NIOSH Training for Nurses on Shift Work and Long Work Hours
Injuries/Errors (Continued)
Both shift length and shift time influence risks. After looking at findings from several studies, researchers estimated the chance for errors and incidents for four types of shift schedules that all use 48 hours of work per week.45 The shift schedules were day work with six 8-hour shifts and four 12-hour shifts, and night work with six 8-hour shifts and four 12-hour shifts. The researchers estimated that the highest risk is for shifts that are both long and during the night (see Figure 3.1).
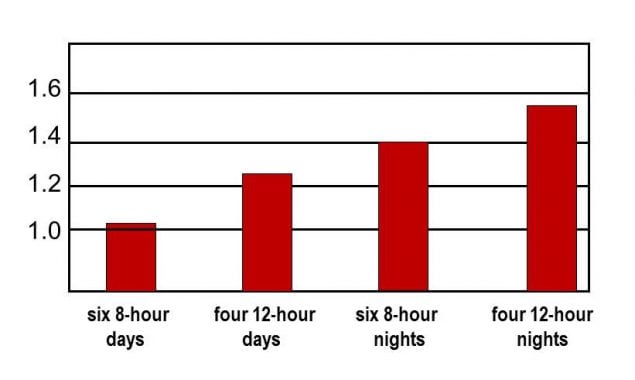
Figure 3.1. Estimated Risk of Incidents for 48-Hour Shifts (adapted from Folkard & Lombardi45)
The researchers concluded that it may be safer to use more frequent short shifts than less frequent long shifts.
Particularly for night shifts, it is safer to use shorter (such as 8-hour) shifts rather than longer shifts.
