At a glance
The PHIN Messaging System (PHINMS) Team and the PHINMS Help Desk shares Frequently Asked Questions. The Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) captured below pertain to Release 3.3. Suggestions to add additional questions can be sent to the PHINMS Web Site point-of-contact using the Support tab.
Questions and Answers
What is a Collaboration Protocol Agreement?
A Collaboration Protocol Agreement (CPA) is a business-level agreement between the PHINMS Sender and Receiver. The CPA stores information necessary for partners to communicate with one another. It includes the transport protocol and security constraints both partners have agreed to use when messaging one another. A CPA is required for each location which has installed PHINMS. The CPA file name consists of the Receiver’s and Sender’s PartyID with an .xml extension. The file is stored in both the PHINMS Receiver’s CPA directory and the Sender’s CPA directory.
What is a CDC PartyID?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) PartyID is a unique object identifier (OID) for each instance of the PHIN MS Sender and Receiver used when sending messages to the CDC. The CDC PHIN MS Help Desk issues the PartyID at no cost. The value of the PartyID must be the same as the Message Receiver’s PartyID in the Collaboration Protocol
Agreement. A PartyID would resemble “1.23.456.7.891234.5.6.7.8.9.0.1”.
What is the difference between a PartyID and an OID?
A PartyID is an object identifier (OID) used by PHIN MS. It is a unique OID assigned to an organization by the CDC PHIN MS Help Desk.
Note: A CDC PartyID is an OID but an OID is not necessarily a PartyID.
What is a Digital Certificate and what is the purpose?
A Digital Certificate is a digital identity of a person, computer, or organization. It is a binary file used for Authentication, Encryption, Signature, etc. Digital Certificates are typically issued by Organizations or Root Certificate Authorities.
Do higher-priced certificates provide more security?
There is no concept of higher-priced certificates rather encryption strength. PHIN MS recommends 1024 bit encryption strength both on Client certificates (Sender) and SSL certificates (IIS Proxy Server).
What is the recommendation bit length for SSL certificates?
SSL Certificates should be 2048 bit length.
What are the different types of Digital Certificates? Which ones are required for a Sender/Receiver to successfully exchange data? Specifically, what does each certificate do and why is it required?
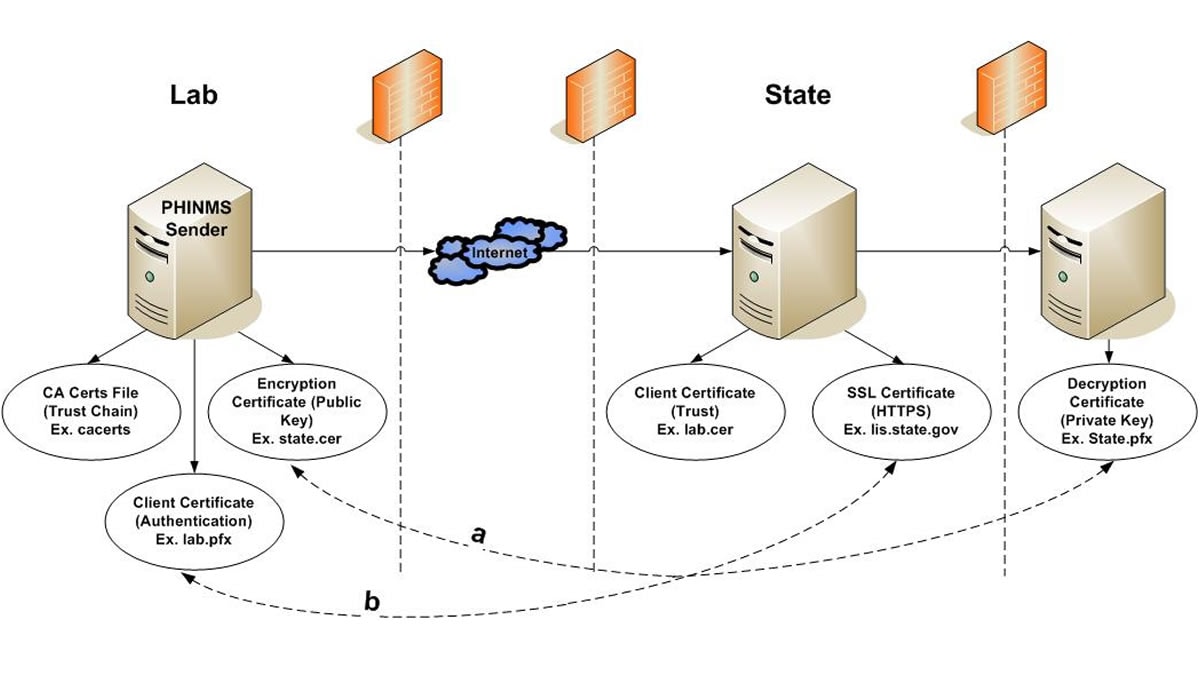
PHINMS Sender Side:
Client Certificate: Most CDC related programs will issue a CDC issued Digital Certificate to an individual. This is used to authenticate the Sender in an Organization to the Receiver (example – sender.pfx). The client certificate is a combination of both a private key and a public key of the Sender’s certificate.
Encryption Certificate: This is the public key of the Receiver (example – state.cer). The encryption certificate can be downloaded by obtaining the information in an email from the Receiver. The data sent to the Receiver is encrypted using the encryption certificate (example – receiver.cer).
Certificate Authority Certificates: A Certificate Authority (CA) Certificate is a Key Store which comes bundled with the PHIN MS product. When a Sender is trying to make a HTTPS SSL (Secure Socket Layer) connection to the Receiver’s IIS server, it needs to validate the certificate chain of the SSL certificate installed on the IIS server. PHIN MS uses this key store to look up for trust chain. When the Root and Intermediate Certificate of the SSL certificate are not present in the CA cert file then the HTTPS connection fails. The Receiver will need to provide the Root and Intermediate of the SSL certificate to the Sender in an email. The Sender will then need to import the information.
What vendors do PHINMS recommend more or less than others?
There are many vendors which issue Digital Certificates like Client Certificate and SSL Server Certificates. Some included are Verisign, Thawte, Entrust, Equifax, Geotrust to name a few. PHINMS does not recommend one over the other. An existing and self-signed certificate may be used.
When and how are expired PHINMS Digital Certificates updated?
An email notification will be sent as a reminder to renew the certificate. The reminders are sent three times (1 month, 15 days, and 5 days) before the certificate's expiration date. Contact PHINTech@cdc.gov to renew the certificate.
What steps need to be taken to correct a certificate problem?
There may be several reasons for a certificate problem. The most convenient way to diagnosis the problem is to review the log files. Some of the most common issues are as follows:
- SSL and Client Certificate expiration,
- encrypting with a wrong public key on the Sender’s side,
- the Sender not being able to trust the Receiver’s SSL certificate chain, and/or
- the wrong private key password using the Sender’s or Receiver’s console.
Does PHINMS require a Digital Certificate?
A Digital Certificate is required for security purposes when using PHINMS to send data to the CDC. A Digital Certificate is not required when partners are sending data directly to other partners and the data are not sent to the CDC. A Digital Certificate can be purchased from a Certificate Authority (CA). Instructions for requesting a Digital Certificate to send data to the CDC are located in the PHINMS 3.3 Implementation Guide.
Which version of PHINMS should be installed?
Currently the latest version is PHINMS 3.3 and recommended for installation. Upgrade options are documented in the PHINMS Implementation Guide.
PHINMS 3.3 Implementation Guide
Which operating system does PHINMS use?
PHINMS is platform-independent. Any operating system can be used; however, PHINMS 3.3 has only been tested with a select few. The following platforms are tested and guaranteed to work with PHINMS and they are supported by the PHINMS team:
- Windows Server 2019.
- Windows 10.
What is the cost to use PHINMS?
There is no cost to use the PHINMS software. The software has been designed by the CDC for the Public Health communities.
What is the difference between a Refresh and a Restart?
When the default database is started any data changes should be reflected when the PHINMS console is refreshed. The request to restart indicates the Tomcat server requires to be stopped then restarted whenever a configuration changes or installing a new component such as Web Services Adapters.
