Initial Evaluation
Medical History
- Collect information on any illness in the past 4 weeks
- Note respiratory and GI symptoms, with or without fever
- Ask about hand, foot, and mouth lesions (possible EV-A71 or similar viral infection)
Physical Exam
Perform physical exam along with an age-appropriate neurological assessment and ask questions to evaluate limb function impairment.
Neurological examination should include documentation of:
- Muscle tone (flaccid/loose vs spastic/tight and firm)
- Muscle strength (full strength, move against gravity with some resistance/pressure, move against gravity but with no resistance/pressure, or little limb movement but not against gravity, no muscle movement at all)
- Reflexes in each extremity (hypo-, hyper, or absent)
- Any cranial nerve deficiencies such as for facial, palatal and shoulder asymmetry, hoarseness or hypophonia and dysphagia (if possible)
Note: Sensory exam is often normal in patients with AFM.
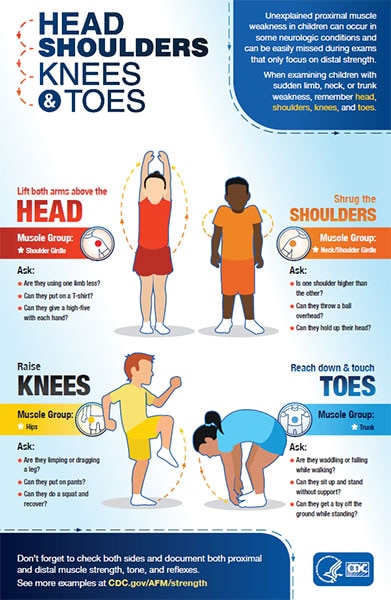
Examining Proximal Muscle Weakness in Children
When examining patients with sudden limb, neck, or trunk weakness, remember to check both proximal and distal muscle strength, as impairment in proximal strength can be easily missed during exams. See Evaluating Proximal Muscle Weakness.
Keep in mind that young children or their parents may not describe their limb function impairment as “weakness.”
Assess the patient’s ability to protect their airway:
- Document respiratory sufficiency
- Negative inspiratory force may be used if the child is old enough and able to cooperate
Check for autonomic manifestations:
- Blood pressure lability
- Body temperature instability
Ask about additional signs and symptoms, including:
- Difficulty holding their head up
- Decreased appetite or difficulty swallowing
- Increased sleepiness or inactivity
- Headache or neck, shoulder, or back pain
- Patients often complain of this prior or concurrent to weakness
- Pain in extremities
- Bowel or bladder changes, particularly constipation