How to Participate in CDC’s AR Lab Network: Lab Testing

Summary of Lab Tests
Detailed Testing Information for Submission
- Colonization Screening for CPOs
- Isolate Testing for CRE and CRPA
- Expanded AST
- Targeted Surveillance Testing of Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumanii
- Testing Types for Resistance Candida Species
- S. pneumoniae Isolate Testing
- Testing for Azole resistance in A. fumigatus Isolates
- Etest of N. gonorrhoeae to Support Clinical Management
U.S. healthcare and clinical labs should work with their local or state public health department to submit isolates or specimens for testing. The public health lab should work with their regional lab. Labs will also work with CDC.
Summary of Lab Tests
The following information is a summary of testing offered through the AR Lab Network, including:
Find Detailed Testing Information for Submission further below on webpage for specifics.
- Acinetobacter baumannii
- Aspergillus fumigatus
- Candida, including C. auris
- CRE
- CRPA
- Clostridioides difficile
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Salmonella (via Pulsenet)
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Colonization Screening
- Some people can carry germs without becoming sick or showing symptoms, known as colonization; people who are colonized can spread the germs to others without knowing it
- When unusual resistance is identified in a patient, healthcare workers use lab tests to screen, or look at, other patients to see if they are colonized with the same resistant germ, which can prompt additional infection control actions
Identification of Pathogens
- Labs identify and confirm the genus and species of resistant germs through one of two methods:
- Biochemical tests: Classifying a particular species by the way it uses different biological chemicals, like proteins or sugars
- Mass spectrometry: A specialized technique that looks for a pathogen’s protein “fingerprint”
Molecular Testing
- A collection of techniques used to detect specific genes within a germ, including those that have and can share resistance
- These tests can be used to diagnose infections and guide treatment for patients
Phenotypic Carbapenemase Test
- Uses culture to determine if the pathogen produces an enzyme called carbapenemase
- If carbapenemase is produced, then a carbapenem antibiotic will not kill the pathogen
AST
- A type of lab test that grows the pathogen to show how sensitive a germ is to different antibiotics
- These tests can be used to help select the best drug choice for an antibiotic-resistant infection, and also provide data to monitor how a pathogen’s resistance profile might change over time
WGS
- A laboratory procedure that provides a very precise DNA fingerprint that can help link cases to one another, allowing an outbreak to be detected and solved sooner.
Isolate Testing for CRE or CRPA
- Testing performed by: 56 state and local jurisdictions, including seven regional labs
- Testing includes:
- Detect carbapenemases in CRE/CRPA isolates
- Identify the resistance mechanism(s)
- Perform AST
Core Testing
- Testing performed by: Seven regional labs
- Testing includes:
- Molecular testing to detect colonization of CPO, including CRE
- Fungal susceptibility of Candida species to identify emerging resistance
- Identification and colonization screening to detect and help prevent spread of C. auris
- Detection and characterization of emerging threats and concerning threats, like mcr-1 and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, and ability to detect changes to known threats, like MRSA
- Perform expanded susceptibility testing to include pan-resistant bacteria to new antibiotics
Additional Testing
- Testing performed by: Select regional labs and the National TB Center to support nationwide needs
- Testing includes:
- C. difficile special projects
- Enhanced detection of drug-resistant N. gonorrhoeae using antimicrobial susceptibility testing, including E-tests, and WGS
- AST and serotyping of multidrug-resistant S. pneumoniae
- Perform WGS for all isolates of M. tuberculosis
- Screen for azole-resistant A. fumigatus
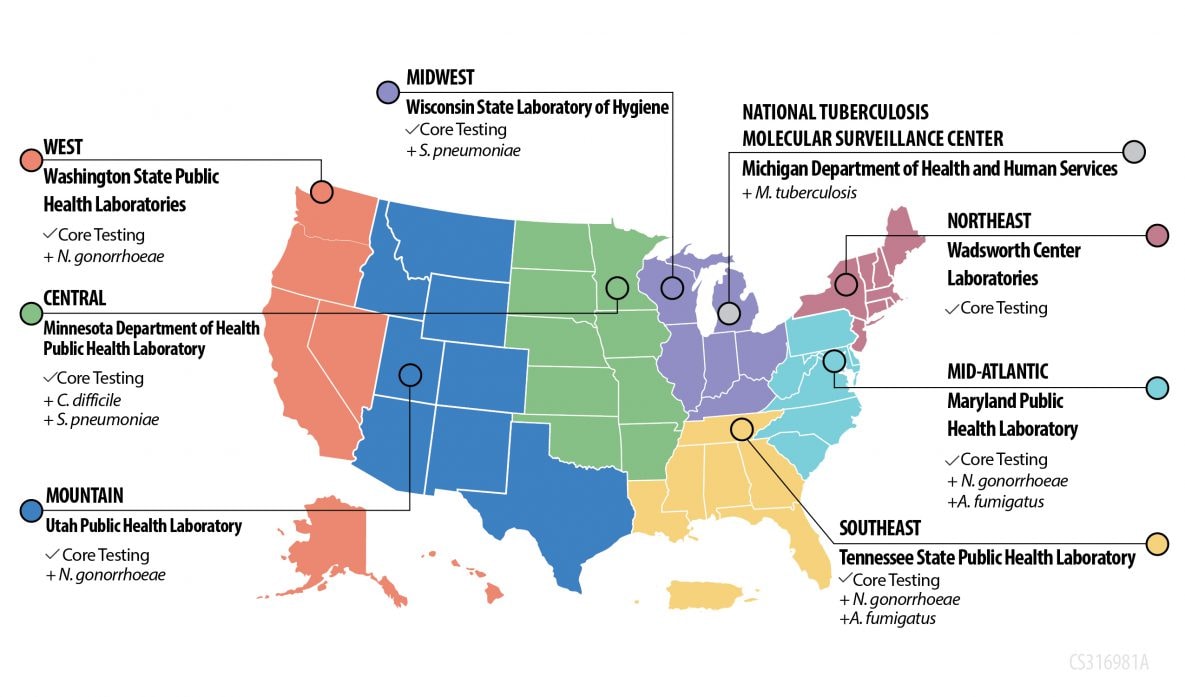
All AR Lab Network regional labs perform Core Testing and select labs perform Additional Testing to support nationwide needs.
Central: Minnesota Department of Health Public Health
- Core Testing + Additional Testing for C. difficile, S. pneumoniae
Mid-Atlantic: Maryland Public Health Laboratory
- Core Testing + Additional Testing for N. gonorrhoeae and A. fumigatus
Midwest: Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene
- Core Testing + Additional Testing for S. pneumoniae
Mountain: Utah Public Health Laboratory
- Core Testing + Additional Testing for N. gonorrhoeae
Northeast: Wadsworth Center Laboratories
- Core Testing
Southeast: Tennessee State Public Health Laboratory
- Core Testing + Additional Testing for N. gonorrhoeae and A. fumigatus
West: Washington State Public Health Laboratories
- Core Testing + Additional Testing for N. gonorrhoeae
National Tuberculosis Molecular Surveillance Center: Michigan Department of Health and Human Services
- Additional Testing for M. tuberculosis
Detailed Testing Information for Submission
The following information is for people submitting specimens or isolates, including healthcare providers, laboratories, or healthcare facilities. Contact your local/state health department or regional lab for more information about AR Lab Network testing capabilities (find contact information on the About AR Lab Network webpage).
CPO colonization screening is performed by the AR Lab Network regional labs in collaboration with public health officials (e.g., state HAI coordinator), healthcare facilities, infection preventionists, and epidemiologists, all of whom can request colonization screening of high-risk patients. Detecting CPO colonization helps prevent transmission within and among facilities.
It is free of charge (including shipment of test kits to the collecting facility and specimen shipment back to the regional lab).
- High-risk patients include those who have had contact with another patient diagnosed with a CPO, or patients that have received healthcare in a foreign country in the past six months.
- CPO colonization screening is focused on CRE, CRPA, and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, and is performed using rectal swabs (FDA-approved Cepheid GeneXpert Carba-R test kit) to detect KPC, NDM, OXA-48, VIM, and IMP-1 genes.
- Culture-based screening is used to detect additional variants (i.e., other IMPs circulating in CRE and CRPA and other OXA variants circulating in Acinetobacter).
Rectal swab screening results for Cepheid targets are rapidly returned to the submitting facility, jurisdictional health department, and state public health lab within two business days of specimen receipt. Public health officials are notified within one day if any carbapenemase producer is detected.
Healthcare and clinical labs should submit to public health labs Enterobacterales isolates that are resistant to ertapenem, imipenem, doripenem, or meropenem, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates that are resistant to imipenem, doripenem, or meropenem. The isolates should be:
- Species-identified (e.g., MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry)
- Confirmed as carbapenemase producers using the mCIM or CarbaNP test
- PCR-tested to detect carbapenemase genes (KPC, NDM, VIM, OXA-48, and IMP)
- Antimicrobial susceptibility tested using a broad panel of antibiotics by broth microdilution, Kirby Bauer testing, and/or Etest
Public health laboratories in the AR Lab Network report to the submitting lab or facility the results of the isolate test. The public health labs immediately notify public health officials when novel or emerging resistance is detected (i.e., pan-resistance, rare, or potentially novel carbapenemase genes).
In 2018, CDC’s AR Lab Network piloted a new program called Expanded AST for Hard-to-Treat Infections (Expanded AST), performed by regional labs free of charge. Expanded AST uses adapted inkjet printing technology to “print” AST panels that test new-to-market antibiotics for Enterobacterales isolates resistant to all beta-lactam antibiotics, which can be hard to treat. Expanded AST can help labs and clinicians decide if a new-to-market antibiotic could effectively treat a very resistant infection. Visit the Expanded AST webpage for FAQs and availability information.
Sentinel surveillance sites at healthcare or clinical labs submit isolates to help monitor emerging antibiotic resistance threats like Acinetobacter baumannii that are resistant to carbapenems.
Submit Acinetobacter baumannii isolates that are resistant to imipenem, doripenem, or meropenem using standard susceptibility testing methods (i.e., minimum inhibitory concentrations of ≥8 µg/mL). The isolates should be:
- Species confirmed using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
- Tested for the presence of carbapenemase genes (KPC, NDM, VIM, OXA-48, OXA-23/24/40/58, and IMP) by multiplex PCR
- Tested for antibiotic susceptibility to a broad panel of antibiotics by broth microdilution, Kirby Bauer testing, and/or Etest
The AR Lab Network regional labs share reports with public health officials and notify them within one day of testing if carbapenemase-positive results are found for Acinetobacter baumanii.
The AR Lab Network’s primary focus for antifungal-resistant Candida testing is to confirm suspected C. auris from any specimen site, Candida species (other than C. albicans) from any specimen site (particularly invasive sites), and yeast isolates that could not be identified by the submitting laboratory. AR Lab Network regional labs:
- Confirm Candida species using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
- Perform antifungal susceptibility testing using a CDC-developed, custom broth microdilution panel
- Report confirmed C. auris cases immediately to public health authorities for containment response
- Return aggregate antibiogram data (antifungal susceptibility profiles) to interested facilities upon request
- Provides whole genome sequencing to track and characterize resistance and strengthens epidemiology investigations to contain an outbreak.
The AR Lab Network regional labs also perform C. auris colonization screening free of charge (including shipment of test kits to collecting facility and specimen shipment back to regional lab). Healthcare facilities and public health departments can request C. auris colonization screening of close contacts of an index patient (first patient identified with an infection) or other patient contacts considered to be high-risk (e.g., those requiring mechanical ventilation). C. auris colonization screening is performed using a swab specimen, typically a combined axillary-groin swab.
PCR-based screening results are available within 3 days and returned to the submitting facility, jurisdictional health department, and state public health laboratory. Culture-based screening results are returned in approximately 9 days.
Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene and Minnesota Department of Health Public Health Laboratory serve as AR Lab Network Streptococcus Reference Centers and provide national testing at no cost for S. pneumoniae including:
- Species Identification by phenotypic or molecular methods
- Serotyping/Serogrouping using molecular methods such as conventional and/or real-time PCR or whole-genome sequencing
- Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) by broth microdilution
The AR Lab Network Streptococcus Reference Centers will report identification and serotyping results back to their submitting institutions using secure methods (secure fax, encrypted e-mail, or secure web portal). AST results will be used for surveillance purposes only and will not be reported back to the submitting institution.
Healthcare and clinical labs should submit to public health labs:
- All CSF isolates, regardless of susceptibility test results
- Invasive isolates (sterile body site such as blood) that are non-susceptible for any clinically relevant antibiotic according to current Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute M100 guidance
- Possible failure of therapy or vaccine, or possible outbreak-related isolates
Please contact your state public health lab, Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene, or Minnesota Department of Health Public Health Laboratory for more information on how to submit isolates
AR Lab Network Aspergillus laboratories, Maryland Public Health Laboratory, and Tennessee State Public Health Laboratory perform screening to monitor and track the emergence of A. fumigatus azole resistance in the United States. Testing is available to all states at no cost and includes:
- Species confirmation
- Screening for azole resistance using the agar plating method
- Confirmatory testing via broth microdilution for the following antifungals: posaconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, and isavuconazole
Results will be reported back to submitting institutions within two weeks of receipt of the isolate.
Healthcare and clinical labs should submit:
- All confirmed or suspected A. fumigatus isolates from any specimen source, especially invasive sites, regardless of whether the patient had an invasive infection or was thought to be colonized
- If AFST was done previously, all A. fumigatus isolates with AFST results indicating azole resistance from any body site (invasive or non-invasive, sterile or non-sterile)
- Only submit A. fumigatus or suspected A. fumigatus isolates; do not submit isolates identified as unspecified Aspergillus species or as another Aspergillus species
For more information on how to submit isolates, please contact your state public health laboratory, Maryland Public Health Laboratory, or Tennessee State Public Health Laboratory.
The Maryland Public Health Laboratory and the Washington Public Health Laboratory offer gradient strip AST using Etest (Biomerieux) on N. gonorrhoeae specimens in cases of suspected drug resistance.
The Maryland and Washington Public Health Laboratories will provide AST for four antibiotics (azithromycin, ceftriaxone, cefixime, and ciprofloxacin) and will report Etest AST results back to submitters in 7 to 10 days to help inform patient care. For more information on how to submit isolates, please contact your state public health laboratory, the Maryland Public Health Laboratory , or the Washington Public Health Laboratories.