What to know
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends hepatitis B (HepB) vaccination among all infants at birth, unvaccinated children younger than 19 years of age, adults aged 19–59 years, and adults aged 60 years and older with risk factors for hepatitis B or without identified risk factors but seeking protection.
Who should be vaccinated
ACIP recommends that the following people should receive hepatitis B (HepB) vaccination:
- All infants.
- Unvaccinated children younger than 19 years of age.
- Adults 19–59 years.
- Adults 60 years and older with risk factors for hepatitis B.
The following groups may also receive HepB vaccination:
- Adults 60 years and older without known risk factors for hepatitis B.
Recommendations for screening, testing, and vaccination
The table below provides recommendations for screening, testing, and vaccination1 among adults and all persons with risk. Prevaccination testing should not be a barrier to vaccination of susceptible people, especially in populations that have less engagement with or access to health care. In settings where testing is not feasible or is refused by the patient, the clinician should offer vaccination and, at future visits, should offer testing again.
Population
Screening and testing recommendation
Vaccination recommendation
Adults with no known risk factors for hepatitis B
- If never previously screened, test for HBsAg, anti-HBs, and total anti-HBc (triple panel)
- Vaccinate § adults aged 19 – 59 years
People with risk factors, regardless of age.*
- If never previously screened, test for HBsAg, anti-HBs, and total anti-HBc (triple panel)
-
- Unless less than aged 18 years and completed a vaccine series as an infant
- If previously screened, but still unvaccinated, offer testing to people who have ongoing risk for exposure
- Vaccinate §
People with additional risk factors, such as:
- Residents and staff of facilities for people with developmental disabilities
- Health care and public safety personnel with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- People with diabetes at the discretion of the treating clinician
- International travelers to countries with high or intermediate levels of endemic hepatitis B virus infection
- If never previously screened, test for HBsAg, anti-HBs, and total anti-HBc (triple panel)
- Unless less than aged 18 years and completed a vaccine series as an infant
- Vaccinate† §
* For additional considerations for patients on dialysis, see Footnote A .A
† For additional considerations for healthcare personnel see Footnote B.B
§ Vaccinate susceptible persons without documentation of a completed hepatitis B vaccination series; testing should not be a barrier to vaccination.
For testing recommendations and assistance interpreting B screening results, see hepatitis B testing guidelines.
Composition and dosage
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has licensed three single-antigen vaccines (Engerix-B, Heplisav-B, and Recombivax HB), and three combination vaccines (Pediarix, Vaxelis, and Twinrix) to protect against hepatitis B. All vaccines contain yeast protein and aluminum adjuvant or a small synthetic nucleotide immunostimulant (Heplisav-B).
No differences in immunogenicity have been observed when one or 2 doses of hepatitis B vaccine produced by one manufacturer are followed by doses from a different manufacturer. Whenever feasible, the same vaccine should be used for the subsequent doses; however, if a different brand is administered, the dose(s) should be considered valid and do not need to be repeated.
Engerix-B
For persons from birth through adulthood
People aged 19 years and younger should receive three doses. People aged 20 years and older should receive three doses. Adults on hemodialysis should receive four doses. See package insert for detailed dosage instructions.
See the Engerix-B package insert.
Heplisav-B
For adults aged 18 years through adulthood
People aged 18 years and older should receive two doses. The safety and effectiveness of Heplisav-B has not been established in adults on hemodialysis. See package insert for indications and detailed dosage instructions.
See the Heplisav-B package insert.
Recombivax HB
For persons from birth through adulthood
People aged 19 years and younger should receive three doses. People aged 20 years and older should receive three doses. Adults on dialysis or predialysis should receive three doses of the dialysis formulation. See package insert for indications and detailed dosage instructions.
See the Recombivax HB package insert.
PreHevbrio
Pediarix
For children aged 6 weeks through age 6 years
People between 6 weeks and 6 years of age should receive three doses. See package insert for detailed dosage instructions.
See the Pediarix package insert.
Vaxelis
For children aged 6 weeks through age 4 years
People between 6 weeks and 4 years of age should receive three doses. See package insert for detailed dosage instructions.
See the Vaxelis package insert.
Twinrix
For adults aged 18 years through adulthood
People aged 18 years and older should receive either three or four doses. See package insert for detailed dosage instructions.
See the Twinrix package insert.
Vaccine effectiveness
Each of the HepB vaccines are highly effective in preventing infection. Studies indicate that immunity persists for at least 30 years among healthy people who initiate HepB vaccination at less than 6 months of age.
Hemodialysis
Providers should vaccinate adult hemodialysis patients needing HepB vaccination with high-dose (40ug) Engerix-B or Recombivax HB. See package insert for detailed dosage instructions.
Pregnancy
Providers should vaccinate pregnant patients needing HepB vaccination with Engerix-B, Heplisav-B, Recombivax HB, or Twinrix.
Safety and precautions
Scientific evidence overwhelmingly supports the safety of HepB vaccines.
As a precaution, clinicians should ask the person getting the vaccine if they've previously experienced an allergic reaction to:
- A previous dose of HepB vaccine.
- Any part of HepB vaccine.
- Yeast.
People who are moderately or severely ill should wait until they recover before getting a HepB vaccine. However, administering the vaccine to people with minor illnesses, such as a cold, is fine. Learn more about contraindications and precautions.
Reporting adverse events
The most frequently reported adverse event associated with HepB vaccination is injection site soreness. Any adverse event suspected to be associated with HepB vaccination should be reported through the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
VAERS is an early warning system, co-managed by CDC and the FDA, that monitors potential vaccine safety problems. Clinicians and vaccine manufacturers are required by law to report certain adverse events following vaccination to VAERS. Patients and caregivers can also submit reports.
Administration
Clinicians should administer the vaccine intramuscularly into the anterolateral aspect of the thigh or the deltoid muscle of the upper arm, depending on the person’s age. When administering multiple vaccines, Clinicians should use different anatomic sites (e.g., separate limbs).
Concurrent administration of other vaccines
Clinicians can administer HepB vaccine concurrently with other vaccines to children and adults. There is no evidence that coadministration reduces the vaccine response or effectiveness.
Vaccine schedules
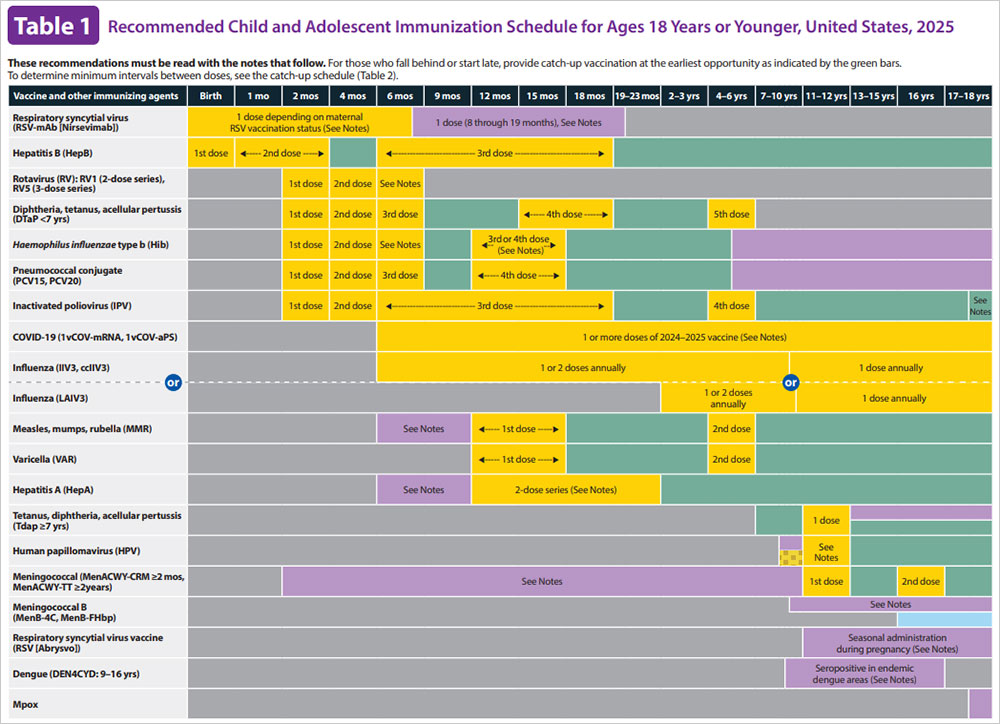
HepB vaccine can be given as a stand-alone vaccine or as part of a combination vaccine. For detailed information on HepB vaccine schedules, see immunization schedules from CDC.
Resources
ACIP Presentation Slides: September 18, 2025
Scientific guidelines and recommendations
Continuing education
Vaccine requirements by state
Standing orders
Vaccine assistance programs
Specific sites and tools
Related pages
Vaccine Information Statement (VIS)
Vaccine Information Statements (VISs) are information sheets produced by CDC that explain both the benefits and risks of a vaccine. View the VIS for HepB vaccine.