Diagnoses of HIV Infection in the United States and Dependent Areas, 2018: Persons Who Inject Drugs

The Special Focus Profiles highlight trends and distribution of HIV in 5 populations of particular interest to HIV prevention programs in state and local health departments: (1) Transgender Persons, (2) Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex With Men, (3) Persons Who Inject Drugs, (4) Women, and (5) Children Aged <13 Years.
Persons who inject drugs (PWID) are at high risk for getting HIV if they use and share needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment (e.g., cookers) that someone with HIV has used. Persons who inject drugs account for about 1 in 15 HIV diagnoses in the United States. In recent years, the opioid (including prescription and synthetic opioids) and heroin crisis has led to increased numbers of PWID. HIV diagnoses among PWID have increased in the 50 states and District of Columbia. IDU in nonurban areas has created prevention challenges and placed new populations at risk for HIV.
Diagnoses of HIV Infection
Figure 18. Diagnoses of HIV Infection among Persons Who Inject Drugs, by Sex at Birth and Race/Ethnicity, 2018—United States and 6 Dependent Areas
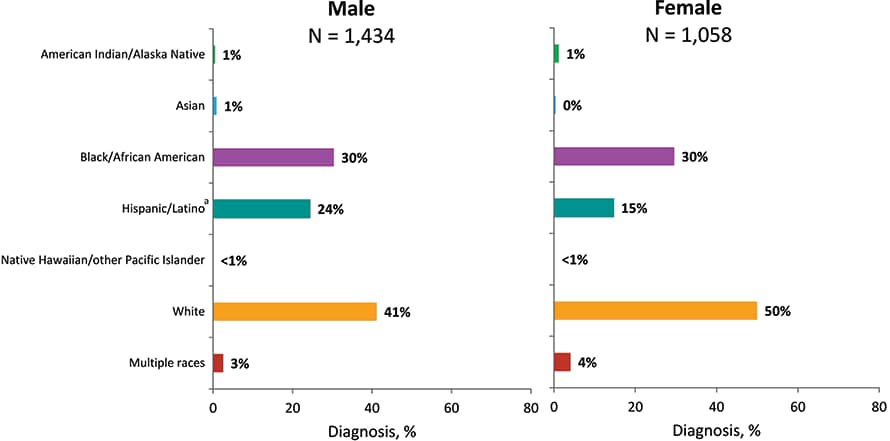
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. See Data Tables, Definitions, and Acronyms for more information on race/ethnicity and transmission categories.
a Hispanics/Latinos can be of any race.
From 2014 through 2018 in the United States and 6 dependent areas, the percentage of diagnoses of HIV infection attributed to injection drug use increased. In 2018, among 1,434 male adult and adolescent PWID with diagnosed HIV infection, approximately 41% were white, 30% were black/African American, and 24% were Hispanic/Latino (Figure 18). Among 1,058 female adult and adolescent PWID with diagnosed HIV infection, 50% were white, 30% black/African American, and 15% Hispanic/Latino. Please use caution when interpreting data for American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander PWID, and persons of multiple races who inject drugs: the numbers are small.
Figure 19. Diagnoses of HIV Infection among Persons Who Inject Drugs, by Region and Race/Ethnicity, 2018—United States and 6 Dependent Areas
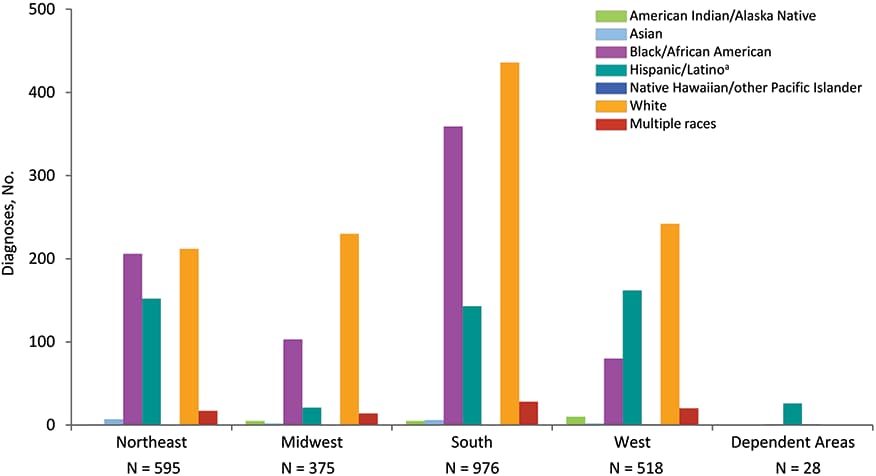
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. See Data Tables, Definitions, and Acronyms for more information on race/ethnicity, transmission categories, and U.S. Census Regions.
a Hispanics/Latinos can be of any race.
In 2018 in the United States and 6 dependent areas, 2,492 diagnosed HIV infections were among PWID. Of these, the largest number of HIV infection diagnoses were in the South (976), followed by the Northeast (595) (Figure 19). In all regions, the largest percentage of diagnosed HIV infections among PWID was among whites. In the South, whites accounted for 436 diagnosed HIV infections among PWID (45%), blacks/African Americans accounted for 359 (37%), and Hispanics/Latinos accounted for 143 (15%) (Table 6b). In the Northeast, whites accounted for 212 diagnosed HIV infections among PWID (36%), blacks/African Americans accounted for 206 (35%), and Hispanics/Latinos accounted for 152 (26%). Please use caution when interpreting data for American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander PWID, and persons of multiple races who inject drugs: the numbers are small.
Prevalence and Race/Ethnicity
At the end of 2018 in the United States and 6 dependent areas, approximately 122,112 adult and adolescent PWID were living with diagnosed HIV infection. Approximately 46% were black/African American, 27% were Hispanic/Latino, and 21% were white. Persons of multiple races accounted for approximately 5% of those living with diagnosed HIV infection among PWID. American Indians/Alaska Natives, Asians, and Native Hawaiians/other Pacific Islanders each accounted for less than 1% of those living with diagnosed HIV infection among PWID (Table 15b).
| Male | Female | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20–24 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 25–29 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 30–34 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 35–39 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| 40–44 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 45–49 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 50–54 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 55–59 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 60–64 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| ≥65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Midwest | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| South | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| West | 4 | 6 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 5 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 10 | 9 | 17 | 17 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Asian | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20–24 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 25–29 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 30–34 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 35–39 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 40–44 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 45–49 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 50–54 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 55–59 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 60–64 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ≥65 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 6 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Midwest | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| South | 8 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| West | 4 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 20 | 21 | 15 | 11 | 13 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| Black/African American | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 8 |
| 20–24 | 31 | 25 | 21 | 21 | 23 | 31 | 25 | 24 | 28 | 22 |
| 25–29 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 37 | 47 | 39 | 43 | 42 | 39 | 29 |
| 30–34 | 39 | 42 | 36 | 53 | 49 | 37 | 34 | 39 | 39 | 39 |
| 35–39 | 36 | 39 | 47 | 45 | 64 | 43 | 34 | 38 | 41 | 36 |
| 40–44 | 47 | 45 | 43 | 37 | 37 | 38 | 33 | 27 | 38 | 30 |
| 45–49 | 66 | 42 | 42 | 48 | 47 | 48 | 44 | 30 | 41 | 35 |
| 50–54 | 62 | 64 | 60 | 47 | 47 | 50 | 40 | 52 | 39 | 34 |
| 55–59 | 74 | 62 | 45 | 56 | 50 | 47 | 35 | 39 | 31 | 37 |
| 60–64 | 43 | 32 | 38 | 33 | 33 | 21 | 26 | 28 | 25 | 26 |
| ≥65 | 38 | 30 | 31 | 28 | 33 | 18 | 14 | 16 | 19 | 17 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 152 | 119 | 115 | 131 | 123 | 107 | 91 | 74 | 91 | 83 |
| Midwest | 44 | 48 | 52 | 60 | 61 | 47 | 50 | 51 | 58 | 42 |
| South | 248 | 207 | 186 | 182 | 207 | 189 | 162 | 177 | 164 | 152 |
| West | 30 | 45 | 48 | 35 | 45 | 38 | 36 | 44 | 37 | 36 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 477 | 419 | 402 | 408 | 436 | 382 | 339 | 346 | 350 | 313 |
| Hispanic/Latinob | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| 20–24 | 22 | 25 | 20 | 19 | 23 | 22 | 27 | 14 | 17 | 20 |
| 25–29 | 39 | 39 | 35 | 43 | 37 | 18 | 16 | 32 | 19 | 18 |
| 30–34 | 42 | 51 | 50 | 59 | 65 | 24 | 18 | 27 | 32 | 25 |
| 35–39 | 41 | 56 | 46 | 40 | 45 | 24 | 22 | 15 | 24 | 24 |
| 40–44 | 54 | 43 | 30 | 43 | 40 | 30 | 18 | 19 | 16 | 13 |
| 45–49 | 59 | 42 | 38 | 45 | 41 | 18 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 19 |
| 50–54 | 42 | 43 | 42 | 48 | 45 | 16 | 16 | 18 | 13 | 15 |
| 55–59 | 34 | 35 | 33 | 27 | 25 | 17 | 9 | 14 | 9 | 9 |
| 60–64 | 18 | 11 | 14 | 16 | 14 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 9 | 7 |
| ≥65 | 9 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 11 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 99 | 102 | 98 | 115 | 104 | 63 | 48 | 54 | 48 | 48 |
| Midwest | 11 | 19 | 13 | 16 | 14 | 13 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| South | 90 | 94 | 80 | 91 | 97 | 52 | 51 | 54 | 47 | 46 |
| West | 106 | 97 | 99 | 108 | 111 | 48 | 38 | 46 | 53 | 51 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 57 | 49 | 38 | 34 | 25 | 14 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 2 |
| Total | 363 | 361 | 327 | 363 | 350 | 189 | 152 | 172 | 166 | 155 |
| Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20–24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 25–29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30–34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 35–39 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40–44 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 45–49 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 50–54 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 55–59 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60–64 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ≥65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Midwest | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| South | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| West | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| White | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 13 | 9 | 5 | 9 | 8 |
| 20–24 | 24 | 41 | 30 | 37 | 37 | 40 | 50 | 43 | 52 | 49 |
| 25–29 | 41 | 81 | 79 | 87 | 98 | 56 | 90 | 94 | 88 | 79 |
| 30–34 | 55 | 78 | 61 | 94 | 111 | 62 | 86 | 66 | 97 | 100 |
| 35–39 | 45 | 50 | 67 | 78 | 114 | 47 | 55 | 58 | 81 | 94 |
| 40–44 | 57 | 53 | 45 | 47 | 63 | 38 | 61 | 45 | 53 | 71 |
| 45–49 | 51 | 66 | 50 | 56 | 50 | 36 | 49 | 43 | 37 | 44 |
| 50–54 | 51 | 56 | 51 | 38 | 51 | 29 | 42 | 39 | 40 | 41 |
| 55–59 | 29 | 32 | 27 | 38 | 36 | 19 | 25 | 22 | 31 | 28 |
| 60–64 | 20 | 20 | 18 | 20 | 18 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 10 | 10 |
| ≥65 | 13 | 9 | 16 | 16 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 6 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 67 | 74 | 84 | 98 | 117 | 62 | 74 | 85 | 92 | 95 |
| Midwest | 52 | 139 | 83 | 95 | 122 | 40 | 134 | 87 | 94 | 108 |
| South | 146 | 153 | 160 | 204 | 217 | 169 | 195 | 179 | 222 | 219 |
| West | 122 | 122 | 121 | 118 | 135 | 82 | 80 | 84 | 94 | 108 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 387 | 489 | 448 | 515 | 591 | 353 | 482 | 435 | 502 | 529 |
| Multiple races | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 20–24 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| 25–29 | 10 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| 30–34 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| 35–39 | 5 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
| 40–44 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| 45–49 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| 50–54 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 55–59 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| 60–64 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| ≥65 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 10 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 12 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 11 |
| Midwest | 9 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 7 |
| South | 15 | 14 | 15 | 9 | 13 | 27 | 16 | 18 | 13 | 15 |
| West | 11 | 6 | 12 | 5 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 10 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 45 | 34 | 38 | 26 | 36 | 51 | 40 | 41 | 36 | 43 |
| Total | ||||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | ||||||||||
| 13–14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 15–19 | 10 | 7 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 31 | 22 | 19 | 25 | 22 |
| 20–24 | 79 | 94 | 76 | 78 | 88 | 98 | 105 | 85 | 103 | 98 |
| 25–29 | 129 | 162 | 160 | 179 | 189 | 120 | 155 | 178 | 156 | 138 |
| 30–34 | 147 | 188 | 150 | 214 | 235 | 133 | 150 | 138 | 172 | 173 |
| 35–39 | 130 | 151 | 171 | 171 | 227 | 124 | 116 | 121 | 153 | 161 |
| 40–44 | 168 | 148 | 126 | 135 | 147 | 115 | 117 | 97 | 113 | 118 |
| 45–49 | 183 | 154 | 137 | 156 | 144 | 110 | 114 | 98 | 102 | 103 |
| 50–54 | 165 | 172 | 162 | 139 | 153 | 101 | 103 | 119 | 99 | 95 |
| 55–59 | 141 | 134 | 114 | 123 | 115 | 88 | 77 | 80 | 75 | 76 |
| 60–64 | 86 | 67 | 72 | 71 | 68 | 37 | 43 | 50 | 44 | 46 |
| ≥65 | 63 | 59 | 66 | 64 | 53 | 34 | 27 | 30 | 29 | 29 |
| Region of residencea | ||||||||||
| Northeast | 334 | 312 | 307 | 355 | 356 | 246 | 221 | 221 | 246 | 239 |
| Midwest | 118 | 214 | 153 | 178 | 207 | 107 | 200 | 155 | 166 | 168 |
| South | 512 | 472 | 448 | 489 | 537 | 439 | 428 | 430 | 452 | 439 |
| West | 278 | 285 | 299 | 285 | 308 | 186 | 174 | 200 | 201 | 210 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 60 | 51 | 39 | 34 | 26 | 15 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 2 |
| Total | 1,302 | 1,334 | 1,247 | 1,342 | 1,434 | 992 | 1,031 | 1,016 | 1,072 | 1,058 |
Note: Numbers less than 12, and trends based on these numbers, should be interpreted with caution.
Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category, therefore values may not sum to column subtotals and total.
Persons whose transmission category is classified as injection drug use are presented based on sex at birth and include transgender persons.
aData are based on residence at time of diagnosis of HIV infection.
bHispanics/Latinos can be of any race.
| American Indian/ Alaska Native |
Asiana | Black/ African American |
Hispanic/ Latinob |
Native Hawaiian/ other Pacific Islander |
White | Multiple races | Totalc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male | 2,285 | 12,354 | 276,028 | 195,367 | 742 | 263,161 | 35,498 | 785,983 |
| Female | 799 | 2,689 | 142,260 | 48,608 | 145 | 39,910 | 11,097 | 245,727 |
| Transgender male-to-femaled | 47 | 166 | 4,754 | 3,234 | 29 | 1,013 | 740 | 9,983 |
| Transgender female-to-maled | 4 | 7 | 189 | 81 | 0 | 94 | 29 | 404 |
| Additional gender identitye | 1 | 6 | 73 | 47 | 0 | 28 | 18 | 173 |
| Age at end of year | ||||||||
| <13 | 7 | 110 | 1,153 | 250 | 3 | 246 | 149 | 1,918 |
| 13–14 | 0 | 35 | 428 | 95 | 2 | 85 | 27 | 672 |
| 15–19 | 16 | 89 | 2,669 | 912 | 5 | 495 | 176 | 4,363 |
| 20–24 | 97 | 430 | 15,029 | 6,572 | 26 | 3,856 | 1,168 | 27,184 |
| 25–29 | 284 | 1,260 | 36,843 | 17,351 | 78 | 12,198 | 3,523 | 71,544 |
| 30–34 | 327 | 1,608 | 41,208 | 23,091 | 113 | 17,994 | 4,371 | 88,720 |
| 35–39 | 366 | 1,796 | 39,673 | 26,615 | 122 | 21,796 | 4,630 | 95,007 |
| 40–44 | 312 | 2,039 | 39,939 | 28,038 | 104 | 23,375 | 4,678 | 98,506 |
| 45–49 | 442 | 2,411 | 48,252 | 32,869 | 119 | 35,911 | 5,814 | 125,890 |
| 50–54 | 440 | 1,972 | 59,522 | 38,453 | 117 | 53,007 | 7,481 | 161,131 |
| 55–59 | 401 | 1,417 | 57,527 | 32,358 | 99 | 57,320 | 6,943 | 156,237 |
| 60–64 | 235 | 961 | 41,837 | 20,654 | 63 | 38,262 | 4,490 | 106,641 |
| ≥65 | 209 | 1,094 | 39,224 | 20,079 | 65 | 39,661 | 3,932 | 104,457 |
| Transmission categoryf | ||||||||
| Male adult or adolescentg | ||||||||
| Male-to-male sexual contact | 1,624 | 10,477 | 178,761 | 142,672 | 649 | 216,006 | 26,221 | 576,787 |
| Injection drug use | 224 | 447 | 32,655 | 22,674 | 26 | 13,503 | 2,624 | 72,227 |
| Male-to-male sexual contact and injection drug use |
299 | 399 | 15,538 | 13,370 | 46 | 22,757 | 4,055 | 56,517 |
| Heterosexual contacth | 164 | 1,040 | 49,723 | 18,048 | 44 | 9,898 | 2,856 | 81,803 |
| Perinatali | 5 | 44 | 2,783 | 1,310 | 3 | 547 | 305 | 5,005 |
| Otherj | 14 | 73 | 812 | 451 | 2 | 1,371 | 131 | 2,858 |
| Subtotal | 2,330 | 12,480 | 280,271 | 198,525 | 770 | 264,082 | 36,192 | 795,198 |
| Female adult or adolescentg | ||||||||
| Injection drug use | 252 | 181 | 23,680 | 10,336 | 22 | 12,498 | 2,841 | 49,885 |
| Heterosexual contacth | 528 | 2,329 | 114,056 | 36,552 | 120 | 26,276 | 7,802 | 187,793 |
| Perinatali | 8 | 57 | 3,347 | 1,400 | 0 | 622 | 321 | 5,761 |
| Otherj | 11 | 65 | 797 | 274 | 1 | 482 | 78 | 1,715 |
| Subtotal | 799 | 2,632 | 141,880 | 48,562 | 143 | 39,878 | 11,041 | 245,154 |
| Child (<13 yrs at end of year) | ||||||||
| Perinatal | 7 | 72 | 934 | 223 | 3 | 172 | 133 | 1,544 |
| Otherj | 0 | 38 | 219 | 27 | 0 | 74 | 16 | 374 |
| Subtotal | 7 | 110 | 1,153 | 250 | 3 | 246 | 149 | 1,918 |
| Region of residencek | ||||||||
| Northeast | 152 | 3,288 | 90,762 | 72,151 | 64 | 54,699 | 14,461 | 235,944 |
| Midwest | 366 | 1,514 | 53,000 | 14,806 | 41 | 47,483 | 5,514 | 122,844 |
| South | 769 | 3,115 | 247,002 | 77,304 | 147 | 115,688 | 19,456 | 463,643 |
| West | 1,847 | 7,243 | 32,230 | 67,056 | 629 | 86,261 | 7,932 | 203,313 |
| U.S. dependent areas | 2 | 62 | 310 | 16,020 | 35 | 75 | 19 | 16,526 |
| Total | 3,136 | 15,222 | 423,304 | 247,337 | 916 | 304,206 | 47,382 | 1,042,270 |
Note: Data for the year 2018 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2019. Numbers less than 12 should be interpreted with caution.
aIncludes Asian/Pacific Islander legacy cases (see Technical Notes).
bHispanics/Latinos can be of any race.
cIncludes persons whose race/ethnicity is unknown.
d“Transgender male-to-female” includes individuals who were assigned “male” sex at birth but have ever identified as “female” gender. “Transgender female-to-male” includes individuals who were assigned “female” sex at birth but have ever identified as “male” gender.
eAdditional gender identity examples include “bigender,” “gender queer,” and “two-spirit.”
fData have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category, therefore values may not sum to column subtotals and total.
gData presented based on sex at birth and includes transgender persons.
hHeterosexual contact with a person known to have, or to be at high risk for, HIV infection.
iIncludes individuals ≥13 years of age at time of diagnosis of HIV infection.
jIncludes hemophilia, blood transfusion, and risk factor not reported or not identified.
kData are based on address of residence at the end of the specified year (i.e., most recent known address).
In the Federal Register [6] for October 30, 1997, the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) announced the Revisions to the Standards for the Classification of Federal Data on Race and Ethnicity. Implementation by January 1, 2003 was mandated. At a minimum, data on the following race categories should be collected:
- American Indian or Alaska Native
- Asian
- black or African American
- Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander
- white
Additionally, systems must be able to retain information when multiple race categories are reported. In addition to data on race, data on 2 categories of ethnicity should be collected:
- Hispanic or Latino
- not Hispanic or Latino
The Asian or Pacific Islander category displayed in annual surveillance reports published prior to the 2007 surveillance report was split into 2 categories: (1) Asian and (2) Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander. The Asian category (in tables where footnoted) includes the cases in Asians/Pacific Islanders (referred to as legacy cases) that were reported before the implementation of the new race categories in 2003 (e.g., cases of HIV infection that were diagnosed and reported to CDC before 2003 but that were classified as stage 3 [AIDS] after 2003) and a small percentage of cases that were reported after 2003 but that were reported according to the old race category (Asian/ Pacific Islander). In tables of diagnoses of HIV infection during 2014–2018, the Asian category does not include Asian/Pacific Islander cases because these cases were diagnosed after 2003 and were reported to CDC in accordance with OMB’s Revisions to the Standards for the Classification of Federal Data on Race and Ethnicity [6].
This report also presents data for persons for whom multiple race categories are reported. In this report, persons categorized by race were not Hispanic or Latino. The number of persons reported in each race category may, however, include persons whose ethnicity was not reported.
Transmission category is the term for the classification of cases that summarizes an adult’s or adolescent’s possible HIV risk factors; the summary classification results from selecting, from the presumed hierarchical order of probability, the 1 (single) risk factor most likely to have been responsible for transmission. For surveillance purposes, a diagnosis of HIV infection is counted only once in the hierarchy of transmission categories [7]. Adults or adolescents with more than 1 reported risk factor for HIV infection are classified in the transmission category listed first in the hierarchy. The exception is men who had sexual contact with other men and injected drugs; this group makes up a separate transmission category.
Hierarchical Categories:
- Male-to-male sexual contact: men who have had sexual contact with men (i.e., homosexual contact) and men who have had sexual contact with both men and women (i.e., bisexual contact)
- Injection drug use (IDU): persons who have injected non-prescription drugs
- Male-to-male sexual contact and injection drug use (male-to-male sexual contact and IDU): men who have had sexual contact with other men and injected non-prescription drugs
- Heterosexual contact: persons who have ever had heterosexual contact with a person known to have, or to be at high risk for, HIV infection
- Perinatal: persons infected through perinatal transmission but aged 13 years and older at time of diagnosis of HIV infection. Prevalence data and tables of death data includes persons infected through perinatal transmission but aged 13 years and older during the specified year or at death.
- Other: all other transmission categories (e.g., blood transfusion, hemophilia, risk factor not reported or not identified).
Cases of HIV infection reported without a risk factor listed in the hierarchy of transmission categories are classified as “no identified risk (NIR).” Cases classified as NIR include cases that are being followed up by local health department staff; cases in persons whose risk-factor information is missing because they died, declined to be interviewed, or were lost to follow-up; and cases in persons who were interviewed or for whom other follow-up information was available but for whom no risk factor was identified.
Because a substantial proportion of cases of HIV infection are reported to CDC without an identified risk factor, multiple imputation is used to assign a transmission category to these cases [7]. Multiple imputation is a statistical approach in which each missing transmission category is replaced with a set of plausible values that represent the uncertainty about the true, but missing, value [8]. Each resulting data set containing the plausible values is analyzed by using standard procedures, and the results from these analyses are then combined to produce the final results. In tables displaying transmission categories, multiple imputation was used for adults and adolescents, but not for children (because the number of cases in children is small, missing transmission categories were not imputed).
Data by region reflect the address at the time of diagnosis of HIV infection for figures and tables that present number of diagnoses (Figures 17, 19, 24; Tables 1a/b–7a/b). For tables presenting prevalence data (14a/b–17a/b), region is based on most recent known address as of the end of the specified year. For the death tables (10a/b–13a/b), region is based on residence at death. When information on residence at death is not available, the state where a person’s death occurred is used.
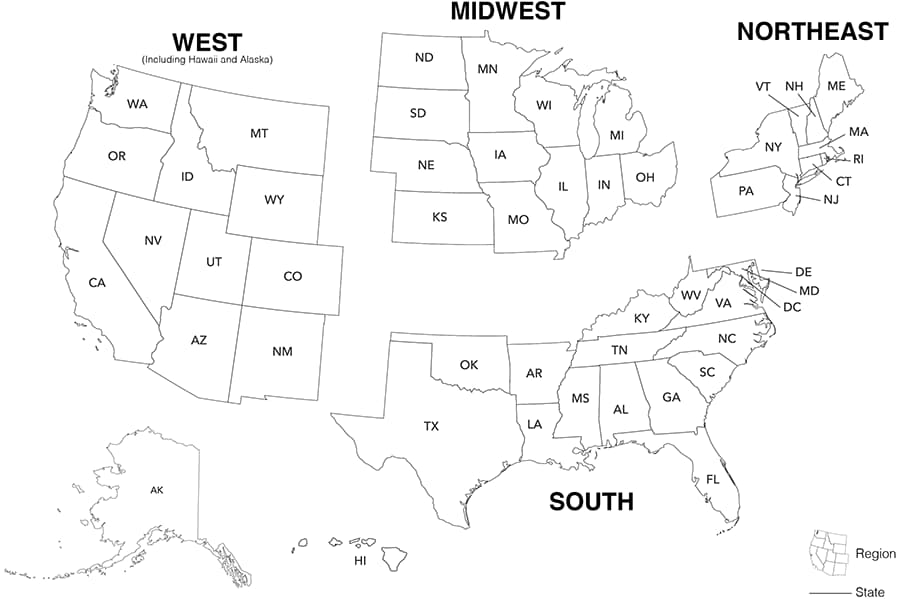
The 4 regions of residence and 6 dependent areas used in this report are defined by the U.S. Census Bureau as follows:
- Northeast: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont
- Midwest: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin
- South: Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, District of Columbia (D.C.), Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia
- West: Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming
- U.S. dependent areas: American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, the Republic of Palau, and the U.S. Virgin Islands
AGI: additional gender identity
AIDS: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
FTM: female-to-male
HIV: human immunodeficiency virus
IDU: injection drug use
MSA: metropolitan statistical area
MSM: gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men
MTF: male-to-female
NHSS: National HIV Surveillance System
NIR: no identified risk factor
OI: opportunistic illness
OMB: Office of Management and Budget
PrEP: preexposure prophylaxis
PWID: persons who inject drugs