Preventing Zika Virus in Puerto Rico: Maternal Use of Protective Measures
Background
Zika virus (Zika) is primarily spread by the bite of a mosquito infected with the virus, but can also be passed during sex from a person infected with Zika to his or her sexual partner. Because the mosquitoes that spread Zika are found throughout Puerto Rico, people living on the island who have not already been infected are at risk for infection.1 A pregnant woman with Zika can also pass the virus to her fetus, which can cause microcephaly, brain abnormalities, and other severe birth defects.2
To evaluate whether pregnant women understood how to protect themselves against Zika, the Puerto Rico Department of Health (PRDH) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) worked together to conduct a population-based survey of women who gave birth to a live infant during August—December 2016.
PRAMS—Zika Postpartum Emergency Response Survey (PRAMS-ZPER)
The Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System—Zika Postpartum Emergency Response (PRAMS-ZPER) survey* asked women about their use of recommended measures to prevent Zika virus infection during their pregnancy.
Most ZPER respondents:
- Were somewhat or very worried about getting Zika during their pregnancy (93%)
- Were somewhat or very worried about microcephaly or another Zika-related birth defect in baby (92%)
Although there are no known ways to prevent the adverse effects of Zika during pregnancy, there are several ways pregnant women and their families can protect themselves from Zika.3
CDC Zika Recommendations for Healthcare Providers Caring for Pregnant Women3, 5
| Environmental Protective Measures to Avoid Mosquito Bites | Prevent Zika from mosquito bites during pregnancy:
|
|---|---|
| Personal Protective Measures to Avoid Mosquito Bites |
|
| Measures to Prevent Passing Zika During Sex |
|
Zika Prevention: Preventing Mosquito Bites
Preventing mosquito bites is one way to prevent Zika. Mosquito bites can be prevented by keeping mosquitoes away from homes, using EPA-registered insect repellent and wearing protective clothing.3
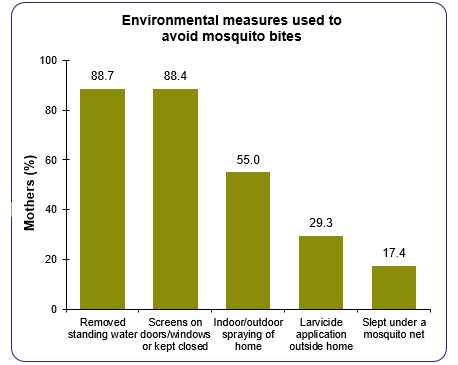
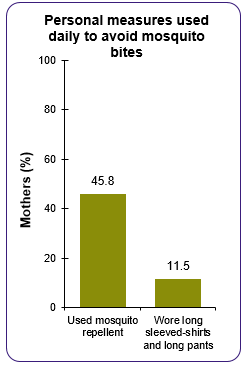
Respondent Reasons for Not Using Mosquito Bite Prevention Strategies
| Reasons women did not wear mosquito repellent | % (95% Confidence Interval) |
|---|---|
| I forgot to apply/reapply it |
51.4 (49.4-53.4) |
| I did not like the way it smelled |
18.8 (17.3-20.4) |
| I worried about the chemicals in the repellent harming my baby |
15.3 (13.9-16.9) |
| I did not like the way it made my skin feel |
11.8 (10.6-13.1) |
| I worried about the chemicals in the repellent harming me |
5.8 (4.9-6.8) |
| I was indoors |
2.7 (2.1-3.5) |
| Mosquito repellent was too expensive |
2.5 (1.9-3.2) |
| I have an allergy |
1.4 (1.0-1.8) |
| Some other reason |
7.9 (6.9-9.0) |
| Reasons women did not wear long sleeves and pants | % (95% Confidence Interval) |
|---|---|
| It was too hot to wear long sleeves or long pants |
76.4 (74.7-78.0) |
| My clothes with long sleeves or long pants no longer fit because of pregnancy |
19.7 (18.1-21.3) |
| I did not have clothes with long sleeves or long pants |
4.7 (4.0-5.7) |
| I was indoors |
2.1 (1.6-2.8) |
| Some other reason |
5.3 (4.5-6.2) |
Zika Prevention: Avoiding Sexual Transmission
Zika can be spread through sex, even when the person with Zika does not have symptoms.4 Pregnant women and their partners should use condoms from start to finish every time during vaginal, anal, and oral sex and the sharing of sex toys, or they should abstain from sex during the pregnancy.6 Most respondents (80%) reported being sexually active during pregnancy.
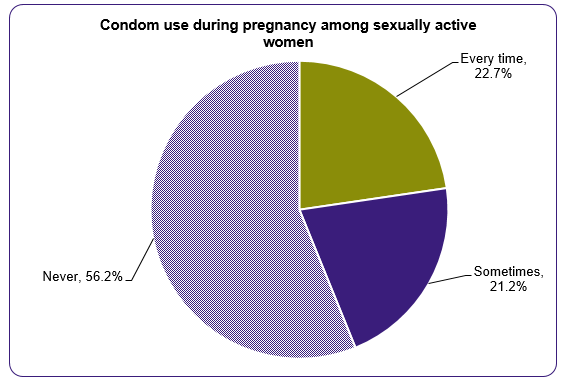
Respondent Reasons for Not Using Strategies to Prevent Sexual Transmission
| Reasons for not using condoms every time when having sex** | % (95% Confidence Interval) |
|---|---|
| I didn’t think my partner had Zika virus | 37.4 (35.0-39.9) |
| I didn’t think I needed to use condoms during pregnancy | 31.8 (29.5-34.3) |
| I didn’t want to use condoms | 20.1 (18.2-22.2) |
| I forgot to use condoms | 12.2 (10.6-13.9) |
| My partner didn’t want to use condoms | 11.0 (9.5-12.7) |
| I didn’t know you could get Zika virus from having sex | 7.3 (6.0-8.9) |
| I didn’t think a condom would prevent Zika infection | 4.7 (3.7-6.0) |
| I was not worried about getting the Zika virus | 3.1 (2.3-4.2) |
| I could not get condoms when I needed them | 2.3 (1.7-3.2) |
| Allergy | 2.1 (1.5-3.0) |
| I could not afford condoms | 1.6 (1.0-2.4) |
| Some other reason | 7.1 (6.0-8.5) |
Summary of Maternal Use of Protective Measures
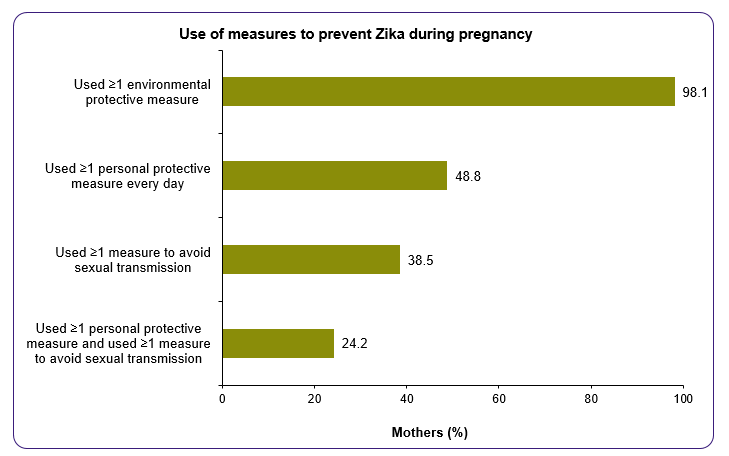
Public Health Action
- Prevention messaging that focuses on reminders to use EPA-registered insect repellent and the safety of repellent use during pregnancy could be helpful, as less than 50% of women reported daily use of insect repellent during pregnancy and few reported wearing protective clothing daily.
- Evaluation of counseling, messaging, and barriers to adhering to recommendations about preventing sexual transmission of Zika are needed to ensure that risk of Zika virus infection from sex during pregnancy is clearly understood by women and their male partners.
Resources:
*PRAMS-ZPER Results: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/66/wr/mm6622a2.htm?s_cid=mm6622a2_e
Questions About Zika: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/about/questions.html
Prevent Mosquito Bites: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/prevention/prevent-mosquito-bites.html
Sexual Transmission & Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/prevention/protect-yourself-during-sex.html
Zika Virus, Print Resources: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/fs-posters/index.html
References:
- Zika Virus: Overview: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/about/overview.html
- Zika Virus: Transmission & Risks: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/prevention/index.html
- Zika Virus: Protect Yourself & Others: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/prevention/protect-yourself-and-others.html
- Zika Virus: Sexual Transmission & Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/prevention/protect-yourself-during-sex.html
- Zika Virus: Controlling Mosquitos at Home: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/prevention/controlling-mosquitoes-at-home.html
- Zika Virus: Women & Their Partners Trying to Become Pregnant: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/pregnancy/women-and-their-partners.html
For more information on PRAMS go to: https://www.cdc.gov/prams/