CDC Agency-wide Responses
Browse the CDC emergency response timeline below and click on an image to read more.
- Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and MariaCDC’s Emergency Operations Center (EOC) activated to bring together CDC staff to work efficiently in responding to public health needs in the aftermath of Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria.
- Flint Michigan Water ContaminationDuring April 25, 2014 – October 15, 2015, approximately 99,000 residents of the City of Flint, MI, were exposed to lead when the drinking water source was switched from the Detroit Water Authority to the Flint Water System (FWS).
- Zika Virus ResponseCDC’s Emergency Operations Center (EOC) activated for the Zika response on January 22, 2016 to assist state, tribal, local, and territorial jurisdictions with their Zika responses in a wide range of activities.
- DoD Lab Sample Investigation (Anthrax)CDC investigated the unintentional transfer of anthrax from the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) to labs in multiple states and overseas.
- Ebola ResponseOn March 23, 2014, the World Health Organization reported cases of Ebola Virus Disease in the forested rural region of southeastern Guinea.
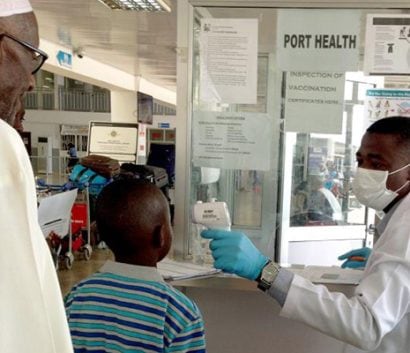
- Respiratory Disease Among Unaccompanied ChildrenDuring October 2013–June 2014, approximately 54,000 unaccompanied children, mostly from Central America, were identified attempting entry into the U.S. from Mexico.
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (2014)In May 2014, CDC confirmed two imported cases of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in the U.S.
- Multistate Cyclospora OutbreakCyclosporiasis is an intestinal illness caused by the microscopic parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis. People can become infected with Cyclospora by consuming food or water contaminated with the parasite.
- Avian Influenza H7N9 ResponseIn March 2013, three human infections with a novel avian influenza A(H7N9) virus were identified in China.
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (2012)Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) was first identified in September 2012 in Saudi Arabia.
- Multistate Meningitis OutbreakCDC collaborated with state and local health departments and the Food and Drug Administration to investigate a multistate outbreak of fungal meningitis and other infections among patients.
- Polio Eradication ResponseOn December 2, 2011, former CDC Director Thomas R. Frieden, MD, MPH, activated CDC’s Emergency Operations Center to strengthen the agency’s partnership engagement through the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI).
- Hurricane IreneCDC worked with state and local governments, and other federal agencies to help communities recover from Hurricane Irene. Irene made U.S. landfall along the East Coast on August 27 and continued to move northeast as a tropical storm.
- Japan Earthquake - Tsunami RadiationOn March 11, CDC immediately activated its Emergency Operations Center (EOC) in Atlanta to respond to the 9.0 magnitude earthquake and subsequent tsunami and radiation release in Japan.
- New Hampshire Anthrax EventIn December 2009, a New Hampshire woman contracted gastrointestinal anthrax in a drumming event where animal-hide drums of multiple ages and origins were played.
- Cholera Outbreak in HaitiOn October 20, 2010, the first outbreak of cholera ever confirmed in Haiti was recognized 10 months after the catastrophic earthquake that killed over 200,000 people and displaced over 1 million.
- Deepwater Horizon Oil SpillOn April 20, 2010, the Deepwater Horizon drilling unit exploded off the coast of Louisiana, resulting in 11 deaths and the largest marine petroleum release in history.
- Haiti EarthquakeA magnitude-7.0 earthquake struck near Port-au-Prince, Haiti on January 12.
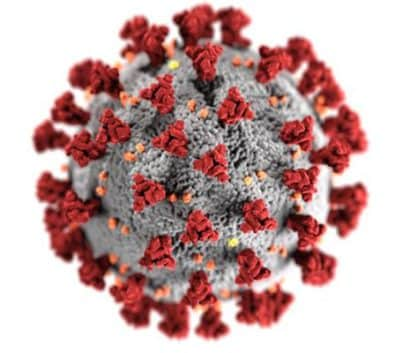
- H1N1 Influenza Pandemic ResponseThe 2009 H1N1 was a unique combination of influenza virus genes never previously identified in either animals or people. This new influenza was first detected in a 10-year-old patient in California on April 15, 2009.
- Salmonella TyphimuriumAs of January 15, 2009, 43 states reported more than 400 individuals who were infected with the outbreak strain of Salmonella Typhimurium.
- Hurricanes Gustav, Hanna, & IkeOn September 1, 2008, Gustav made landfall as a category 2 hurricane near Cocodrie, Louisiana. It left more than 1.4 million households without power and caused $4.6 billion of damage.
- Tropical Storm EdouardTropical Storm Edouard started as a tropical depression in the northern Gulf of Mexico on August 3, 2008.
- Hurricane DollyHurricane Dolly, a Category 2 storm, struck the Texas-Mexico coastline on July 23, 2008.
- Salmonella SaintpaulOn May 22, 2008, CDC received notification from the New Mexico Department of Health and the Indian Health Service. They were investigating a cluster of illnesses: 19 people sick with symptoms of foodborne disease.
- E. Coli Multi-State ResponseCDC, state departments of health and agriculture in several states, and the United States Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service investigated a multi-state outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections.
- Hurricane DeanHurricane Dean formed west of the southernmost Cape Verde Islands as a tropical depression on August 13, 2007.
- Extensively Drug Resistant TuberculosisIn 2007, a U.S. air traveler sparked interested in this rate type of TB that is resistant to almost all drugs.
- E. Coli Outbreak (Spinach)In 2006, a CDC investigation with the State of California and the Food and Drug Administration linked a multistate outbreak of Escherichia coli (E. coli) 0157:H7 to fresh bagged spinach from California.
- Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Rhode IslandMycoplasma pneumoniae is a leading cause of respiratory infections. From September 2006 to February 2007, there was a M. pneumoniae outbreak among students at four schools in Rhode Island.
- Tropical Storm ErnestoCDC activated its EOC to support public health needs in the aftermath of Tropical Storm Ernesto.
- Botulism Outbreak (Carrot Juice)A commercial brand of carrot juice caused two events of foodborne botulism in 2006. Three residents of Georgia consumed commercially produced carrot juice from the same bottle.
- Mumps in IowaMumps is an acute viral infection characterized by fever and nonsuppurative swelling of the salivary glands.
- Indonesia Earthquake – TsunamiOn December 26, 2004, an earthquake measuring 9.2 on the Richter scale off the northwest coast of the island of Sumatra, Indonesia, produced a tsunami that caused the deaths of an estimated 230,000 persons in India, Indonesia, the Maldives, Somalia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- Hurricanes Rita and WilmaHurricane Rita made landfall 26 days after Hurricane Katrina near the Texas-Louisiana border, forcing cessation of hurricane-response activities in New Orleans and evacuation of coastal regions of Louisiana and Texas.
- Hurricane KatrinaHurricane Katrina struck the coastal areas of Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi on August 29, 2005, causing substantial numbers of deaths among both humans and animals, infrastructure damage, and flooding.
- Marburg Virus OutbreakMarburg virus disease is a rare but severe hemorrhagic fever that affects both people and non-human primates.
- Hurricanes Charley, Frances, Ivan, & JeanneDuring August 13, 2004 – September 25, 2004, Florida experienced four major hurricanes: Charley and Frances (both Category 4) and Ivan and Jeanne (both Category 3).
- West Nile VirusWest Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of mosquito-borne disease in the continental United States. In 2004, a total of 36 states reported 1,053 cases of human WNV illness to CDC
- Avian InfluenzaIn January 2004, highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus of the H5N1 subtype was first confirmed in poultry and humans in Thailand.
- Mad Cow DiseaseOn December 23, 2003, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) discovered bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), also known as mad cow disease, in a single “downer” (i.e., nonambulatory disabled) dairy cow in Washington state.
- California WildfireOn October 25, 2003, a massive wildfire began in San Diego County. Over a period of three days, the air quality deteriorated to unhealthy and hazardous levels, prompting school cancellations and the public to stay at home.
- Investigation of a Ricin-Containing EnvelopeOn October 15, 2003, an envelope with a threatening note and a sealed container was processed at a mail processing and distribution facility in Greenville, South Carolina.
- Hurricane IsabelOn September 18, 2003, Hurricane Isabel, a Category 2 hurricane, made landfall on the Outer Banks of North Carolina (NC).
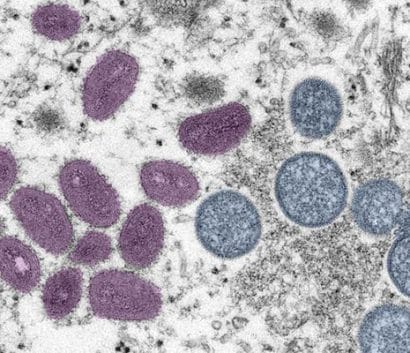
- Mpox VirusIn 2003, the United States experienced an outbreak of mpox, the first time human mpox was reported outside of Africa.
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) was a global disease outbreak in 2003 that was caused by a coronavirus called SARS-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV). The illness was first reported in Asia in February 2003.
- Space Shuttle Columbia DisasterOn February 01, 2003, the Space Shuttle Columbia disintegrated when it re-entered Earth’s atmosphere. Debris from the shuttle was found in a wide area underneath its path, mainly in eastern Texas and Louisiana.
- AnthraxFollowing the September 11 attacks in New York City and Washington DC, the United States suffered through another national scare. Multiple bioterrorism attacks using B. anthracis (anthrax) spores were sent through the mail, resulting in several deaths and numerous exposures.
- September 11 AttacksOn September 11, 2001, terrorists hijacked two passenger planes and crashed them into the two towers of the World Trade Center (WTC) in New York City. These synchronized attacks were the largest act of terrorism ever committed on U.S. soil.