Surveillance
CDC tracks invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease using 2 surveillance systems:
Invasive disease refers to when the bacteria invade parts of the body, like blood, that are normally free from germs. CDC does not track non-invasive H. influenzae disease, such as ear infections.
National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System
CDC conducts national surveillance for invasive H. influenzae disease through NNDSS. CDC receives NNDSS data weekly regarding cases of nationally notifiable diseases.
Analyze and visualize ABCs H. influenzae data using Bact Facts Interactive.
Active Bacterial Core surveillance
CDC also tracks invasive H. influenzae disease with active laboratory-based surveillance through ABCs. As part of the Emerging Infections Program, ABCs aims to:
- Determine the incidence and epidemiologic characteristics of invasive H. influenzae disease
- Monitor impact of the H. influenzae type b vaccination program
- Monitor emergence of disease due to non-type b H. influenzae (i.e., types a, c, d, e, f, and nontypeable bacteria)
- Determine appropriate verification and validation criteria for serotyping
Disease trends
The epidemiology of invasive H. influenzae disease in the United States has shifted since the introduction of the Hib vaccine. The United States began using Hib vaccine for children in 1987 and for infants in 1990. Since then, the annual incidence of invasive Hib disease in children aged younger than 5 years old decreased by 99%. In contrast, rates of nontypeable and H. influenzae types a and f are increasing.
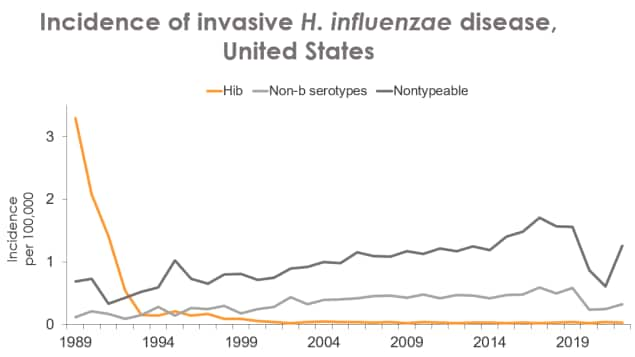
Figure 1 shows estimated incidence rates (per 100,000 persons) of invasive H. influenzae disease caused by serotype b, other serotypes excluding b, and nontypeable bacteria in the United States from 1994 through 2022. Disease caused by type b remains low, while disease caused by non-b and nontypeable bacteria were increasing until 2020. Since 2021, disease caused by non-b and nontypeable bacteria have begun increasing again.
Source: Active Bacterial Core surveillance
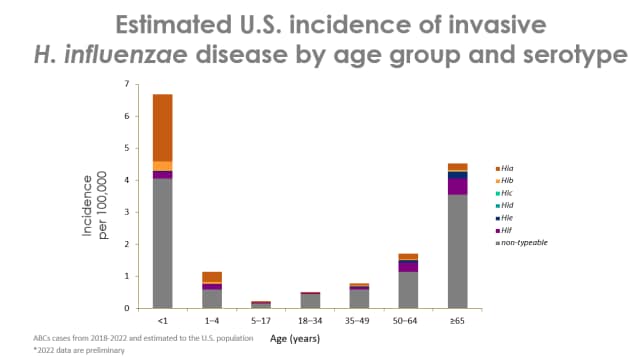
Figure 2 shows estimated incidence rates (per 100,000 persons) of invasive H. influenzae disease by serotype and age in the United States from 2018 through 2022. Children younger than 1 year old and adults older than 65 years old have the highest incidence of H. influenzae disease. Across age groups, nontypeable bacteria cause the highest incidence of H. influenzae disease.
Source: Active Bacterial Core surveillance
