Key points
- You can lower your risk of getting liver cancer in several ways.
- Keep a healthy weight and get enough physical activity.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B and tested for hepatitis C.
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol.
- Don't smoke cigarettes.
What it is
Liver cancer is a disease in which cells in the liver grow out of control. The liver is in the upper abdomen near the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, and pancreas. Intrahepatic bile ducts are a network of small tubes that carry bile inside the liver.
The liver does many jobs, including:
- Storing nutrients.
- Removing waste products and worn-out cells from the blood.
- Filtering and processing chemicals in food, alcohol, and medications.
- Producing bile, a solution that helps digest fats and eliminate waste products.
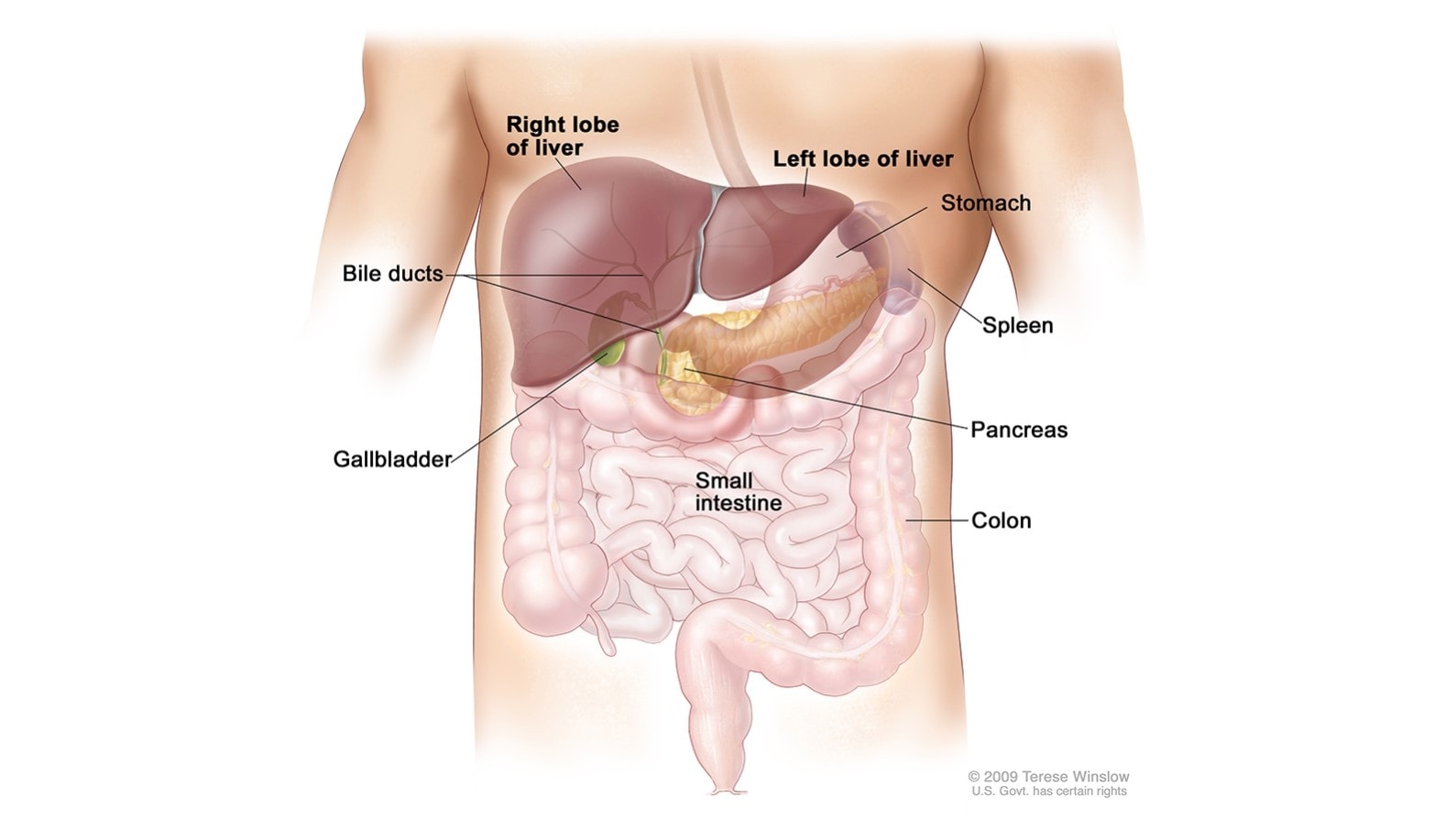
© 2010 Terese Winslow LLC. US government has certain rights. Used with permission. Contact artist at www.teresewinslow.com for licensing.
Symptoms
In its early stages, liver cancer may not have symptoms that can be seen or felt. However, as the cancer grows larger, people may notice one or more of these common symptoms. It's important to remember that these symptoms could also be caused by other health conditions. If you have any of these symptoms, talk to your doctor.
Liver cancer symptoms may include:
- Discomfort in the upper abdomen on the right side.
- A swollen abdomen.
- A hard lump on the right side just below the rib cage.
- Pain near the right shoulder blade or in the back.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes).
- Easy bruising or bleeding.
- Unusual tiredness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss for no known reason.
Risk factors
Behaviors and conditions that increase risk for getting liver cancer are:
- Being overweight or having obesity.
- Having a long-term hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus infection.
- Smoking cigarettes.
- Drinking alcohol.
- Having cirrhosis (scarring of the liver, which can also be caused by hepatitis and alcohol use).
- Having nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (extra fat in the liver that is not caused by alcohol).
- Having diabetes.
- Having hemochromatosis, a condition in which the body takes up and stores more iron than it needs.
- Eating foods that have aflatoxin (a fungus that can grow on foods, such as grains and nuts that have not been stored properly).
I Have Liver Cancer, But You Don't Have To
Reducing risk
You can lower your risk of getting liver cancer in the following ways:
- Keep a healthy weight and get enough physical activity.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Get tested for hepatitis C, and get medical care if you have it.
- Don't smoke, or quit if you do.
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol.
Statistics
The Data Visualizations tool makes it easy for anyone to explore and use the latest official federal government cancer data from United States Cancer Statistics. It includes the latest cancer data covering the US population.
- Cancer Statistics At a Glance: See rates or numbers of new liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancers, or cancer deaths, for the entire United States and individual states. Also, see the top 10 cancers for men and women.
- Cancers by Age, Sex, Race, and Ethnicity: See rates or numbers of new liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancers, or cancer deaths, by race and ethnicity, sex, and age group.
- Trends: See how the rates of new liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancers or cancer deaths changed over time for the entire United States and individual states.
Comprehensive cancer control projects
Many comprehensive cancer control plans include liver cancer prevention. Several National Comprehensive Cancer Control Program (NCCCP) recipients have joined projects related to liver cancer prevention. For example:
- People who inject drugs are at higher risk of getting hepatitis C and hepatitis B through use of shared equipment. CDC conducted a project to increase awareness of the link between injecting drugs and getting hepatitis and liver cancer. Four NCCCP recipients participated.
- In 2019, the NCCCP funded a project to reduce liver, cervical, and skin cancer. The Pennsylvania Comprehensive Cancer Control Program developed materials to educate patients and health care providers about hepatitis B and C screening and hepatitis B vaccination.
Resources
- Liver and Bile Duct Cancer (National Cancer Institute)
- Video: Hepatitis and Liver Cancer Statistics (National Cancer Institute)
- Alcohol and Cancer (CDC)
- Viral Hepatitis and Liver Cancer Prevention Profiles
