2021 Annual Report for the Emerging Infections Program for Clostridioides difficile Infection
2021 Annual Report Print Version [PDF – 7 Pages]
Surveillance data from 2021 represent the eleventh year of population-based surveillance for CDI conducted among all 10 Emerging Infections Program sites. The crude overall incidence rate of CDI in 2021 was 110.2 cases per 100,000 persons, with a slightly higher incidence of community associated cases (55.9 cases per 100,000 persons) compared with healthcare-associated cases (54.3 cases per 100,000 persons). The incidence rate of CDI increased with age and was higher in women than in men and higher in White persons than in persons of other races.
Underlying conditions were commonly reported among CDI cases, with 41 percent having a Charlson comorbidity index of ≥2. Antibiotic use in the prior 12 weeks was reported for 61 percent of CDI cases. Eighty-five percent of CDI cases were treated, with vancomycin being the most common treatment given. CDI-related complications, such as toxic megacolon and ileus, were rare.
California (1 county San Francisco area), Colorado (5 county Denver area); Connecticut (1 county New Haven area); Georgia (8 county Atlanta area); Maryland (9 Eastern Shore and 2 western counties); Minnesota (5 counties); New Mexico (1 county Albuquerque area); New York (1 county Rochester area); Oregon (1 rural county); and Tennessee (1 county Nashville area).
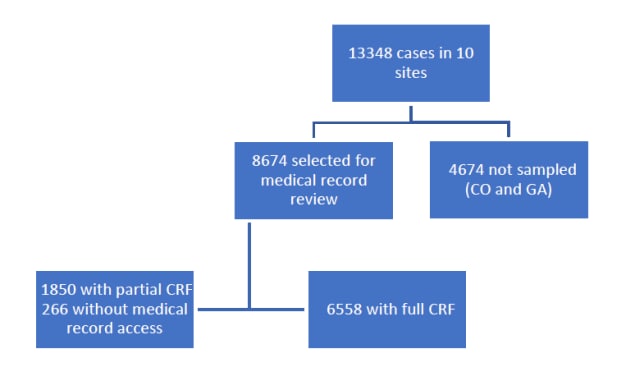
Case finding was active, laboratory-based, and population-based. Laboratories serving the surveillance catchment areas reported positive C. difficile tests to EIP staff and were routinely audited with a goal of complete case ascertainment. An initial chart review was performed on all CDI cases in eight EIP sites and on all pediatric cases and a 1/3 random sample of cases age 18 years and older in the two remaining EIP sites with the largest surveillance catchment areas (CO and GA). A subsequent comprehensive chart review was performed on all community-onset cases and a subset of healthcare-facility onset cases.
A standardized case report form (CRF) was completed for each incident case through review of medical records. Inpatient and outpatient medical records were reviewed for information on patient demographics, clinical syndrome, outcome of illness, and relevant healthcare exposures.
A convenience sample of stool specimens or swabs was sent to reference laboratories for C. difficile isolation. Recovered isolates were sent to CDC for molecular typing and characterization.
A CDI case was classified as community-associated (CA) if the C. difficile-positive stool specimen was collected on an outpatient basis or within 3 days after hospital admission in a person with no documented overnight stay in a healthcare facility in the preceding 12 weeks. All CDI cases that did not meet the aforementioned criteria were classified as healthcare-associated (HA). HA cases with disease onset outside of a healthcare facility but with documented overnight stay in a healthcare facility in the preceding 12 weeks were classified as community-onset, healthcare-facility associated (CO-HCFA). HA cases with disease onset in a healthcare facility were classified as healthcare-facility onset (HCFO). HCFO cases were further classified into hospital onset or long-term care facility onset. Incidence rates were calculated using US Census population estimates.
CDI surveillance data undergo regular data cleaning to ensure accuracy and completeness. Patients with case data as of 05/26/2023 were included in this analysis. Because data can be updated as needed, analyses of datasets generated on a different date may yield slightly different results.
| Sex | Population ≥1 Year of Age | Community Associated CDIa No.c | Community Associated CDIa Incidenceb | Healthcare Associated CDIa No.c | Healthcare Associated CDIa Incidenceb | All CDI No.c | All CDI Incidenceb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 5,952,832 | 2478 | 41.6 | 3099 | 52.1 | 5577 | 93.7 |
| Female | 6,156,889 | 4291 | 69.7 | 3480 | 56.5 | 7771 | 126.2 |
| Age Group | Population ≥1 Year of Age | Community Associated CDIa No.c | Community Associated CDIa Incidenceb | Healthcare Associated CDIa No.c | Healthcare Associated CDIa Incidenceb | All CDI No.c | All CDI Incidenceb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-17 years | 2,506,710 | 418 | 16.7 | 178 | 7.1 | 596 | 23.8 |
| 18-44 years | 4,728,721 | 1668 | 35.3 | 839 | 17.7 | 2507 | 53.0 |
| 45-49 years | 764,997 | 336 | 43.9 | 301 | 39.4 | 637 | 83.3 |
| 50-54 years | 794,283 | 494 | 62.1 | 373 | 47.0 | 867 | 109.2 |
| 55-59 years | 780,720 | 545 | 69.8 | 540 | 69.2 | 1085 | 139.0 |
| 60-64 years | 732,551 | 651 | 88.9 | 700 | 95.5 | 1351 | 184.4 |
| 65-70 years | 613,116 | 599 | 97.7 | 744 | 121.4 | 1343 | 219.0 |
| 70-74 years | 499,997 | 711 | 142.3 | 881 | 176.2 | 1592 | 318.4 |
| 75-79 years | 310,774 | 555 | 178.7 | 773 | 248.7 | 1328 | 427.3 |
| 80+ years | 377,852 | 793 | 209.9 | 1249 | 330.6 | 2042 | 540.4 |
| Racea | Population ≥1 Year of Age | Community Associated CDIa No.c | Community Associated CDIa Incidenceb | Healthcare Associated CDIa No.c | Healthcare Associated CDIa Incidenceb | All CDI No.c | All CDI Incidenceb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 8,022,836 | 5292 | 66.0 | 4680 | 58.3 | 9972 | 124.3 |
| Other | 4,086,885 | 1477 | 36.1 | 1899 | 46.5 | 3376 | 82.6 |
| Total | Population ≥1 Year of Age | Community Associated CDIa No.c | Community Associated CDIa Incidenceb | Healthcare Associated CDIa No.c | Healthcare Associated CDIa Incidenceb | All CDI No.c | All CDI Incidenceb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Cases | 12,109,721 | 6769 | 55.9 | 6579 | 54.3 | 13348 | 110.2 |
a The epidemiologic classification was statistically imputed for 3% of the CDI cases selected for medical record review, and race was statistically imputed for 15% of the CDI cases selected for medical record review. The weighted frequency of cases in Colorado and Georgia was based on 33% random sampling for cases aged ≥18 years.
b Cases per 100,000 persons.
c Subcategories may not add to total due to rounding.
| Diagnostic assay | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Toxin positive | 4140 | 31 |
| Nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) positive/toxin negative | 4465 | 33 |
| NAAT positive/toxin result unknowna | 4742 | 36 |
| Unspecified assay | 1 | <1 |
a Includes cases diagnosed mainly by NAAT or multiplex PCR panel (i.e., toxin enzyme immunoassay or cell cytotoxicity assay was not performed) or by NAAT as part of a multistep algorithm where the toxin result was not readily known
| Epidemiologic classification | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital onset | 1710 | 13 |
| LTCF onset | 633 | 5 |
| COHCFA | 1773 | 13 |
| CA | 4292 | 32 |
| Unknowna | 4940 | 37 |
a Includes 4674 non-sampled cases
| Race/Ethnicity | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Hispanic, any race | 893 | 7 |
| Not known to be Hispanica – Whiteb | 6446 | 48 |
| Not known to be Hispanica – Black or African Americanc | 2107 | 16 |
| Not known to be Hispanica – Asiand | 322 | 2 |
| Not known to be Hispanica – Other or multiple racese | 118 | <1 |
| Non-Hispanic- Unknown race | 225 | 2 |
| Unknown ethnicity and race | 3237 | 24 |
a Records either indicated ethnicity was non-Hispanic, or ethnicity was not known
b 531 cases with unknown ethnicity
c 99 cases with unknown ethnicity
d 47 cases with unknown ethnicity
e American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, or ≥2 races reported; 11 cases with unknown ethnicity
| Location of patient before incident specimen collection | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Private residence | 5970 | 69 |
| Long-term care facility | 650 | 7 |
| Acute-care hospital (inpatient) | 1633 | 19 |
| Long-term care acute care hospital | 45 | <1 |
| Homeless | 96 | 1 |
| Incarcerated | 7 | <1 |
| Other | 7 | <1 |
| Unknown | 266 | 3 |
| Location of incident specimen collection | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Outpatient setting or emergency department | 4370 | 50 |
| Acute care hospital | 3566 | 41 |
| Long-term care facility | 428 | 5 |
| Long-term acute care hospital | 39 | <1 |
| Other | 3 | <1 |
| Unknown | 268 | 3 |
| Clinical characteristic | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Charlson comorbidity index – 0 | 2642 | 40 |
| Charlson comorbidity index – 1 | 1254 | 19 |
| Charlson comorbidity index – ≥2 | 2662 | 41 |
| Underlying conditions – Cardiovascular diseasea,b | 1382 | 21 |
| Underlying conditions – Diabetes mellitusa | 1407 | 21 |
| Underlying conditions – Chronic pulmonary diseasea,c | 1419 | 22 |
| Underlying conditions – Gastrointestinal diseasea,d | 1665 | 25 |
| Underlying conditions – Gastrointestinal disease – Diverticular diseasea | 747 | 11 |
| Underlying conditions – Gastrointestinal disease – Inflammatory bowel diseasea | 453 | 7 |
| Underlying conditions – Gastrointestinal disease – Peptic ulcer diseasea | 174 | 3 |
| Underlying conditions – Gastrointestinal disease – Short gut syndromea | 20 | <1 |
| Underlying conditions – Gastrointestinal disease – Liver diseasea | 439 | 7 |
| Underlying conditions – Chronic renal diseasea | 1241 | 19 |
| Underlying conditions – Neurologic condition, anya | 1309 | 20 |
| Underlying conditions – Malignancy (hematologic or solid organ)a | 1121 | 17 |
| Underlying conditions – Transplant (hematopoietic stem cell or solid organ)a | 205 | 3 |
| Positive test for SARS-CoV-2 during hospitalization and on or before date of incident specimen collectione | 95 | 3 |
a Underlying conditions are not mutually exclusive
b Defined as myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, congenital heart disease, stroke, transient ischemic attack, or peripheral vascular disease
c Defined as cystic fibrosis or any chronic respiratory condition resulting in symptomatic dyspnea
d Defined as diverticular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, peptic ulcer disease, short gut syndrome, or liver disease
e Among patients in the hospital on the date of incident specimen collection (N=2666). Excludes patients who were admitted to the hospital after the date of incident specimen collection. A positive SARS-CoV-2 test was defined as any positive viral test for SARS-CoV-2, including antigen and nucleic acid amplification tests.
| Healthcare Exposurea | CA (N=4292), N |
CA (N=4292), % |
COHCFA (N=1773), N |
COHCFA (N=1773), % |
HCFO (N=493), N |
HCFO (N=493), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute care hospitalization | 0 | 0 | 1734 | 98 | 244 | 49 |
| Long-term care facility residence | 0 | 0 | 187 | 11 | 178 | 36 |
| Long-term acute care hospitalization | 0 | 0 | 7 | <1 | 9 | 2 |
| Surgery | 196 | 5 | 491 | 28 | 125 | 25 |
| Emergency room | 881 | 21 | 740 | 42 | 142 | 29 |
| Observation unit | 69 | 2 | 103 | 6 | 17 | 3 |
| Chronic dialysis | 106 | 2 | 163 | 9 | 51 | 10 |
a Healthcare exposure categories are not mutually exclusive.
| Antibiotica | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Any antibiotic | 4005 | 61 |
| Aminoglycosides | 86 | 1 |
| Beta-lactam / beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations | 1283 | 20 |
| Carbapenems | 164 | 3 |
| Cephalosporins | 2062 | 31 |
| Clindamycins | 464 | 7 |
| Fluoroquinolones | 806 | 12 |
| Glycopeptides | 1179 | 18 |
| Macrolides | 262 | 4 |
| Monobactam | 16 | <1 |
| Penicillins | 386 | 6 |
| Trimethoprim or Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 366 | 6 |
| Tetracyclines | 276 | 4 |
| Other antibiotic | 1155 | 18 |
a Antibiotic use categories are not mutually exclusive.
| Treatmenta | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Any treatmentb | 5604 | 85 |
| Oral or rectal vancomycin (excluding vancomycin tapers)c | 4724 | 72 |
| Vancomycin tapers | 390 | 6 |
| Metronidazole | 1079 | 16 |
| Fidaxomicin | 409 | 6 |
| Bezlotoxumab | 25 | <1 |
| Stool transplant | 33 | <1 |
a Treatment categories are not mutually exclusive.
b Includes any course of CDI antibiotic therapy, bezlotoxumab, or stool transplant.
c Includes 3 patients receiving vancomycin prophylaxis after treatment of incident CDI.
| Outcome | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Toxic megacolona | 18 | <1 |
| Ileusa | 156 | 2 |
| Pseudomembranous colitisa | 32 | <1 |
| White blood cell count (WBC) >= 15,000/µla | 1107 | 17 |
| Recurrent infectiona | 758 | 12 |
| Hospitalization on the day of or within 6 days after the date of incident specimen collectiona,b | 2868 | 44 |
| ICU admission one day before, the day of, or within 6 days after the date of incident specimen collectiona | 384 | 6 |
| In-hospital deatha | 177 | 3 |
| Discharge location after acute-care hospitalization among patients who survivedc – Private Residence | 2184 | 81 |
| Discharge location after acute-care hospitalization among patients who survivedc – Long-term care facility | 401 | 15 |
| Discharge location after acute-care hospitalization among patients who survivedc – Long-term acute care hospital | 12 | <1 |
| Discharge location after acute-care hospitalization among patients who survivedc – Other | 75 | 3 |
| Discharge location after acute-care hospitalization among patients who survivedc – Unknown | 19 | <1 |
a Outcomes, except for location of discharge from acute care hospitalization, are not mutually exclusive.
b Data include 345 cases considered to be hospital-onset
c N=2691
This section will be updated once the data are available.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023. Emerging Infections Program, Healthcare-Associated Infections – Community Interface Surveillance Report, Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI), 2021 [PDF – 7 Pages]. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hai/eip/pdf/cdiff/2021-CDI-Report-H.pdf [PDF – 7 Pages].
- Clostridioides difficile Infection (CDI) Tracking https://www.cdc.gov/hai/eip/cdiff-tracking.html
- Healthcare-Associated Infections – Community Interface Data Visualization (HAICViz) https://www.cdc.gov/hai/eip/haicviz.html
- Clostridioides difficile Infection https://www.cdc.gov/hai/organisms/cdiff/Cdiff_infect.html