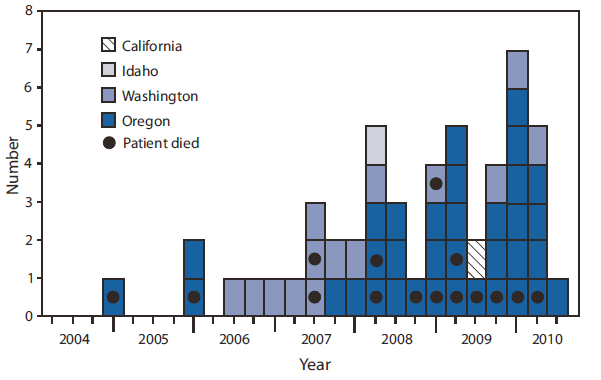
FIGURE. Cases of Cryptococcus gattii infection* (n = 51) with known illness onset date,† by quarter --- California, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington, 2004--2010
Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to: mmwrq@cdc.gov. Type 508 Accommodation and the title of the report in the subject line of e-mail.
Emergence of Cryptococcus gattii--- Pacific Northwest, 2004--2010
Cryptococcus is a genus of fungi, of which two species, Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii, cause nearly all human and animal cryptococcal infections. Whereas C. neoformans primarily affects persons infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) worldwide, C. gattii primarily affects HIV-uninfected persons in tropical and subtropical regions (1). In December 2004, a case of human C. gattii infection was reported in Oregon, associated with an outbreak on Vancouver Island and in mainland British Columbia, Canada (2). A second C. gattii case was reported in Oregon in 2005, and 12 more cases were reported in 2006 and 2007. In 2008, in response to the emergence of C. gattii in the United States, CDC, state and local public health authorities, and the British Columbia Centre for Disease Control (BCCDC) formed the Cryptococcus gattii Public Health Working Group (1). States began collecting epidemiologic information on patients and sending isolates to CDC. By July 2010, a total of 60 human cases had been reported to CDC from four states (California, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington) in the Pacific Northwest. Among 52 patients for whom travel history was known, 46 (88%) said they had not traveled to British Columbia or any other C. gattii--endemic areas, suggesting they acquired the infection locally. Among 45 patients with known outcomes, nine (20%) died because of C. gattii infection, and six (13%) died with C. gattii infection. Physicians should consider C. gattii as a possible etiology of a cryptococcal infection among persons living in or traveling to the Pacific Northwest or traveling to other C. gattii--endemic areas.
Multilocus sequence typing subcategorizes C. gattii into four genotypes: VGI, VGII, VGIII, and VGIV. Further genetic analysis divides the VGII genotype into three subtypes: VGIIa, VGIIb, and VGIIc (3). Although VGII is the genotype most commonly associated with the outbreak in the United States and British Columbia, it is uncommon in other C. gattii--endemic parts of the world, where VGI is isolated most frequently (3).
During 1999, C. gattii began appearing in animals and humans on Vancouver Island and, beginning in 2004, among mainland British Columbia residents who had no exposure to Vancouver Island (2,4). By the end of 2007, a total of 218 human cases had been reported to BCCDC (5). Studies from British Columbia and elsewhere showed a median incubation period of 6--7 months, with a range of 2--13 months (1). The median age of patients in British Columbia was 59 years, with age-specific incidence highest among persons aged 70--79 years (5). Only 38% of patients had an identifiable immunosuppressive condition (5). Reported case-fatality rates either from or with C. gattii infection was 9% (5). Studies on Vancouver Island found C. gattii spores in the environment, often in association with trees and soil (6).
The two human infections reported from Oregon in 2004 and 2005 were from C. gattii subtypes VGIIa and VGIIc (3). The VGIIc subtype had not been found previously anywhere in the world; the VGIIa isolate was genetically distinct from the British Columbia VGIIa isolates (4). Neither patient had traveled to Vancouver Island or any other known C. gattii--endemic area. In early 2006, a resident of Orcas Island, Washington, developed C. gattii VGIIa infection with a strain indistinguishable from the British Columbia VGIIa strain (7).
In October 2009, the C. gattii Public Health Working Group formalized a surveillance system for C. gattii and housed it at CDC. The system includes standardized human and veterinary case report forms and isolate submission protocols. Standardized case report forms include questions about patient demographics, health history, and illness onset and course, and are completed by state or local health departments through interviews with patients or their family members. For the surveillance system, a case is defined as an illness occurring on or after January 1, 2004, in a U.S. resident or animal with a culture-confirmed isolate of C. gattii. Case report forms are completed after a patient isolate is confirmed as C. gattii at CDC. Chart reviews and patient or family member interviews for collection of patient information are carried out by state and local health departments to gather data on symptoms and illness course. For patients whose illness occurred before the surveillance system was initiated, isolates were sent to CDC or BCCDC at the time of illness; chart reviews and patient or family member interviews carried out at the time of illness were used to complete the case report forms.
During January 1, 2004--July 1, 2010, a total of 60 human cases of C. gattii infection were reported to CDC (Figure): 43 from Oregon, 15 from Washington, one from California, and one from Idaho. Approximately half (54%) of the patients were male (Table); patients ranged in age from 15 to 95 years, with the highest proportion of patients (45%) aged 50--69 years (Table). Among 47 patients for whom such information was known, 38 (81%) had an underlying condition that might have predisposed them to infection, including three patients with HIV infections. Of all patient isolates, 50% were subtype VGIIa, 32% were VGIIc, 10% were VGIIb, 5% were VGI, and 3% were VGIII. The most common clinical finding was pneumonia, occurring among 57% of patients.
Among the 45 patients for whom outcome was known, nine (20%) died because of C. gattii infection and six (13%) died with C. gattii infection; two of the nine who died from C. gattii infection had no predisposing condition. In addition to human cases, 52 veterinary cases (among cats, dogs, ferrets, sheep, camelids, elk, horses, goats, and porpoises) were reported to CDC from California, Hawaii, Oregon, and Washington.
Reported by
E DeBess, DVM, PR Cieslak, MD, Oregon Public Health Div. N Marsden-Haug, MPH, M Goldoft, MD, R Wohrle, DVM, C Free, E Dykstra, PhD, Washington State Dept of Health. RJ Nett, MD, Div of Vector Borne Infectious Diseases; T Chiller, MD, SR Lockhart, PhD, J Harris, PhD, Div of Foodborne, Bacterial, and Mycotic Diseases, National Center for Zoonotic, Vector-Borne, and Enteric Diseases, CDC.
Editorial Note
C. gattii is an emerging infection in the United States. C. gattii appears to differ from its sibling species, C. neoformans, both in its clinical aspects (e.g., less responsive to antifungal drugs and more likely to cause tumor-like lesions called cryptococcomas) and its ecologic niche (2,8). In addition, whereas the primary risk factor for C. neoformans cryptococcosis is severe immunosuppression (e.g., from HIV infection), risk factors for C. gattii infection in the United States appear to include both immunocompromise and exposure to specific regions of environmental fungal colonization (2,8). Many cases of C. gattii infection are likely not recognized because distinguishing between C. gattii and C. neoformans requires plating on differential media not routinely available in clinical microbiology laboratories; therefore, many cryptococcal infections are never speciated. In addition, cryptococcal infections generally are not notifiable diseases in the United States, although C. gattii is now reportable in one state, Washington, as a rare disease of public health importance.
Until 1999, most human C. gattii infections were reported from Australia and other tropical and subtropical regions, including parts of Africa, Asia, the Mediterranean, South America, and southern California (8). Fungal spores are known to colonize the nasal cavity and spread to other body sites, causing meningitis, pneumonia, and the development of lung, brain, or muscle cryptococcomas (8). The infection is not known to be transmitted among or within animal species. Although C. gattii had been isolated rarely from environmental sources and patients in the United States before 2004 (2), U.S. outbreaks had not been reported.
Because C. gattii typically has been regarded as tropical or subtropical in geographic distribution, its emergence in a temperate climate suggests that the pathogen might have adapted to a new climatic niche, or that climatic warming might have created an environment in which minimum threshold conditions for C. gattii spore survival and propagation are attained consistently (1,2). Alternatively, the environmental conditions supportive of C. gattii might be broader than previously suspected, or earlier propagation might have been inhibited by low concentrations of pathogen in the environment. In addition, infections might have occurred in the Pacific Northwest before the recognized increase in human cases, but too rarely to attract attention. However, retrospective speciation of 49 cryptococcal isolates from the Pacific Northwest obtained from 1997 through 2003 (7) and 31 isolates from Vancouver Island obtained from 1987 through 1998 (9) revealed exclusively C. neoformans, suggesting that the recent increase in reports of C. gattii represent actual emergence of the species in the region and not just an increase in disease awareness and reporting.
Additional systematic surveillance is needed to track C. gattii infection, along with increased awareness of the infection among public health practitioners, physicians, and veterinarians. In 2010, for the first time, surveillance data for C. gattii were reported at the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists meeting. The C. gattii Public Health Working Group is continuing disease surveillance and planning to conduct speciation of banked isolates of Cryptococcus. Improved surveillance should enable better assessment of the incidence of the disease and also its clinical manifestation and course.
Physicians should consider C. gattii as a possible etiology of infection when treating patients (particularly those who are HIV negative) who have signs and symptoms of cryptococcal infection, and should ask patients about recent travel to the Pacific Northwest, British Columbia, or other C. gattii--endemic areas. Physicians, particularly in the Pacific Northwest, should report suspected C. gattii infections and submit clinical isolates to their state health departments when requested.
Acknowledgments
The findings in this report are based, in part, on contributions by the Cryptococcus gattii Public Health Working Group, state laboratories, and the British Columbia Centre for Disease Control and Prevention.
References
- Dixit A, Carroll SF, Qureshi ST. Cryptococcus gattii: an emerging cause of fungal disease in North America. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis 2009:840452. Epub May 25, 2009.
- Datta K, Bartlett KH; Baer R, et al. Spread of Cryptococcus gattii into Pacific Northwest Region of the United States. Emerg Infect Dis 2009;15:1185--91.
- Byrnes EJ III, Bildfell RJ, Frank SA, Mitchell TG, Marr KA, Heitman J. Molecular evidence that the range of the Vancouver Island outbreak of Cryptococcus gattii infection has expanded into the Pacific Northwest in the United States. J Infect Dis 2009;199:1081--6.
- MacDougall L, Kidd SE, Galanis E, et al. Spread of Cryptococcus gattii in British Columbia, Canada, and detection in the Pacific Northwest, USA. Emerg Infect Dis 2007;13:42--50.
- Galanis E, Macdougall L. Epidemiology of Cryptococcus gattii, British Columbia, Canada, 1999--2007. Emerg Infect Dis 2010;16:251--7.
- Kidd SE, Chow Y, Mak S, et al. Characterization of environmental sources of the human and animal pathogen Cryptococcus gattii in British Columbia, Canada, and the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007;73:1433--43.
- Upton A, Fraser JA, Kidd SE, et al. First contemporary case of human infection with Cryptococcus gattii in Puget Sound: evidence for spread of the Vancouver Island outbreak. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:3086--8.
- Sorrell TC. Cryptococcus neoformans variety gattii. Med Mycol 2001;39:155--68.
- Fyfe M, MacDougall L, Romney M, et al. Cryptococcus gattii infections on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada: emergence of a tropical fungus in a temperate environment. Can Commun Dis Rep 2008;34:1--12.
What is already known on this topic?
Human Cryptococcus gattii infection, formerly limited to tropical and subtropical regions of the world, emerged in British Columbia in 1999, causing approximately 200 infections, with a reported case-fatality rate of 9%.
What is added by this report?
Since 2004, C. gattii has emerged as a pathogen of humans and animals in the U.S. Pacific Northwest, resulting in 60 human infections and at least 15 deaths among persons infected.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Physicians should consider C. gattii as a possible etiology of infection when treating patients (particularly those who are HIV negative) who have signs and symptoms of cryptococcal infection, and should ask patients about recent travel to the Pacific Northwest, British Columbia, or other C. gattii--endemic areas. Physicians, particularly in the Pacific Northwest, should report suspected C. gattii infections and submit clinical isolates to their state health departments when requested.
Source: Cryptococcus gattii Public Health Working Group.
* Defined as illness occurring on or after January 1, 2004, in a U.S. resident with a culture-confirmed isolate of C. gattii.
† Includes estimated date for one patient each in 2007, 2008, and 2010, and two patients in 2009.
Alternate Text: The figure above shows cases of Cryptococcus gattii infection (n = 51) with known illness onset date, by quarter, in California, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington. During January 1, 2004-July 1, 2010, 60 human cases of C. gattii infection were reported to CDC: 43 from Oregon, 15 from Washington, one from California, and one from Idaho.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services.
References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are
provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply
endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content
of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of
the date of publication.
All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from typeset documents.
This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version.
Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr)
and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S.
Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC 20402-9371;
telephone: (202) 512-1800. Contact GPO for current prices.
**Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to
mmwrq@cdc.gov.


