Study Shows Linking Statewide Data for ASD Prevalence is Effective
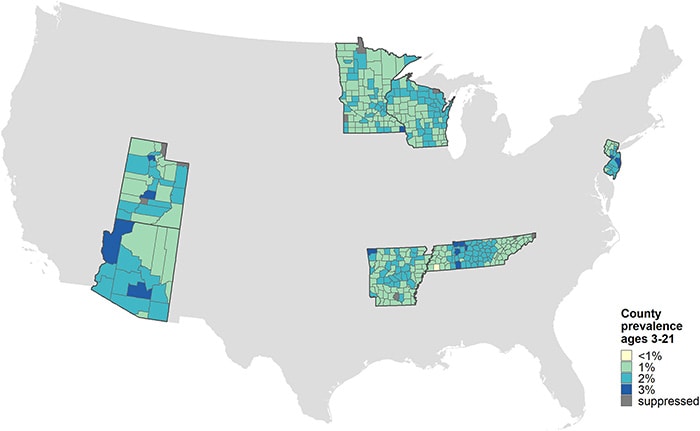
The infrastructure to track statewide autism spectrum disorder (ASD) prevalence varies from state to state and depends on the availability of resources. Seven existing 2018 Autism Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network sites (Arizona, Arkansas, Minnesota, New Jersey, Tennessee, Utah, and Wisconsin) linked statewide health and education data for the first time to calculate statewide and county-level ASD estimates and compare results with more resource-intensive record review methods. The manuscript shared tradeoffs and lessons learned from the approach.
County-level ASD prevalence ranged from 0.5% to 2.9% in the counties included in the study; a table of estimates can be viewed at county-level ASD prevalence estimates.
Within the 2018 ADDM Network surveillance areas for the seven participating sites, ASD prevalence estimates for children aged 8 years were similar between the previous ADDM Network estimate and the new statewide county-level ASD prevalence estimates. Because estimates among 8-year-olds were similar to more resource-intensive methods, linking statewide data sets to determine ASD prevalence is an effective way for states to have actionable local information that may be less detailed but are available when resources are limited. This will help communities, healthcare and education providers, and policymakers identify needs, plan services, and provide support for individuals with ASD and their families.
Reference
Shaw KA, Williams S, Hughes MM, et al. Statewide county-level autism spectrum disorder prevalence estimates-seven U.S. states, 2018 [published online ahead of print, 2023 Jan 18]. Ann Epidemiol. 2023;79:39-43. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2023.01.010
