Key points
- Cellulitis is a common bacterial infection of the deeper layers of the skin.
- It causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area.
- If untreated, cellulitis can spread and cause serious health problems.
- Healthcare providers diagnose cellulitis by how it looks and treat it with antibiotics.
- Speak to a healthcare provider if you have concerns about cellulitis.
What it is
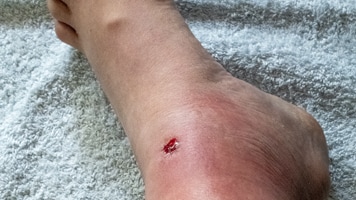
Different bacteria can cause cellulitis, which is an infection of the deeper layers of the skin. This page focuses on one of the most common causes of cellulitis: group A Streptococcus (group A strep bacteria).
Symptoms
Generally, skin affected by cellulitis is
- Painful
- Red
- Swollen
- Tender to the touch
- Warm
The skin may look pitted, like the peel of an orange. Blisters may appear on the affected skin.
Other symptoms: Some people may also develop fever and chills.
Cellulitis can appear anywhere on the body, but it's most common on the feet and legs.
When to seek immediate medical attention
Complications
Complications from cellulitis are uncommon but can include serious infections:
- Bacteremia (bloodstream infection)
- Endocarditis (swelling of the heart's valves and inner lining)
- Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
- Suppurative arthritis (bacterial infection in a joint)
Cellulitis can cause thrombophlebitis (swelling in a vein due to a blood clot).
Risk factors
Anyone can get cellulitis, but some factors can increase the risk of getting this infection.
Infections or injuries that break skin
The following risk factors allow bacteria to get through the skin:
- Chickenpox and shingles
- Chronic skin conditions (like athlete's foot and eczema)
- Injection drug use
- Injuries that break the skin
Injuries that break the skin can include cuts, ulcers, bites, puncture wounds, tattoos, and piercings.
For many people who get cellulitis, experts don't know how the bacteria get into the body.
Other health factors
Other factors that increase risk for cellulitis include being overweight and chronic edema. Chronic edema is when limbs, like feet, legs, hands, or arms, stay swollen.
Lymphedema and a coronary artery bypass graft are two conditions that can cause chronic edema.
Lymphedema happens when the lymphatic system doesn't drain the way that it should. As part of the body's immune system, the lymphatic system moves fluid containing infection-fighting cells throughout the body.
A coronary artery bypass graft includes removing a healthy vein from the leg and connecting it to the coronary artery. This surgery helps to improve blood flow to the heart.
Causes
Group A strep bacteria are a common cause of cellulitis.
In general, people cannot catch cellulitis from others.
Prevention
There are things people can do to protect themselves and others from group A strep infections, including cellulitis.
Testing and diagnosis
Healthcare providers typically diagnose cellulitis by looking at the affected skin during a physical examination. Blood or other lab tests aren't usually needed.
Treatment and recovery
Healthcare providers treat cellulitis with antibiotics. They can be oral antibiotics (medicine taken by mouth) or intravenous (IV) antibiotics (medicine given directly into a vein).
Healthcare providers use oral antibiotics to treat most cellulitis infections. IV antibiotics can be used to treat more serious infections.
Keeping the affected limb (arm or leg) elevated can help decrease swelling and speed up recovery.
