2018 STD Prevention Conference
August 28, 2018 – New CDC Analysis Shows Steep and Sustained Increases in STDs
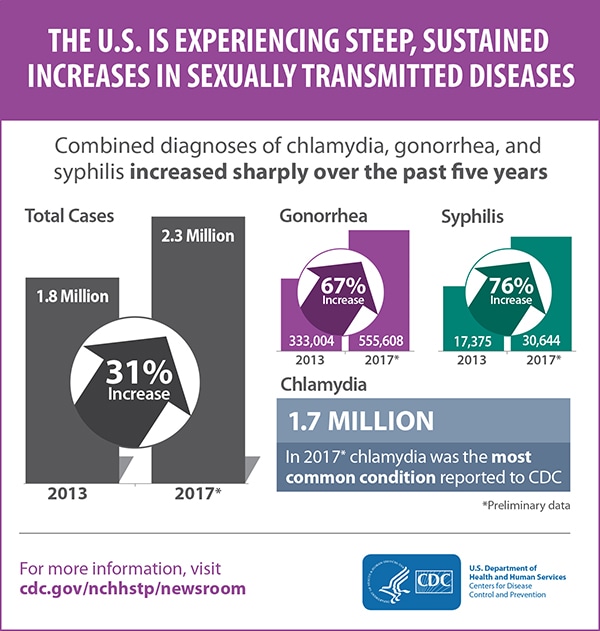
The biennial National STD Prevention Conference took place in Washington, D.C., from Aug. 27-30, 2018, under the theme, “Intersecting Epidemics, Integrated Solutions.” As part of the official conference press briefing, CDC presented preliminary data showing five-year trends in sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) that included preliminary data for 2017. The analysis found that the nearly 2.3 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis reported to CDC for 2017 exceeded the previous 2016 record by more than 200,000 cases. It also found that from 2013 to 2017:
- Recent increases in STDs have continued for four consecutive years.
- Syphilis cases nearly doubled.
- Gonorrhea cases increased by 67%.
- Chlamydia remained at record highs.
The latest information on the continued threat of untreatable gonorrhea was also discussed, along with solutions to counter the nation’s STD epidemic.
- Press Release: New CDC analysis shows steep and sustained increases in STDs in recent years
- Telebriefing Transcript: Full Press Briefing Remarks
- Bio and Headshot: Gail Bolan, M.D., Director, CDC’s Division of STD Prevention
- Data Table: STD Diagnoses Among Key U.S. Populations, 5-Year Trends Cdc-pdf
Graphics:
These high-resolution, public domain images are ready to download and print in your publication. Click on a graphic to see it in high-resolution. For your convenience, we have included a table that contains the specific data from the report used to generate these charts. These images are in the public domain and are thus free of any copyright restrictions. As a matter of courtesy, we ask that the content provider be credited and notified of any public or private usage of an image.
View High Resolution Version | PDFCdc-pdf
CDC’s preliminary surveillance data found recent increases in STDs have continued for four consecutive years — and that the nearly 2.3 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis reported to CDC for 2017 exceed the previous 2016 record by more than 200,000 cases. Additionally, the threat of untreatable gonorrhea persists in the United States.
View High Resolution Version
Preliminary data found that from 2013 to 2017:
- Recent increases in STDs have continued for four consecutive years.
- Syphilis cases nearly doubled.
- Gonorrhea cases increased by 67%.
- Chlamydia remained at record highs.
View High Resolution Version
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis are curable with antibiotics, yet most cases go undiagnosed and untreated — which can lead to severe adverse health effects.
View High Resolution Version
In addition to the sharp increase in gonorrhea cases, new CDC data show that we continue to see warning signs that resistance is emerging — and that the threat of untreatable gonorrhea persists in the United States.