Reported Tuberculosis in the United States, 2021
State & Local Data
Reporting areas include:
- 50 U.S. states, New York City, and the District of Columbia (D.C.) unless otherwise specified
- Five U.S. territories (American Samoa, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands)
- Three independent countries that are in compacts of free association with the United States (Federated States of Micronesia, Republic of the Marshall Islands, and Republic of Palau)
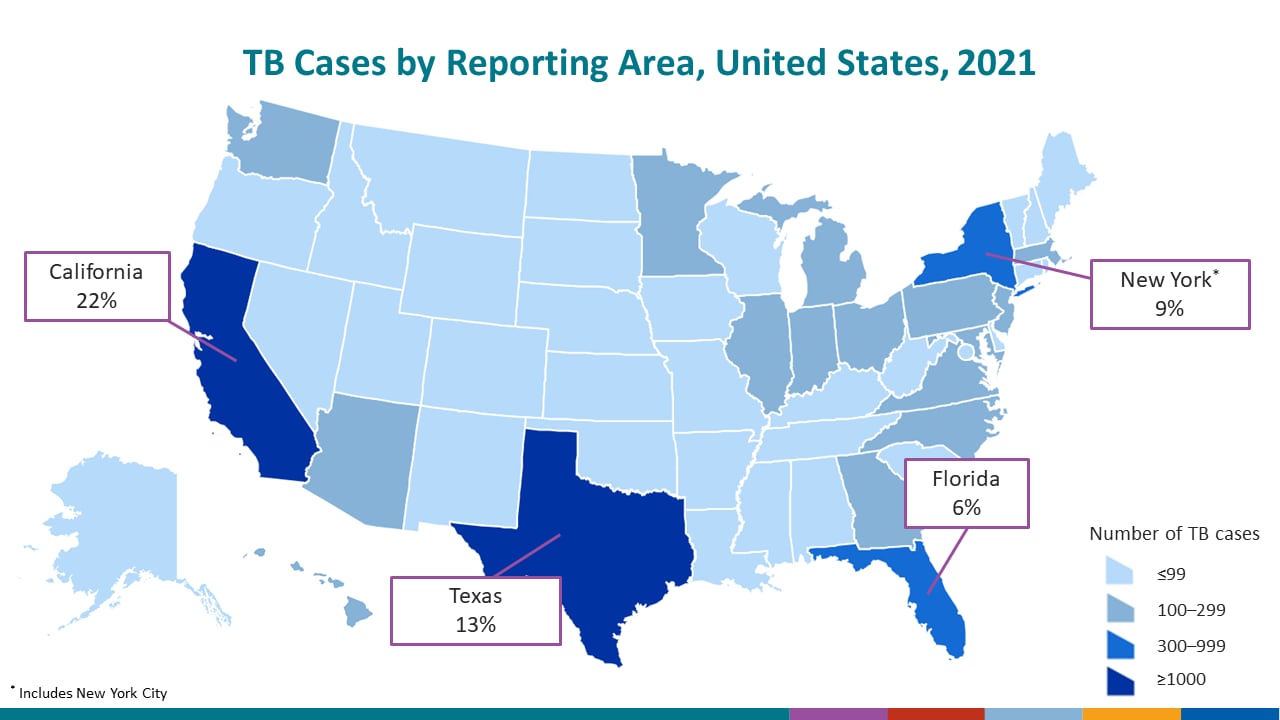
As in past years, four U.S. states combined reported nearly half of all U.S. TB cases in 2021:
- California (22.2%)
- Texas (12.7%)
- New York, including New York City (8.7%)
- Florida (6.3%)
These states are also the most populous states in the United States, and represent about a third of the total U.S. population.
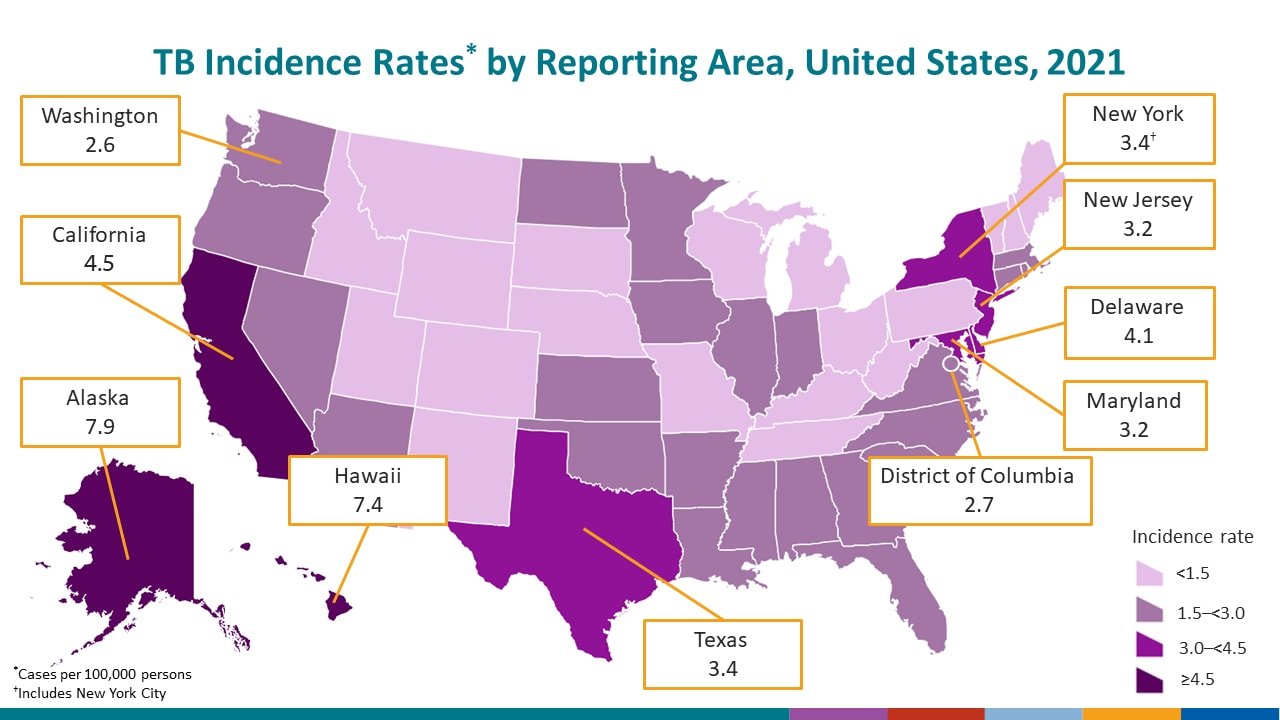
In 2021, the reporting areas with TB incidence rates (cases per 100,000 persons) above the national incidence rate included:
- Alaska, 7.9
- Hawaii, 7.4
- New York, including New York City*, 3.4
- California, 4.5
- Delaware, 4.1
- Texas, 3.4
- Maryland, 3.2
- New Jersey, 3.2
- District of Columbia, 2.7
- Washington, 2.6
*New York City, which is a distinct reporting area, had an incidence rate of 6.2 cases per 100,000 persons. When New York City is analyzed separately, the remainder of New York state has an incidence rate of 1.4 cases per 100,000 persons.
The TB incidence rates (cases per 100,000 persons) among the U.S. territories and freely associated states were:
- Republic of the Marshall Islands, 280.6
- Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, 67.8
- Federated States of Micronesia, 62.8
- Republic of Palau, 33.3
- Guam, 34.4
- American Samoa, 8.6
- U.S. Virgin Islands, 1.9
- Puerto Rico, 0.6
Source: TB by Reporting Areas: 2021 and 2020
Learn more in the Executive Commentary.