QuickStats: Percentage* of Adults Aged ≥18 Years Who Met the Federal Guidelines for Muscle-Strengthening Physical Activity,† by Age Group and Sex — National Health Interview Survey, United States, 2020§
Weekly / May 6, 2022 / 71(18);642
Altmetric:
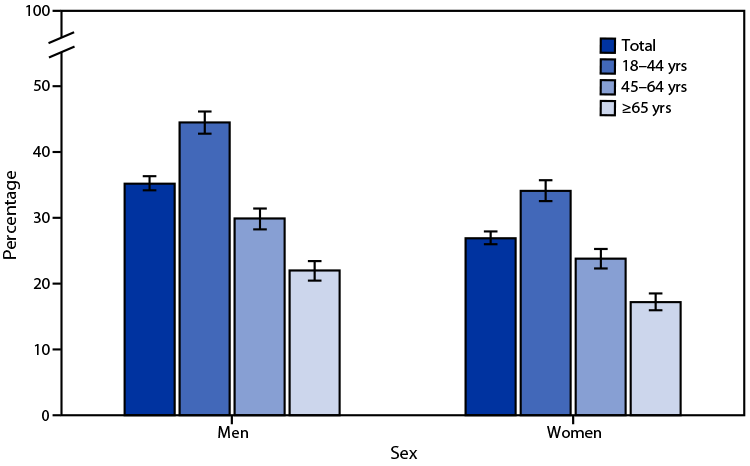
* With 95% CIs indicated by error bars.
† Per U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd edition (https://health.gov/paguidelines). Respondents met the muscle-strengthening guideline if they reported engaging in leisure-time physical activities specifically designed to strengthen muscles, such as sit-ups, push-ups, or lifting weights, at least two times per week.
§ Estimates are based on household interviews of a sample of the civilian, noninstitutionalized U.S. population.
In 2020, 35.2% of men and 26.9% of women aged ≥18 years met the federal guideline for muscle-strengthening physical activity. The percentage of men who met the muscle-strengthening guideline decreased with age from 44.5% for those aged 18–44 years, to 29.9% for those aged 45–64 years, and to 22.0% for those aged ≥65 years. The percentage also decreased with age among women from 34.1% for those aged 18–44 years, to 23.8% for those aged 45–64 years, and to 17.2% for those aged ≥65 years. Men were more likely to have met the muscle-strengthening guideline than women in all age groups.
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, National Health Interview Survey, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.htm
Reported by: Elizabeth Heitz, MPH, eheitz@cdc.gov, 301-458-4515.
Suggested citation for this article: QuickStats: Percentage of Adults Aged ≥18 Years Who Met the Federal Guidelines for Muscle-Strengthening Physical Activity,† by Age Group and Sex — National Health Interview Survey, United States, 2020§. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022;71:642. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7118a6.
MMWR and Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report are service marks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services.
References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are
provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply
endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content
of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of
the date of publication.
All HTML versions of MMWR articles are generated from final proofs through an automated process. This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr) and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to mmwrq@cdc.gov.