Lifecycle of Blacklegged Ticks
The lifecycle of blacklegged ticks (Ixodes scapularis and Ixodes pacificus) generally lasts two years. During this time, they go through four life stages: egg, six-legged larva, eight-legged nymph, and adult. After the eggs hatch, the ticks must have a blood meal at every stage to survive.

Relative sizes of several ticks at different life stages. In general, adult ticks are approximately the size of a sesame seed and nymphal ticks are approximately the size of a poppy seed.
Blacklegged ticks can feed from mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. The ticks need to have a new host at each stage of their life, as shown below:
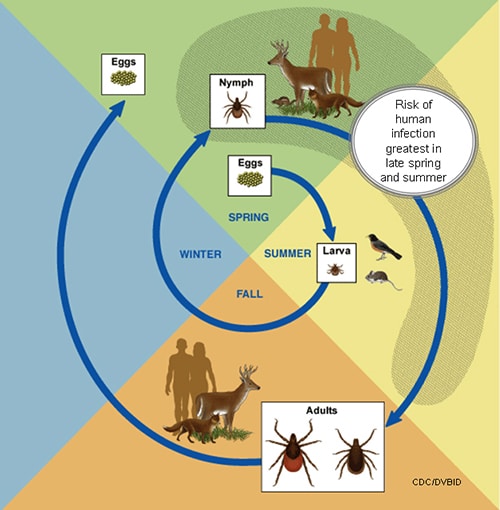
This diagram shows the lifecycle of blacklegged ticks that can transmit Lyme disease.
How ticks find their hosts
Ticks can't fly or jump. Instead, they wait for a host, resting on the tips of grasses and shrubs in a position known as "questing". While questing, ticks hold onto leaves and grass by their lower legs. They hold their upper pair of legs outstretched, waiting to climb onto a passing host. When a host brushes the spot where a tick is waiting, it quickly climbs aboard. It then finds a suitable place to bite its host.
How ticks spread disease
The tick feeding process makes ticks very good at transmitting infection:
- Depending on the tick species and its stage of life, preparing to feed can take from 10 minutes to 2 hours. When the tick finds a feeding spot, it grasps the skin and cuts into the surface. The tick then inserts its feeding tube. Many species also secrete a cement-like substance that keeps them firmly attached during the meal. The feeding tube can have barbs which help keep the tick in place.
- Ticks also can secrete small amounts of saliva with anesthetic properties so that the animal or person can't feel that the tick has attached itself. If the tick is in a sheltered spot, it can go unnoticed.
- A blacklegged tick will attach to its host and suck the blood slowly for several days. If the host animal has certain bloodborne infections, such as the Lyme disease agent, the tick may ingest the pathogen and become infected. If the tick later feeds on a human, that human can become infected.
- After feeding, the blacklegged tick drops off and prepares for the next life stage. At its next feeding, it can then transmit the infection to the new host. Once infected, a tick can transmit infection throughout its life.
- If you remove a tick quickly (within 24 hours) you can greatly reduce your chances of getting Lyme disease. It takes some time for the Lyme disease-causing bacteria to move from the tick to the host. The longer the tick is attached, the greater the risk of acquiring disease from it.
Contact Us:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Bacterial Diseases Branch
Foothills Campus
Fort Collins, CO 80521 - 800-CDC-INFO
(800-232-4636)
TTY: (888) 232-6348 - Contact CDC–INFO


