Candida auris Testing
Information for Patients
Candida auris (also called C. auris) is a fungus that can cause serious infections. C. auris can spread from one patient to another in hospitals and nursing homes. Patients can carry C. auris somewhere on their body, even if it is not making them sick. This is called colonization. When people in hospitals and nursing homes are colonized, C. auris can spread from their bodies and can get on other people or nearby objects, allowing the fungus to spread to people around them.
CDC recommends testing patients who may have come in contact with C. auris to see if they are carrying this fungus. This allows healthcare providers to know who is carrying the fungus and take steps to prevent it from spreading to other people.
Why am I being tested for C. auris?
- It can cause serious infections.
- It is often resistant to medicines, making it difficult to treat.
- It is becoming more common.
- It is difficult to identify by routine lab tests.
- It can spread in hospitals and nursing homes.
You may have come in contact with C. auris while you were in this or another healthcare facility.
To keep the fungus from spreading, we are testing patients to see if they are now carrying the fungus. You may be carrying it on your skin without having an infection or symptoms of an infection. This is called colonization.
Fortunately, most people who carry C. auris do not get sick from it.
Getting tested for C. auris helps our healthcare facility and the health department prevent the fungus from spreading in the facility and in the community.
What should I expect if I get tested?
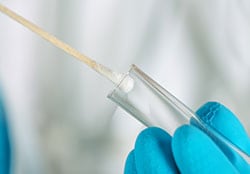
- The nurse or doctor will wipe or rub a cotton swab on the skin near your armpits and the area where your leg joins your body (groin). The test is not painful.
- The swab will be sent to a lab, and in 1 to 2 weeks, the lab will tell your doctor the results.
- If the test shows you are carrying the fungus, then your nurse or doctor will talk to you about the results and what to do next.
You can choose not to be tested. Talk to your nurse or doctor if you have questions or concerns about testing.
