At a glance
One Health is a collaborative, multisectoral, and transdisciplinary approach — working at the local, regional, national, and global levels — with the goal of achieving optimal health outcomes recognizing the interconnection between people, animals, plants, and their shared environment.
What is One Health?
One Health is an approach that recognizes that the health of people is closely connected to the health of animals and our shared environment. One Health is not new, but it has become more important in recent years. This is because many factors have changed interactions between people, animals, plants, and our environment.

- Human populations are growing and expanding into new geographic areas. As a result, more people live in close contact with wild and domestic animals, both livestock and pets. Animals play an important role in our lives, whether for food, fiber, livelihoods, travel, sport, education, or companionship. Close contact with animals and their environments provides more opportunities for diseases to pass between animals and people.
- The earth has experienced changes in climate and land use, such as deforestation and intensive farming practices. Disruptions in environmental conditions and habitats can provide new opportunities for diseases to pass to animals.
- The movement of people, animals, and animal products has increased from international travel and trade. As a result, diseases can spread quickly across borders and around the globe.
These changes have led to the spread of existing or known (endemic) and new or emerging zoonotic diseases, which are diseases that can spread between animals and people. Every year, millions of people and animals around the world are affected by zoonotic diseases. Examples of zoonotic diseases include:
- Rabies
- Salmonella infection
- West Nile virus infection
- Q Fever (Coxiella burnetii)
- Anthrax
- Brucellosis
- Lyme disease
- Ringworm
- Ebola
Similar to humans, animals are also at risk of getting sick from some diseases and environmental hazards. Because of this, they can sometimes serve as early warning signs of potential human illness. For example, birds often die of West Nile virus before people in the same area get sick with West Nile virus infection.
One Health Fact Sheet
What are common One Health issues?
One Health issues include emerging, re-emerging, and endemic zoonotic diseases, neglected tropical diseases, vector-borne diseases, antimicrobial resistance, food safety and food security, environmental contamination, climate change and other health threats shared by people, animals, and the environment. For example:
- Antimicrobial-resistant germs can quickly spread through communities, the food supply, healthcare facilities, and the environment (soil, water), making it harder to treat certain infections in animals and people.
- Vector-borne diseases are on the rise with warmer temperatures and expanded mosquito and tick habitats.
- Diseases in food animals can threaten supplies, livelihoods, and economies.
- The human-animal bond can help improve mental well-being.
- Contamination of water used for drinking, recreation, and more can make people and animals sick.
Even the fields of chronic disease, mental health, injury, occupational health, and noncommunicable diseases can benefit from a One Health approach involving collaboration across disciplines and sectors.
How does a One Health approach work?
One Health is gaining recognition in the United States and globally as an effective way to fight health issues at the human-animal-environment interface, including zoonotic diseases. CDC uses a One Health approach by involving experts in human, animal, environmental health, and other relevant disciplines and sectors in monitoring and controlling public health threats and to learn about how diseases spread among people, animals, plants, and the environment.
Successful public health interventions require the cooperation of human, animal, and environmental health partners. Professionals in human health (doctors, nurses, public health practitioners, epidemiologists), animal health (veterinarians, paraprofessionals, agricultural workers), environment (ecologists, wildlife experts), and other areas of expertise need to communicate, collaborate on, and coordinate activities. Other relevant players in a One Health approach could include law enforcement, policymakers, agriculture, communities, and even pet owners. No one person, organization, or sector can address issues at the animal-human-environment interface alone.
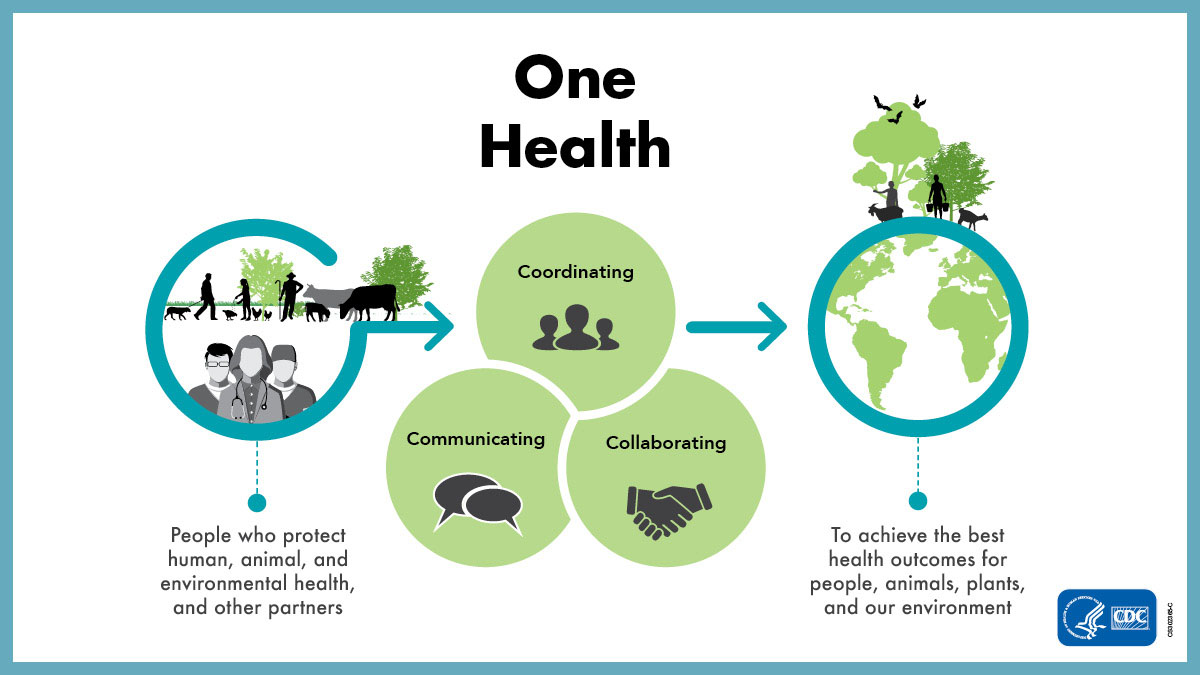
The One Health approach can:
- Prevent outbreaks of zoonotic disease in animals and people.
- Improve food safety and security.
- Reduce antimicrobial-resistant infections and improve human and animal health.
- Protect global health security.
- Protect biodiversity and conservation.
By promoting collaboration across all sectors, a One Health approach can achieve the best health outcomes for people, animals, and plants in a shared environment.