National Health Interview Survey
NCHS Fact Sheet, December 2020
About NCHS
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) is the nation’s principal health statistics agency, providing data to identify and address health issues. NCHS compiles statistical information to help guide public health and health policy decisions.
Collaborating with other public and private health partners, NCHS uses a variety of data collection mechanisms to obtain accurate information from multiple sources. This process provides a broad perspective to help understand the population’s health, influences on health, and health outcomes.
National Health Interview Survey
The National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) provides information on the health of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population through confidential interviews conducted in households. NHIS is one of the nation’s largest in-person household health surveys. It provides data for analyzing health trends and tracking progress toward achieving national health objectives.
These data, continuously collected throughout the year, are also used for epidemiological and policy analysis, such as characterizing those with various health conditions, determining barriers to accessing and using appropriate health care, and evaluating federal health programs.
Major health topics addressed
The NHIS questionnaire was redesigned in 2019 to increase relevance, enhance data quality, and minimize respondent burden. Topics covered in 2020 include:
- Physical and mental health status
- Chronic conditions, including asthma and diabetes
- Measures of functioning and disability
- Access to and use of health care services
- Health insurance coverage and type of coverage
- Chronic pain, pain management, and prescription opioid use
- Demographics and social determinants of health
Examples of NHIS data
Mental health
Data from 2019 on symptoms of anxiety and depression in adults show:
- The percentage of adults aged 18 and over who experienced mild, moderate, or severe symptoms of anxiety in the past 2 weeks was 9.5%, 3.4%, and 2.7%, respectively.
- The percentage of adults aged 18 and over who experienced any severity of symptoms of anxiety in the past 2 weeks decreased with age, were higher among women (19.0%) than men (11.9%), and were higher among non-Hispanic white adults (16.5%) compared with non-Hispanic black (14.6%), Hispanic (14.5%), and non-Hispanic Asian (8.5%) adults.
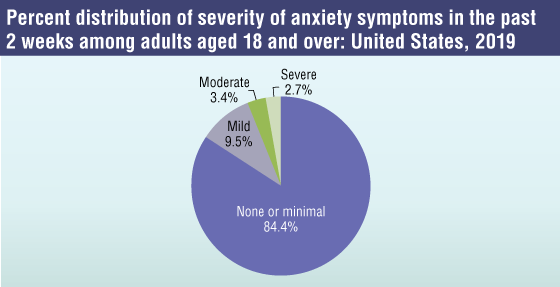
NOTES: Severity of anxiety symptoms was based on the seven-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale (GAD–7) and summarized into none or minimal (values 0–4), mild (values 5–9), moderate (values 10–14), and severe (values 15–21). Estimates are based on household interviews of a sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized population.
SOURCE: National Center for Health Statistics, National Health Interview Survey, 2019.
- The percentage of adults aged 18 and over who experienced mild, moderate, or severe symptoms of depression in the past 2 weeks was 11.5%, 4.2%, and 2.8%, respectively.
- Non-Hispanic white (19.3%) and non-Hispanic black (19.3%) adults were the most likely to have experienced any severity of depression symptoms in the past 2 weeks, followed by Hispanic adults (16.9%), while non-Hispanic Asian adults (10.2%) were least likely.
Data from 2019 on mental health treatment among school-aged children and adults show:
- Children aged 12–17 years were more likely to have taken prescription medication, received counseling or therapy from a mental health professional, or both (16.8%) in the past 12 months compared with children aged 5–11 years (10.8%).
- In 2019, 19.2% of adults aged 18 and over had taken prescription medication for their mental health, received counseling or therapy from a mental health professional, or both in the past 12 months.
Health insurance
Data from 2019 show:
- An estimated 33.2 million persons of all ages (10.3%) were uninsured at the time of interview. In the second half of 2019, 35.7 million persons of all ages (11.0%) were uninsured—significantly higher than the first 6 months of 2019 (30.7 million, 9.5%).
- Among adults aged 18–64, Hispanic adults (29.7%) were more likely than non-Hispanic black (14.7%), non-Hispanic white (10.5%), and non-Hispanic Asian (7.5%) adults to be uninsured.
- Among adults aged 18–64, 4.4% (8.7 million) were covered by private health insurance plans obtained through the Health Insurance Marketplace or state-based exchanges.
Other NHIS data from 2019
- The percentage of adults aged 18 and over who were current cigarette smokers was 14.2%.
- The percentage of adults aged 18 and over who were current electronic cigarette users was 4.4%.
- The percentage of adults aged 18 and over who did not get needed medical care due to cost in the past 12 months was 8.3%.
- The percentage of adults aged 18 and over who did not take medication as prescribed to save money in the past 12 months was 9.7%.
Challenges and future opportunities
- Ensure minimal disruptions to interviewing due to COVID-19 by conducting more interviews by telephone, where possible
- Prepare and release the 2020 public-use data files in 2021
- Plan and launch two pilot studies to modernize NHIS with the addition of new modes of data collection: In-home examinations for blood samples and anthropomorphic measurement, and online surveys for adolescent self-response (NHIS-Teen)
- Design and implement new systems to manage metadata from NHIS for quality assurance, improved documentation, and development of searchable online catalogues
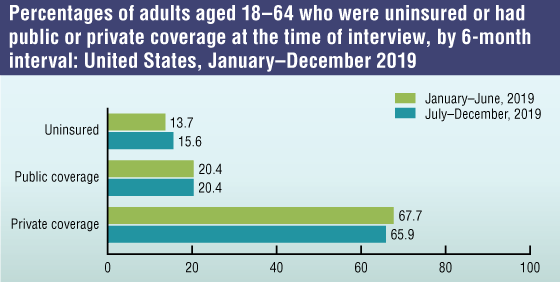
NOTES: Persons were defined as uninsured if they did not have any private health insurance, Medicare, Medicaid, Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), state-sponsored or other government plan, or military plan. Persons were also defined as uninsured if they had only Indian Health Service coverage or had only a private plan that paid for one type of service, such as accidents or dental care. Public coverage includes Medicaid, CHIP, state-sponsored or other government-sponsored health plan, Medicare, and military plans. Private coverage includes any comprehensive private insurance plan (including health maintenance and preferred provider organizations). These plans include those obtained through an employer, purchased directly, purchased through local or community programs, or purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplace or a state-based exchange. Private coverage excludes plans that pay for only one type of service, such as accidents or dental care. A small number of persons were covered by both public and private plans and were included in both categories. Data are based on household interviews of a sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized population.
SOURCE: National Center for Health Statistics, National Health Interview Survey, 2019.
For more information about NCHS, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/.
For more information about NHIS, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.htm.