At a glance
Laboratory tests for vitamin D are used to determine a person’s vitamin D status, and to identify persons with vitamin D deficiency. These tests must be accurate to ensure correct diagnoses and treatment of patients with vitamin D deficiency.

Standardization of Vitamin D
Did you know?
Vitamin D tests are used to determine a person’s vitamin D status and to aid in the diagnosis of diseases associated with bone metabolism and diseases such as cystic fibrosis and Crohn disease. Vitamin D is among the most commonly requested laboratory tests. These tests must be accurate to ensure correct diagnoses and treatment of patients with vitamin D deficiency.
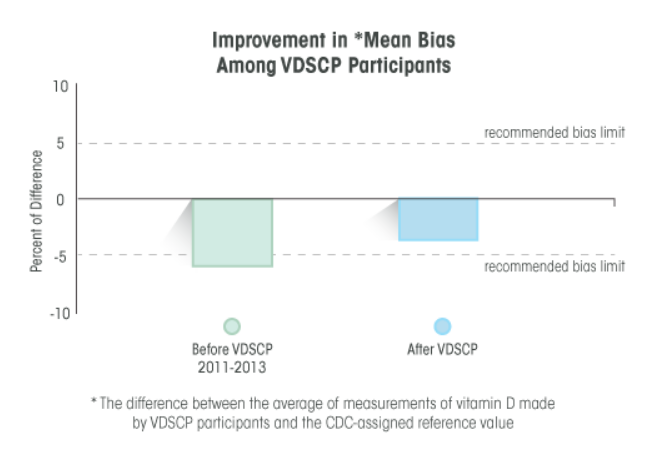
CDC improves the detection and diagnosis of bone diseases by ensuring that laboratory tests for vitamin D are accurate and reliable. CDC's Vitamin D Reference Method Laboratory and the Vitamin D Standardization Certification Program work to:
- Provide reference measurements for total 25-hydroxyvitamin D. [Vitamin D Reference Laboratory]
- Assess and certify the analytical performance (accuracy and precision) of vitamin D tests used in patient care, research and public health. [Improving Performance - VDSCP]
- Monitor the accuracy of measurements performed in routine laboratories over time. [Monitoring Accuracy - AMP Vitamin D]
- Provide technical support to external quality assurance programs, proficiency testing programs, and research studies that ensure vitamin D tests are accurate and reliable.
More on Vitamin D and the CDC VDSCP
What is Vitamin D?
The biologically active form of vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) is a hormone whose main function is to keep serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations in blood within normal ranges.
In patient care and public health assessments, vitamin D is defined as the sum of 25-hydroxyergocalciferol (25-hydroxyvitamin D2) and calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3). Our bodies convert both compounds to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Levels of 25-hydroxyergocalciferol and calcifediol in blood describe a person's vitamin D status.
How is vitamin D status assessed?
Blood tests for assessing a person's vitamin D status measure two forms: 25-hydroxyergocalciferol (25-hydroxyvitamin D2) and calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3). These reflect the cumulative effects of exposure to sunlight and dietary intake of vitamin D--the two ways people get vitamin D. Clinicians use the tests to determine one's vitamin D status.
What Does the Vitamin D Reference Method Laboratory Do?
CDC's Vitamin D Reference Laboratory uses a highly accurate and precise reference method for measuring 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (total 25-hydroxyvitamin D). It uses this reference method to assign reference values to serum samples.
What is the Vitamin D Standardization-Certification Program?
CDC's Vitamin D Standardization-Certification Program evaluates the accuracy and reliability of vitamin D tests using well-established procedures. We certify those that have a certain level of accuracy and precision.
- 1Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. 2016. Arthritis, osteoporosis, and chronic back conditions. In: Healthy People 2020. Washington, DC [accessed 2017 May 18]. Available from https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topics-objectives/topic/Arthritis-Osteoporosis-and-Chronic-Back-Conditions.
