Reported Tuberculosis in the United States, 2020
‹View Table of Contents
Drug-Resistant TB

Drug-resistant TB disease is a concern in the United States and globally.
- Resistance to isoniazid, one of the most common anti-TB drugs, can be a precursor to multidrug-resistant (MDR) TB, which is defined as resistance to at least isoniazid and rifampin.
- For the purposes of this report, extensively drug-resistant (XDR) TB is defined as resistance to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one injectable second-line drug.
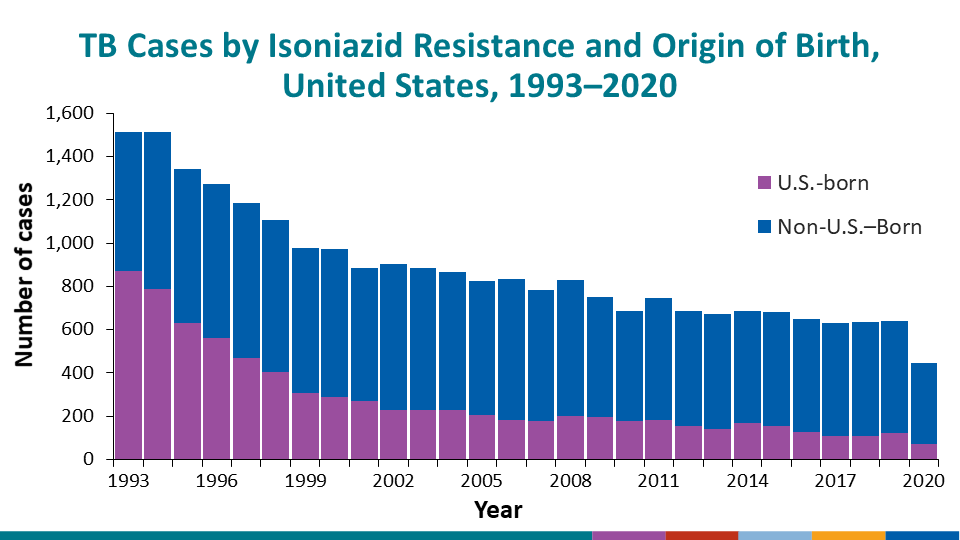
During 2020, isoniazid resistance at initial diagnosis was reported for 456 cases in the United States, including 4.8% of cases among U.S.-born persons and 9.5% of cases among non-U.S.–born persons (TB by Resistance to Isoniazid (INH): 1993–2020).
MDR TB at initial diagnosis was reported for 56 cases, including 0.2% of cases among U.S.-born persons and 1.3% of cases among non-U.S.–born persons (TB by Multidrug Resistance (MDR): 1993–2020).
XDR TB continues to be rare in the United States, with only 1 case reported in 2020.
Learn more in the Executive Commentary.