Reported Tuberculosis in the United States, 2020
‹View Table of Contents
Risk Factors
Some people are at greater risk of TB disease compared with others. CDC analyzes factors that increase a person’s risk of becoming infected with or developing TB disease.
- Medical conditions that weaken the immune system include:
- Social and occupational factors include:
- Employment or residence in a correctional facility or long-term care facility,
- Experiencing homelessness, and
- Substance use.
Medical conditions that weaken the immune system can increase a person’s risk of developing TB disease if they are infected.
Diabetes mellitus
TB disease is a serious health threat, especially for persons with diabetes.
In 2020, diabetes mellitus (22.5%) was the most commonly reported medical risk factor for TB (TB Risk Factors, by Origin and Race/Ethnicity: 2020 and TB Risk Factors: Reporting Areas, 2020).
Among persons with TB disease in 2020, diabetes mellitus is more common among non-U.S.–born persons (25.8%) than U.S.-born persons (14.3%) (TB Risk Factors, by Origin and Race/Ethnicity: 2020).
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
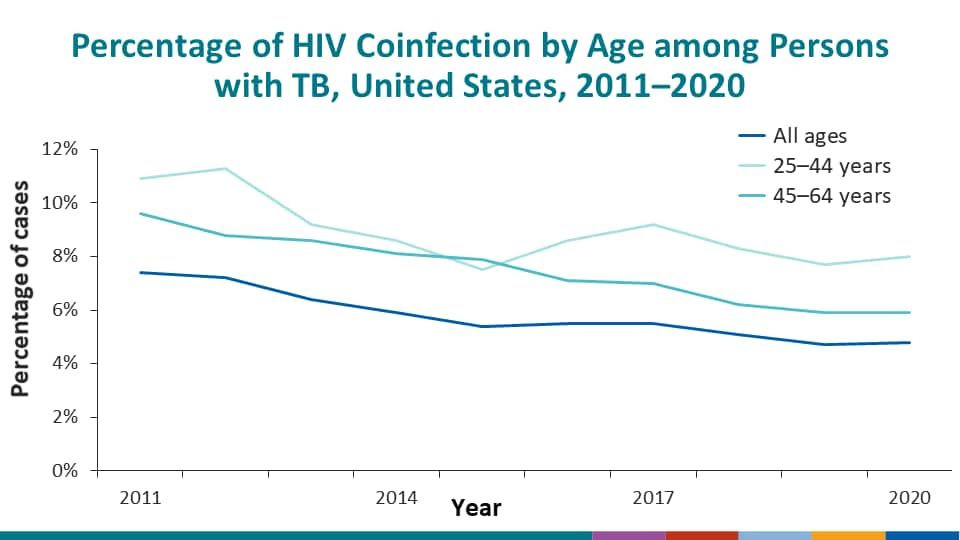
Coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a major risk factor for progression of latent TB infection to TB disease.
Among persons with TB disease in 2020 who were alive at diagnosis, HIV status was known for 89.8%. Of those persons with TB disease and known HIV status, 4.8% were also living with HIV.
Among persons with TB disease with known HIV status, HIV coinfection occurred for 8.0% of persons aged 25–44 years and 5.9% of persons aged 45–64 years (TB Among Persons with HIV Coinfection: 2011–2020).
People living in congregate settings, including correctional facilities, detention centers, long-term care facilities, and homeless shelters, are at increased risk of becoming infected with TB due to shared airspaces. TB bacteria are spread through the air from one person to another. Many congregate settings have shared airspace, which can increase a person’s exposure to TB bacteria and enable the spread of TB bacteria.
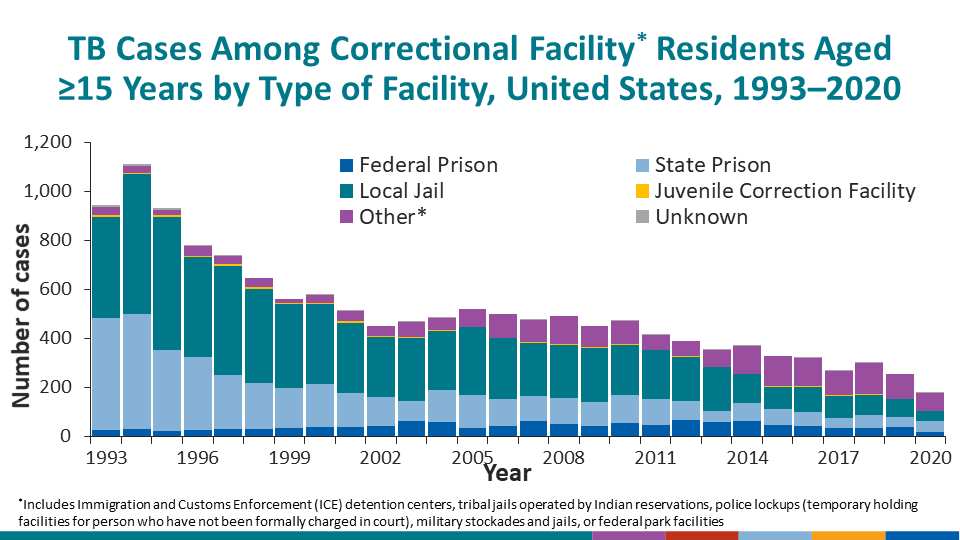
Residents of correctional facilities
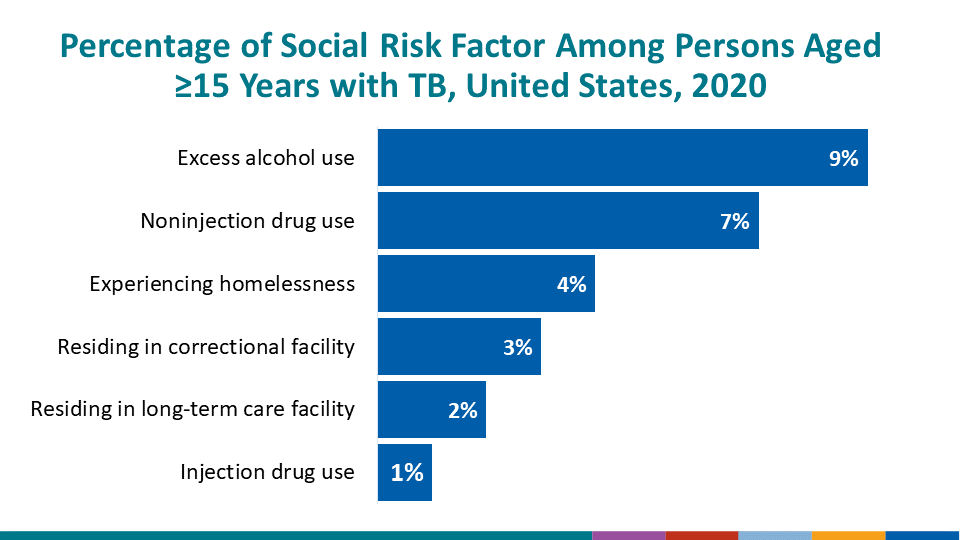
In 2020, 2.6% of persons 15 years of age or older diagnosed with TB disease were current residents of correctional facilities at the time of diagnosis (TB in Correctional Facilities, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020).
Among the 2.6% of persons 15 years of age or older diagnosed with TB disease who were current residents of correctional facilities*,
- 10.1% were current residents of federal prisons,
- 25.1% were current residents of state prisons,
- 22.9% were current residents of local jails,
- 39.1% were current residents of other facilities.
*1.1% were current residents of juvenile facilities and 1.7% were unknown.
Residents of long-term care facilities
During 2020, 1.7% of persons 15 years of age or older diagnosed with TB disease were current residents of long-term care facilities (TB in Long-Term Care Facilities, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020).
People experiencing homelessness
Among persons 15 years of age or older with TB disease in 2020, 290 (4.3%) reported experiencing homelessness within the 12 months prior to TB diagnosis compared with 383 (4.6%) in 2019 (TB in Persons Experiencing Homelessness, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020).
Substance use is also a risk factor for becoming infected with TB disease. In 2020, among persons with TB disease aged ≥15 years, the most commonly reported types of substance use during the year preceding diagnosis were
- Excess alcohol use; 9.0%
Source: TB Among Persons with Excess Alcohol Use, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- Noninjection drug use; 6.9%, and
Source: TB Among Noninjection Drug Users, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- Injection drug use; 1.1%.
Source: TB Among Injection Drug Users, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
Learn more in the Executive Commentary.
- TB in Correctional Facilities, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- TB in Persons Experiencing Homelessness, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- TB in Long–Term Care Facilities, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- TB Among Injection Drug Users, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- TB Among Noninjection Drug Users, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- TB Among Persons with Excess Alcohol Use, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020
- TB by Primary Occupation, Ages ≥15 Years: Reporting Areas, 2020