CDC Vital Signs: HIV Testing and Diagnosis Delays
November 28, 2017 – Frequency of HIV Testing and Time from Infection to Diagnosis Improve
A new CDC Vital Signs report published today finds that HIV is being diagnosed sooner after infection than was previously reported. The analysis includes the latest data on HIV testing frequency among Americans at increased risk of infection and on how long people are living with HIV before they find out they have it.
According to the report, the estimated median time from HIV infection to diagnosis was three years in 2015. CDC previously estimated that, in 2011, the median time from HIV infection to diagnosis was three years and seven months. The Vital Signs analysis also found that the percentages of people at increased risk for HIV who reported getting an HIV test the previous year has increased. Despite that progress, too few are tested.
- Press Release: Frequency of HIV Testing and Time from Infection to Diagnosis Improve
- MMWR: Vital Signs: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Testing and Diagnosis Delays — United States
- Vital Signs: HIV Testing and Diagnosis Delays
- HIV Risk Reduction Tool
Graphic: HIV Testing and Diagnosis Delays
The following graphic highlight major findings from CDC’s analysis. These high-resolution, public domain images are ready to download and print in your publication. Click on a graphic to see it in high-resolution.
These images are in the public domain and are thus free of any copyright restrictions. As a matter of courtesy, we ask that the content provider be credited and notified of any public or private usage of an image.
View High Resolution Version
In 2015, estimated timing from HIV infection to diagnosis varied by risk group and by race/ethnicity.
Estimated timing from HIV infection to diagnosis ranged from a median of five years for heterosexual males to two-and-a-half years for heterosexual females and females who inject drugs.
Estimated timing from HIV infection to diagnosis ranged from a median of four years for Asian Americans to two years for white Americans and about three years for African Americans and Latinos.
View High Resolution Version
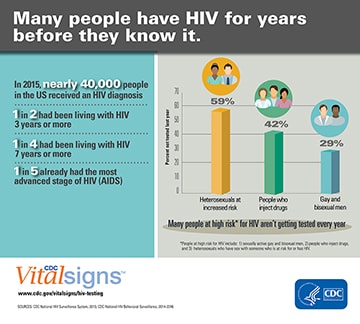
In 2015, nearly 40,000 people in the U.S. received an HIV diagnosis. While the median time from HIV infection to diagnosis has declined, half of Americans with HIV diagnosed in 2015 had been living with HIV for at least 3 years, and a quarter had been infected for seven or more years.