Key points
- Molluscum contagiosum is an infection that causes small, raised sores on your body.
- You can catch the disease if you touch someone else who has it.
- You can also get it if you touch surfaces or objects that have been touched by someone with molluscum.
- Molluscum contagiosum mostly occurs in kids ages 1 to 10.
Overview
Molluscum contagiosum is very common in the United States. It's so common you shouldn't be surprised if you or your family catch it. Anyone can get infected, but it's most common in children between 1 and 10 years old.
The infection is usually mild and goes away without any treatment. You can catch the infection more than once in your lifetime if you're around someone who has it.
Signs and symptoms
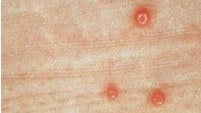
Molluscum contagiosum causes small, raised bumps that:
- Usually look white, pink or the same color as your skin
- Feel firm, sometimes with a dip in the center
- Appear anywhere on your body
- Are about the size of a pinhead to a pencil eraser
The sores may be itchy, sore, red, or swollen. They typically go away in six months to a year. But they can also take longer to resolve. They usually don't leave scars.
Risk factors
You are at increased risk for getting the disease if you:
- Have a weakened immune system (such as from HIV or cancer).
- Have eczema.
- Live in warm, humid climates with crowded living conditions.
How it spreads
You can get mollsucum if you touch someone who has it. It can also spread when you touch items that have the virus on it. Examples include towels, clothing, toys, or pool equipment used by someone who has molluscum.
If you have molluscum, you can spread it to other areas of your body. This can happen if you touch or scratch the sores, shave over them or have hair removal procedures on the area.
You can also catch molluscum if you have sex with someone who has it. Many molluscum infections in adults occur this way.
Treatment and recovery
Healthy people usually recover from molluscum without treatment. So, treatment isn't usually needed.
One exception is if you have sores around your genitals (penis, vulva, vagina, or anus). In this case, treatment is usually recommended. See a healthcare provider as soon as you can. They can determine if the sores are caused by molluscum or another disease. They can also suggest appropriate treatment.
Be aware that some treatments available on the internet may not be effective and may be harmful.
Do not try and remove the sores or the fluid inside them yourself. This can spread the infection to other areas of your body. It can also cause the sores to become infected.
