History of Anthrax
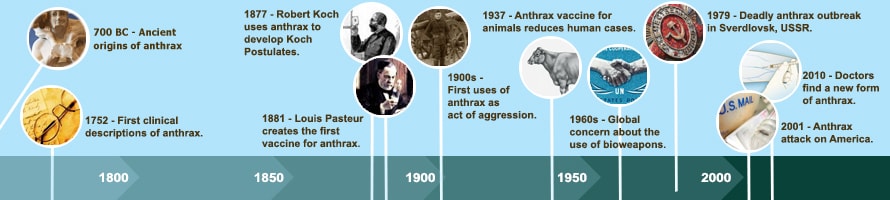
Throughout history, from biblical times to modern day, many sicknesses have been described with symptoms that resemble anthrax. Although we cannot know for sure whether these earliest reports of illness were, in fact, anthrax, many researchers believe that they were.
Naturally Occurring Anthrax
Anthrax Used as a Biological Weapon
Sources
Blaney D, Lehman M (2012). Multi-agency investigation of inhalation anthrax—United States, 2011 [Powerpoint slides].
Brachman PS (2002). Bioterrorism: an update with a focus on anthrax. American Journal of Epidemiology, 155(11), 981-987.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2012). A medical victory remains a medical mystery In: NCEZID: Our Work, Our Stories 2011–2012. Atlanta, GA: National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/ncezid/pdf/annual-report.pdfpdf icon pdf icon[PDF – 27.8MB]
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006). Inhalation anthrax associated with dried animal hides—Pennsylvania and New York City, 2006. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 55(10);280-282. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5510a4.htm
Christopher GW, Cieslak TJ, Pavlin JA, and Eitzen Jr EM (1997). Biological warfare: a historical prospective. Journal of the American Medical Association, 278(5), 412-417.
Inglesby TV, Henderson DA, Bartlett JG, Ascher MS, Eitzen E, Friedlander AM, Hauer J, McDade J, Osterholm MT, O’Toole T, Parker G, Perl TM, Russell PK, Tonat K (1999). Anthrax as a biological weapon, medical and public health management. Journal of the American Medical Association, 281(18), 1735-1963.
Inglesby TVexternal iconexternal icon, O’Toole Texternal iconexternal icon, Henderson DAexternal iconexternal icon, Bartlett JGexternal iconexternal icon, Ascher MSexternal iconexternal icon, Eitzen Eexternal iconexternal icon, Friedlander AMexternal iconexternal icon, Gerberding Jexternal iconexternal icon, Hauer Jexternal iconexternal icon, Hughes Jexternal iconexternal icon, McDade Jexternal iconexternal icon, Osterholm MTexternal iconexternal icon, Parker Gexternal iconexternal icon, Perl TMexternal iconexternal icon, Russell PKexternal iconexternal icon, Tonat Kexternal iconexternal icon; Working Group on Civilian Biodefenseexternal iconexternal icon (2002). Anthrax as a biological weapon, 2002, updated recommendations for management. Journal of the American Medical Association, 287(17), 2236-2252.
Jernigan JA, Stephens DS, Ashford DA, Omenaca C, Topiel MS, Galbraith M, Tapper M, Fisk TL, Zaki S, Popovic T, Meyer RF, Quinn CP, Harper SA, Fridkin SK, Sejvar SJ, Shepard CW, McConnell M, Guarner J, Shieh W-J, Malecki JM, Gerberding JL, Hughes JM, Perkins BA, and members of the Anthrax Bioterrorism Investigation Team (2001). Bioterrorism-related inhalational anthrax: the first 10 cases reported in the United States. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 7(6), 933-944.
Jernigan DBexternal iconexternal icon, Raghunathan PLexternal iconexternal icon, Bell BPexternal iconexternal icon, Brechner Rexternal iconexternal icon, Bresnitz EAexternal iconexternal icon, Butler JCexternal iconexternal icon, Cetron Mexternal iconexternal icon, Cohen Mexternal iconexternal icon, Doyle Texternal iconexternal icon, Fischer Mexternal iconexternal icon, Greene Cexternal iconexternal icon, Griffith KSexternal iconexternal icon, Guarner Jexternal iconexternal icon, Hadler JLexternal iconexternal icon, Hayslett JAexternal iconexternal icon, Meyer Rexternal iconexternal icon, Petersen LRexternal iconexternal icon, Phillips Mexternal iconexternal icon, Pinner Rexternal iconexternal icon, Popovic Texternal iconexternal icon, Quinn CPexternal iconexternal icon, Reefhuis Jexternal iconexternal icon, Reissman Dexternal iconexternal icon, Rosenstein Nexternal iconexternal icon, Schuchat Aexternal iconexternal icon, Shieh WJexternal iconexternal icon, Siegal Lexternal iconexternal icon, Swerdlow DLexternal iconexternal icon, Tenover FCexternal iconexternal icon, Traeger Mexternal iconexternal icon, Ward JWexternal iconexternal icon, Weisfuse Iexternal iconexternal icon, Wiersma Sexternal iconexternal icon, Yeskey Kexternal iconexternal icon, Zaki Sexternal iconexternal icon, Ashford DAexternal iconexternal icon, Perkins BAexternal iconexternal icon, Ostroff Sexternal iconexternal icon, Hughes Jexternal iconexternal icon, Fleming Dexternal iconexternal icon, Koplan JPexternal iconexternal icon, Gerberding JLexternal iconexternal icon, and National Anthrax Epidemiologic Investigation Teamexternal iconexternal icon (2002). Investigation of bioterrorism-related anthrax, United States, 2001: epidemiologic findings. Emerging Infectious Disesases, 8(10), 1019-1028.
Knox D, Murray G, Millar M, Hamilton D, Connor M, Ferdinand RD, Jones, GA (2011). Subcutaneous anthrax in three intravenous drug users. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery, 93-B(3), 414-417.
Lehman MW, Traxler R, Blaney D, Shadomy S, Gomez T, Rubin C, Snippes Vagnone P, Lees C, Miller T, Kightlinger L, Horan V, Murphy T, Amuso P, Schmitz A, Wong D, Treadwell T, Lynfield R (2012). Utilizing partnerships for enhanced surveillance following a case of inhalation anthrax. In: 61st Annual Epidemic Intelligence Service (EIS) Conference, April 16–20, 2012, Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Meselson M, Guillemin J, Hugh-Jones M, Langmuir A, Popova I, Shelokov A, Yampolskaya O (1994). The Sverdlovsk anthrax outbreak of 1979. Science Magazine, 266, 1202-1207.
Turnbull PCB, Shadomy SV (2010). Anthrax from 5000BC to AD 2010. In: Bacillus anthracis and Anthrax. NH Bergman, ed., Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell.
Sternbach G (2003). The history of anthrax. Journal of Emergency Medicine, 24(4), 463-467.