ALARA – As Low As Reasonably Achievable
The guiding principle of radiation safety is “ALARA”. ALARA stands for “as low as reasonably achievable”. ALARA means avoiding exposure to radiation that does not have a direct benefit to you, even if the dose is small.
To do this, you can use three basic protective measures in radiation safety: time, distance, and shielding.
Time:

“Time” simply refers to the amount of time you spend near a radioactive source. Minimize your time near a radioactive source to only what it takes to get the job done. If you are in an area where radiation levels are elevated,
- complete your work as quickly as possible, and then
- leave the area.
There is no reason to spend more time around it than necessary.
For an example of minimizing time, click here
Distance:

“Distance” refers to how close you are to a radioactive source. Maximize your distance from a radioactive source as much as you can. If you increase your distance, you decrease your dose.
For an example of maximizing distance, click here
Shielding:

To shield yourself from a radiation source, you need to put something between you and the radiation source. The most effective shielding will depend on what kind of radiation the source is emitting. Some radionuclides emit more than one kind of radiation.
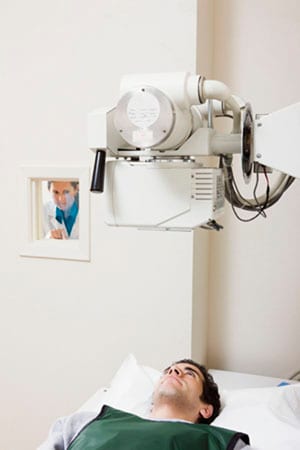
You can see how these principles work together when you have an x-ray at your doctor’s office or clinic. The radiation technician goes behind a barrier while taking the x-ray image. The barrier protects them from repeated daily exposure to radiation.
If there is a radiation emergency, use time, distance, and shielding to protect yourself and your family.
Time
If a radiation emergency happens, get inside a stable building as quickly as possible.
Distance
How long you need to stay inside will depend on
- the type and magnitude of the incident and
- the amount of damage to critical infrastructure, like roads and bridges.
Emergency officials will instruct you when it is safe to leave the area.
Shielding
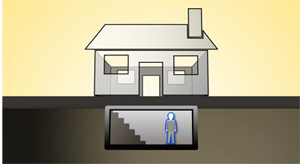
If you are in a multistory building, move to the center floors.
If you are in a single story building, stay in the center away from windows, doors, and exterior walls.
You can also take shelter in a basement.
If you are a first responder or radiation worker, you can use personal protective equipment (PPE) to minimize your exposure.
- Respirators will help protect from inhalation hazards.
- Protective clothing helps keep radioactive material off of skin and hair.
- Alarming dosimeters help manage stay time and track your accumulated doses in an area with elevated radiation levels.
If radioactive material gets on skin, clothing, or hair, it’s important to get it off as quickly as possible.
For information on decontaminating yourself, click here
Anybody who works with radiation should work with their safety officers and radiation safety professionals. They should work together to determine PPE and instrumentation needed to stay safe.
ALARA Examples
Imagine sitting very close to a fireplace. You can feel the heat and may even be uncomfortable.

If you go to the other side of the room, you would be more comfortable. So as you move away, the intensity decreases.

You can use something as thin as a sheet of paper to shield yourself from alpha particles. Our outer layer of dead skin cells can also act as a shield.

You can shield yourself from beta particles using a few inches of plastic or a layer of clothing.

You can shield yourself from gamma rays by adding
- a few inches of lead or
- other dense substance
between you and the source of radiation.