Basic Information About Lung Cancer
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the lungs, it is called lung cancer.
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers in the United States. Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer diagnosed in the United States, followed by breast cancer (among women) and prostate cancer (among men). More people in the United States die from lung cancer than any other type of cancer. This is true for both men and women. After increasing for decades, lung cancer rates are decreasing nationally, as fewer people smoke cigarettes and as lung cancer treatments improve. People with lung cancer are living longer after their diagnosis because more cases are found early, when treatment works best.
Cigarette smoking is the number one cause of lung cancer. Lung cancer also can be caused by using other types of tobacco (such as pipes or cigars), breathing secondhand smoke, being exposed to substances such as asbestos or radon at home or work, having certain gene mutations (unusual changes made when your body’s cells are dividing), or having a family history of lung cancer. Lung cancer can happen in people who never smoked or smoked fewer than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime.
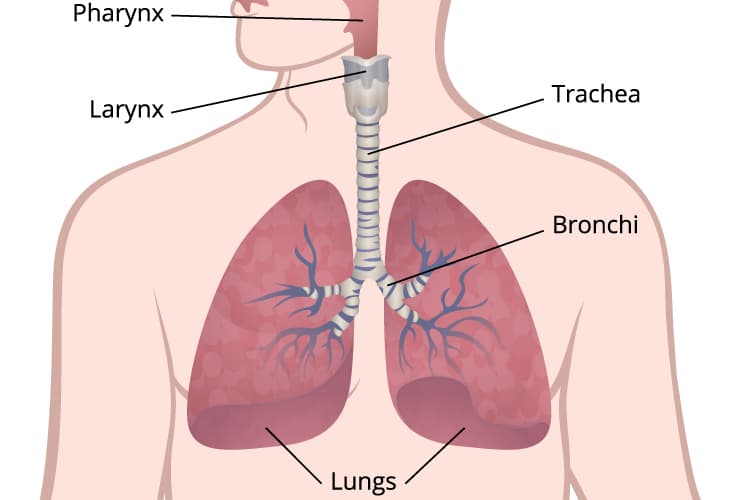
When cancer starts in the lungs, it is called lung cancer. Lung cancers usually are grouped into two main types called small cell and non-small cell.
Research has found several risk factors that may increase your chances of getting lung cancer.

Different people have different symptoms for lung cancer. Most people with lung cancer don’t have symptoms until the cancer is advanced.
To lower your risk of getting lung cancer, don’t smoke, avoid secondhand smoke, and get your home tested for radon.

Lung cancer screening is recommended only for adults who have no symptoms but who are at high risk for developing the disease because of their smoking history and age.

Lung cancer is treated in several ways, depending on the type of lung cancer and how far it has spread. People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.