Understanding the HIV Window Period

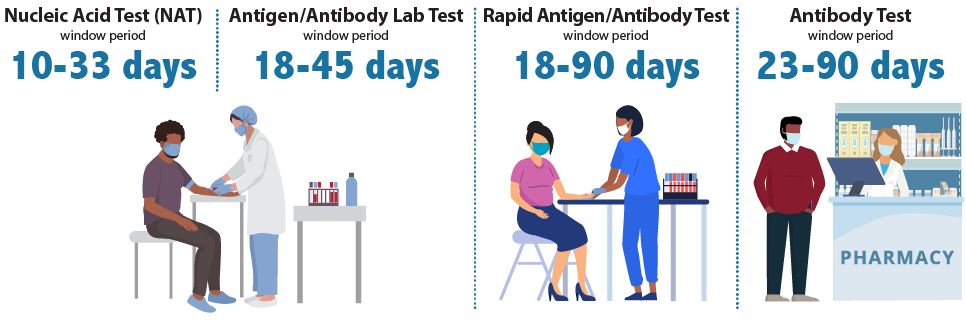
The window period for an HIV test refers to the time between HIV exposure and when a test can detect HIV in your body. The window period depends on the type of HIV test used.
- Antibody tests can usually detect HIV 23 to 90 days after exposure. Most rapid tests and self-tests are antibody tests.
- A rapid antigen/antibody test done with blood from a finger stick can usually detect HIV 18 to 90 days after exposure.
- An antigen/antibody lab test using blood from a vein can usually detect HIV 18 to 45 days after exposure.
- A nucleic acid test (NAT) can usually detect HIV 10 to 33 days after exposure.
If you get an HIV test after a potential HIV exposure and the result is negative, get tested again after the window period for the test you took. Learn more about what a negative test result means.
Page last reviewed: June 22, 2022