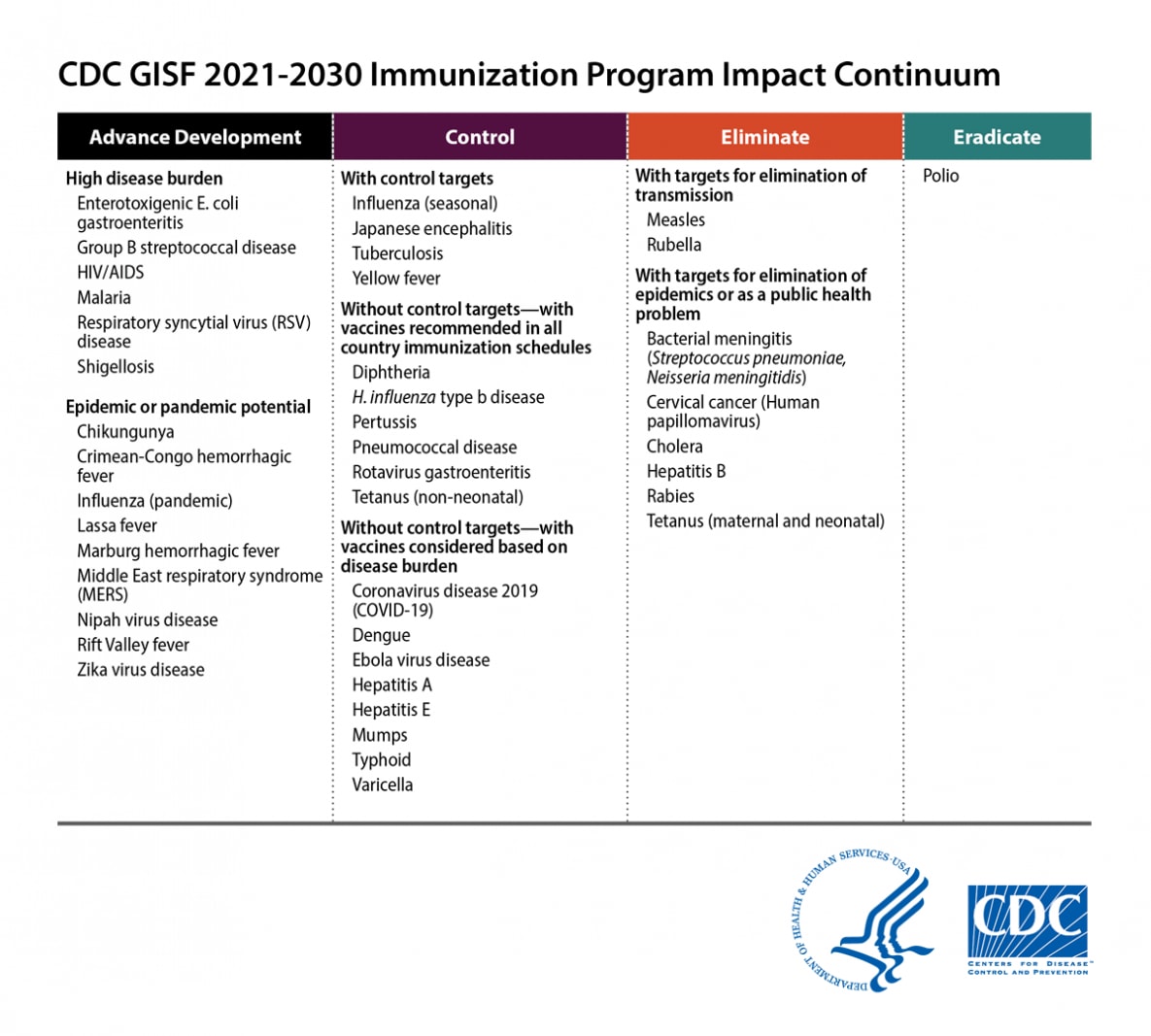
CDC GISF 2021-2030 Immunization Program Impact Continuum
Updated May 19, 2021
The immunization program impact continuum has four broad phases, starting from advancing development of new vaccines and then, once vaccines are available, moving to control, then to elimination, and finally to eradication of disease. These four phases reflect the types of impacts that immunization programs can have against disease. The table lists the diseases included in each phase as of February 2021.
Under the first phase of the continuum, which is focused on advancing development of new vaccines (“Advance Development”), there are two sub-categories of diseases included. The first sub-category is diseases that represent a high burden (based on the World Health Organization vaccine pipeline tracker, Gavi Vaccine Investment Strategy, and the Institute for Health Metrics Global Burden of Disease). Diseases of high disease burden for which vaccines are in development are: enterotoxigenic E. coli gastroenteritis, group B streptococcal disease, HIV/AIDS, malaria, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease, and shigellosis. The second sub-category of diseases within the phase of advancing development of new vaccines are those with epidemic or pandemic potential (based on the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations and the World Health Organization Blueprint for Action to Prevent Epidemics). Diseases of epidemic or pandemic potential are: chikungunya, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, pandemic influenza, Lassa fever, Marburg hemorrhagic fever, Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), Nipah virus disease, Rift Valley fever, and Zika virus disease. It should be noted that CDC also works on vaccines for other diseases that are not high-burden or of epidemic potential, and on the development of new vaccines for diseases already in the control, elimination, or eradication stages of the continuum.
Under the second phase of the continuum, focused on controlling disease (“Control”), there are three sub-categories of vaccine-preventable diseases. The first sub-category is vaccine-preventable diseases with control targets. Diseases included in this sub-category are: seasonal influenza, Japanese encephalitis, tuberculosis, and yellow fever. The second sub-category is vaccine-preventable diseases without control targets but with vaccines recommended in all country immunization schedules. Diseases included in this second sub-category are diphtheria, H. influenzae type b disease, pertussis, pneumococcal disease, rotavirus gastroenteritis, and non-neonatal tetanus. The third sub-category under the control phase of the continuum is vaccine-preventable diseases without control targets but with vaccines considered based on disease burden. Diseases included in this third sub-category are coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), dengue, Ebola virus disease, hepatitis A, hepatitis E, mumps, typhoid, and varicella. COVID-19 and Ebola are included in this category based on interim recommendations of the World Health Organization Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization.
Under the third phase of the continuum, focused on eliminating disease (“Eliminate”), there are two sub-categories of vaccine-preventable diseases. The first sub-category is vaccine-preventable diseases with targets for elimination of transmission. Diseases included in this category are measles and rubella. The second sub-category is vaccine-preventable diseases with targets for elimination of epidemics or as a public health problem. Diseases included in this category are bacterial meningitis (caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or Neisseria meningitidis); cervical cancer (caused by human papillomavirus), cholera, hepatitis B, rabies, and maternal and neonatal tetanus.
The final phase of the continuum, focused on eradicating disease (“Eradicate”),currently includes only one vaccine-preventable disease: polio.