The Federal Statistical System
NCHS Fact Sheet, Feburary 2019
PDF Versionpdf icon (1.1 MB)
What is a federal statistical agency?
The U.S. federal statistical system is composed of the 13 principal federal statistical agencies (see Figure), each of which has a principal mission to produce a substantial portion of official federal statistics. The Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB) Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA) coordinates the nation’s decentralized federal statistical system through the Interagency Council on Statistical Policy (ICSP), which enables the exchange of information about statistical programs and activities. Within this system, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) functions as the federal agency responsible for the collection and dissemination of the nation’s vital and health statistics.
Federal statistical agencies are charged with providing relevant, accurate, and timely data to inform public and private decision making. To meet this charge, agencies rely on the Principles and Practices for a Federal Statistical Agency developed by the National Research Council (NRC) of the National Academies to guide their strategic planning, daily operations, and interactions with stakeholders. Agencies embrace a common set of professional standards and operational practices designed to ensure the quality, integrity, and credibility of their statistical activities. This allows them to provide objective information that is relevant to issues of public policy. Independence is key to maintaining the trust of those who provide and use the information. Actual or perceived violations of any of these principles undermines the scientific integrity of, and public confidence in, the data produced by principal statistical agencies.
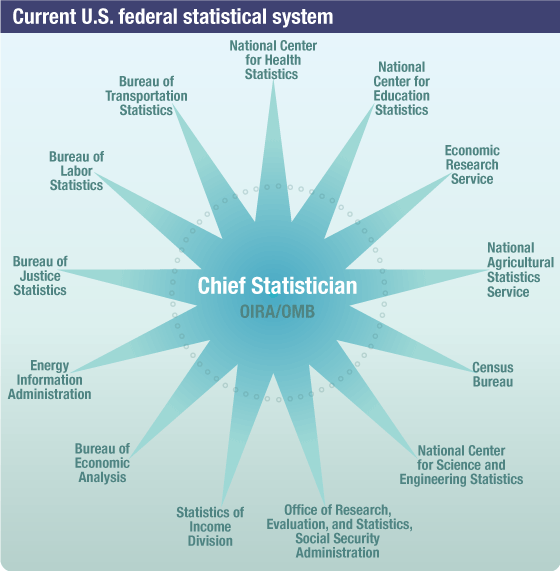 image icon
image icon
About NCHS
NCHS is the nation’s principal health statistics agency, providing data to identify and address health issues. NCHS compiles statistical information to help guide public health and health policy decisions.
Secretarial designation
By statute, the NCHS director is appointed by the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). While the NCHS director reports to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) regarding NCHS operations, the director reports directly to the Secretary of HHS as a senior advisor on health statistics. The NCHS director is co-chair of the HHS Data Council, which is the principal advisory body to the Secretary on health and human services data policy.
Statistical policy directives: OMB has issued several statistical policy directives to guide statistical agencies and to ensure that federal statistics are objective, credible, relevant, accurate, and timely. Two of the most important are:
Statistical policy directives: OMB has issued several statistical policy directives to guide statistical agencies and to ensure that federal statistics are objective, credible, relevant, accurate, and timely. Two of the most important are:
- Directive 1: Fundamental responsibilities of federal statistical agencies and recognized statistical units (trust directive)—Provides a framework that supports federal statistical policy, serves as a foundation for federal statistical activities, and calls on HHS to enable, support, and facilitate NCHS as it implements four core responsibilities to:
- produce and disseminate relevant and timely information;
- conduct credible and reliable statistical activities;
- protect the trust of data providers by ensuring the confidentiality and exclusively statistical use of their data; and
- conduct objective statistical activities.
- Directive 4: Release and dissemination of statistical products produced by federal statistical agencies—Establishes requirements for equitable access to and transparency on the release and dissemination of statistical products.
OMB directives in practice
- NCHS must avoid even the appearance that the design, collection, processing, editing, compilation, storage, analysis, release, and dissemination of data may be manipulated or influenced by those outside of NCHS.
- NCHS has autonomy in determining the timing and release of statistical products. HHS and CDC leadership do not influence the dates when statistical products will be released. In addition, NCHS releases public-use data files as soon as they are ready for dissemination.
- NCHS provides extensive information about how the data were collected and any known or potential data limitations or sources of error; ensures that all users, including those internal to HHS and CDC, have equitable access to the data at the same time; and maintains safeguards to protect the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
As a statistical agency, NCHS does not make policy recommendations in reports and publications and these products must be free from any perceived or actual partisan intervention. Instead, NCHS provides the high-quality data that inform the development of policy. Like all federal statistical agencies, NCHS adheres to high standards of objectivity, fostering public trust in the quality and credibility of the data in its statistical publications. In addition, the Confidential Information Protection and Statistical Efficiency Act provides strong protection for information that is obtained for exclusively statistical purposes under a pledge of confidentiality.
 image icon
image icon
While the rest of CDC may offer recommendations, NCHS must only provide objective statistical descriptions of data.
 image icon
image icon
Data Brief, Key findings
- In 2017, there were 70,237 drug overdose deaths in the United States.
- The age-adjusted rate of drug overdose deaths in 2017 (21.7 per 100,000) was 9.6% higher than the rate in 2016 (19.8).
- Adults aged 25–34, 35–44, and 45–54 had higher rates of drug overdose deaths in 2017 than those aged 15–24, 55–64, and 65 and over.
- West Virginia (57.8 per 100,000), Ohio (46.3), Pennsylvania (44.3), and the District of Columbia (44.0) had the highest age-adjusted drug overdose death rates in 2017.
- The age-adjusted rate of drug overdose deaths involving synthetic opioids other than methadone (drugs such as fentanyl, fentanyl analogs, and tramadol) increased by 45% between 2016 and 2017, from 6.2 to 9.0 per 100,000.
For more information about NCHS, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs.