Visit the COVID-19 and HIV page for the latest updates on the novel coronavirus outbreak and HIV.

About the Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S. Initiative
Launched in 2019 and led by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S. (EHE) is an ambitious multi-agency and whole-of-society initiative to reduce new HIV infections in the United States by 90% by 2030.
EHE increases the nation’s investment in proven HIV prevention tools and newer innovative technologies and programs, while ensuring they reach the communities and populations most affected by HIV. EHE also complements the National HIV/AIDS Strategy, which provides a roadmap for a whole-of-society response to ending the HIV epidemic and reducing HIV-related disparities and health inequities.
Approach
EHE is rooted in equity and focused on implementing community-specific strategies, due to the critical role community-based organizations continue to play in providing HIV services to people who need them. A portion of recipient funding must support activities implemented by community-based organizations. Each health department that receives EHE funding is required to develop a unique implementation plan for their jurisdiction that includes community-driven, locally tailored, and equity-centered solutions for reducing HIV transmissions. These plans require that recipients develop strategies that promote health equity and programs that consider social determinants of health. CDC encourages the adoption of status neutral approaches that offer HIV prevention and treatment as part of comprehensive care, which include the provision of culturally affirming, holistic, and stigma-free services.
Jurisdictions
Stopping HIV transmission starts at the local level, which is why EHE provides resources to 50 local areas where more than half of new HIV diagnoses occur (48 counties; Washington, D.C.; and San Juan, Puerto Rico) and seven states with a substantial rural burden.
CDC funds and closely collaborates with these communities to accelerate progress by identifying and implementing innovative methods for delivering HIV prevention and care, building local infectious disease control capacity, and scaling up high-impact activities in areas hardest hit by HIV.
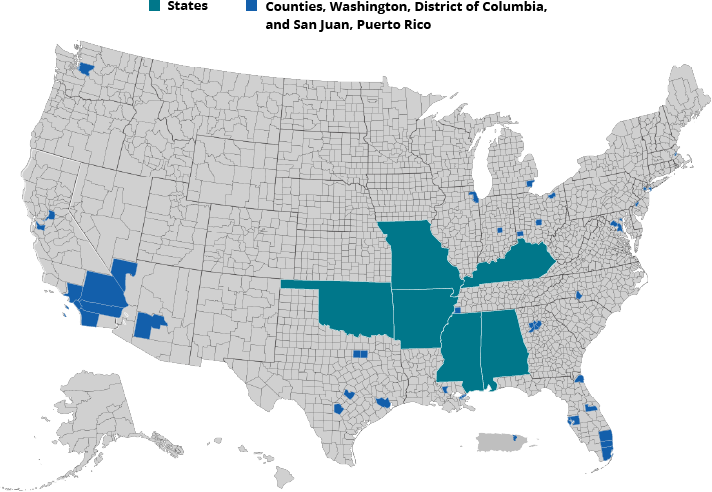
Counties*
Arizona
- Maricopa County
California
- Alameda County
- Los Angeles County
- Orange County
- Riverside County
- Sacramento County
- San Bernadino County
- San Diego County
- San Francisco County
Florida
- Broward County
- Duval County
- Hillsborough County
- Miami-Dade County
- Orange County
- Palm Beach County
- Pinellas County
Georgia
- Cobb County
- DeKalb County
- Fulton County
- Gwinnett County
Illinois
- Cook County
Indiana
- Marion County
Louisiana
- East Baton Rouge Parish
- Orleans Parish
Maryland
- Baltimore City
- Montgomery County
- Prince George’s County
Massachusetts
- Suffolk County
Michigan
- Wayne County
Nevada
- Clark County
New Jersey
- Essex County
- Hudson County
New York
- Bronx County
- Kings County
- New York County
- Queens County
North Carolina
- Mecklenburg County
Ohio
- Cuyahoga County
- Franklin County
- Hamilton County
Pennsylvania
- Philadelphia County
Tennessee
- Shelby County
Texas
- Bexar County
- Dallas County
- Harris County
- Tarrant County
- Travis County
Washington
- King County
Washington, D.C.
Territories*
Puerto Rico
- San Juan Municipio
States**
- Alabama
- Arkansas
- Kentucky
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Oklahoma
- South Carolina
* 2016-2017 data was used to identify these jurisdictions.
** States where 10% or more of new diagnoses in 2016 and 2017 were in rural areas (less than 50,000 population); at least 75 total new diagnoses statewide; and the state did not have a priority county.

America’s HIV Epidemic Analysis Dashboard (AHEAD) supports EHE by tracking data on six annual HIV indicators used to measure progress toward reaching EHE goals: HIV incidence, knowledge of HIV status, diagnoses, linkage to HIV medical care, viral suppression, and PrEP coverage. CDC’s National HIV Surveillance System provides the data for five of the six core indicators. The sixth core indicator, PrEP coverage, is calculated using several different data sources.
Go to AHEAD