed as an underlying or contributing cause of death on the death certificate and four listed influenza, indicating that the current increase in PIC mortality is due primarily to COVID-19 and not influenza.
Weekly mortality surveillance data include a combination of machine coded and manually coded causes of death collected from death certificates. Prior to week 4 (the week ending January 30, 2021), the percentages of deaths due to PIC were higher among manually coded records than more rapidly available machine coded records. Improvements have been made to the machine coding process that allow for more COVID-19 related deaths to be machine coded, and going forward, the percentage of PIC deaths among machine coded and manually coded data are expected to be more similar. The data presented are preliminary and expected to change as more data are received and processed, but the amount of change in the percentage of deaths due to PIC should be lower going forward. Weeks for which the largest changes in the percentage of deaths due to PIC may occur are highlighted in gray in the figure below and should be interpreted with caution.
While the percent of all deaths due to P&I has increased during weeks 9-13 (7.4-10.0%), the percent of all deaths with Influenza listed as a cause have decreased (from 1.0% to 0.7%) over this same time period. The increase in pneumonia deaths during this time period are likely associated with COVID-19 rather than influenza.
Additional pneumonia and influenza mortality surveillance information for current and past seasons:
Surveillance Methods | FluView Interactive
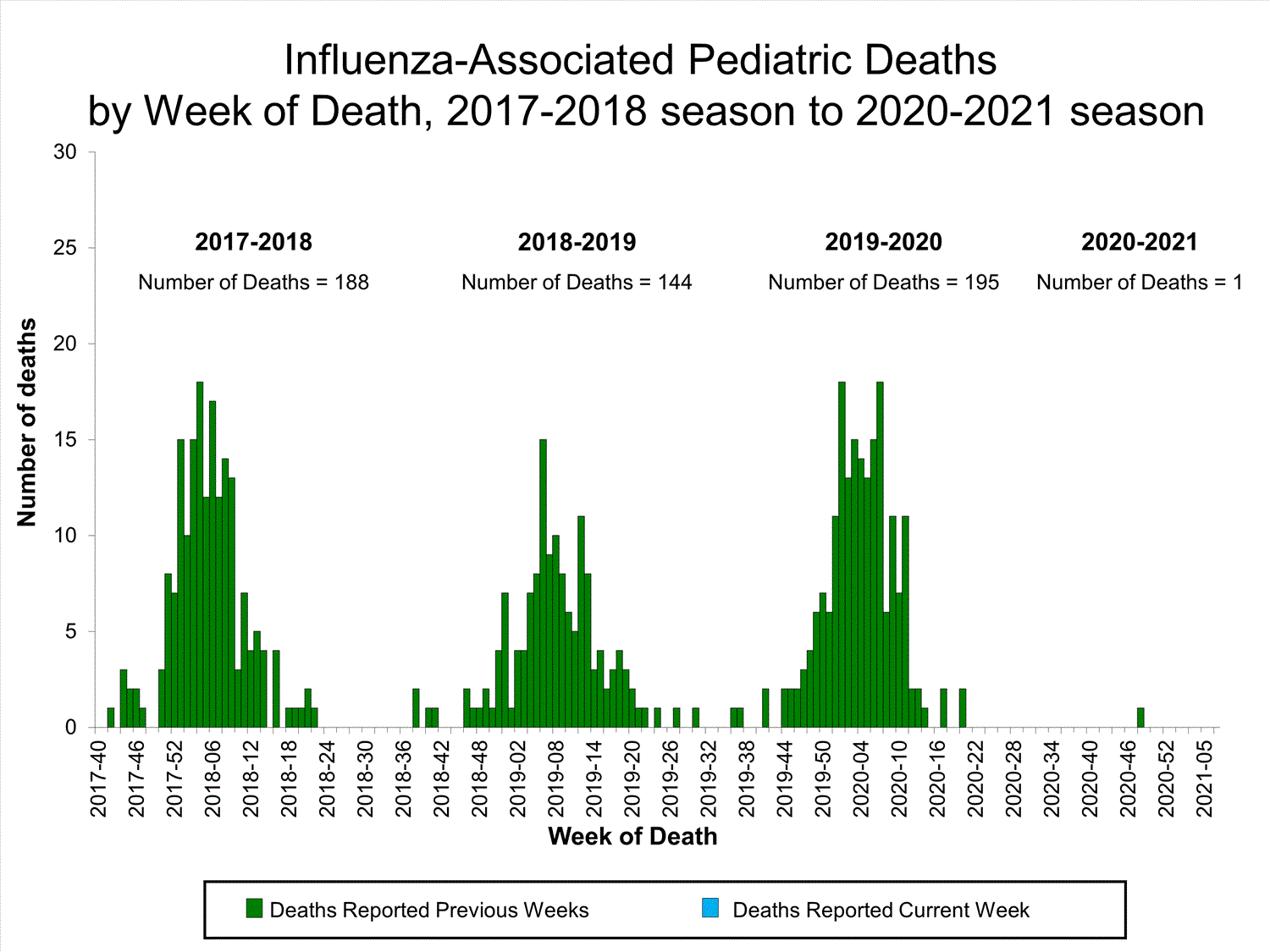
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality
No influenza-associated pediatric deaths were reported to CDC during week 7.
One influenza-associated pediatric death occurring during the 2020-2021 season has been reported to CDC.
Additional pediatric mortality surveillance information for current and past seasons:
Surveillance Methods | FluView Interactive
Additional National and International Influenza Surveillance Information
FluView Interactive: FluView includes enhanced web-based interactive applications that can provide dynamic visuals of the influenza data collected and analyzed by CDC. These FluView Interactive applications allow people to create customized, visual interpretations of influenza data, as well as make comparisons across flu seasons, regions, age groups and a variety of other demographics.
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health: Monthly surveillance data on the prevalence of health-related workplace absenteeism among full-time workers in the United States are available from NIOSH.
U.S. State and local influenza surveillance: Select a jurisdiction below to access the latest local influenza information.
World Health Organization:
Additional influenza surveillance information from participating WHO member nations is available through
FluNet and the Global Epidemiology Reports.
WHO Collaborating Centers for Influenza:
Australia, China, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States (CDC in Atlanta, Georgia)
Europe:
The most up-to-date influenza information from Europe is available from WHO/Europe and the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control.
Public Health Agency of Canada:
The most up-to-date influenza information from Canada is available in Canada’s weekly FluWatch report.
Public Health England:
The most up-to-date influenza information from the United Kingdom is available from Public Health England.
Any links provided to non-Federal organizations are provided solely as a service to our users. These links do not constitute an endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the Federal Government, and none should be inferred. CDC is not responsible for the content of the individual organization web pages found at these links.
A description of the CDC influenza surveillance system, including methodology and detailed descriptions of each data component is available on the surveillance methods page.