Statistics & Maps
As of November 2022, more than 60 cases of Heartland virus disease have been reported from states in the Midwestern, Northeastern, and Southern United States. Most people diagnosed with the disease became sick from May through September.
All residents of and visitors to areas where Heartland virus activity has been identified are at risk of Heartland virus infection, particularly people who engage in outdoor work and recreational activities.
Heartland virus is not currently a notifiable disease, but CDC asks that states report possible cases of Heartland virus on a voluntary basis.
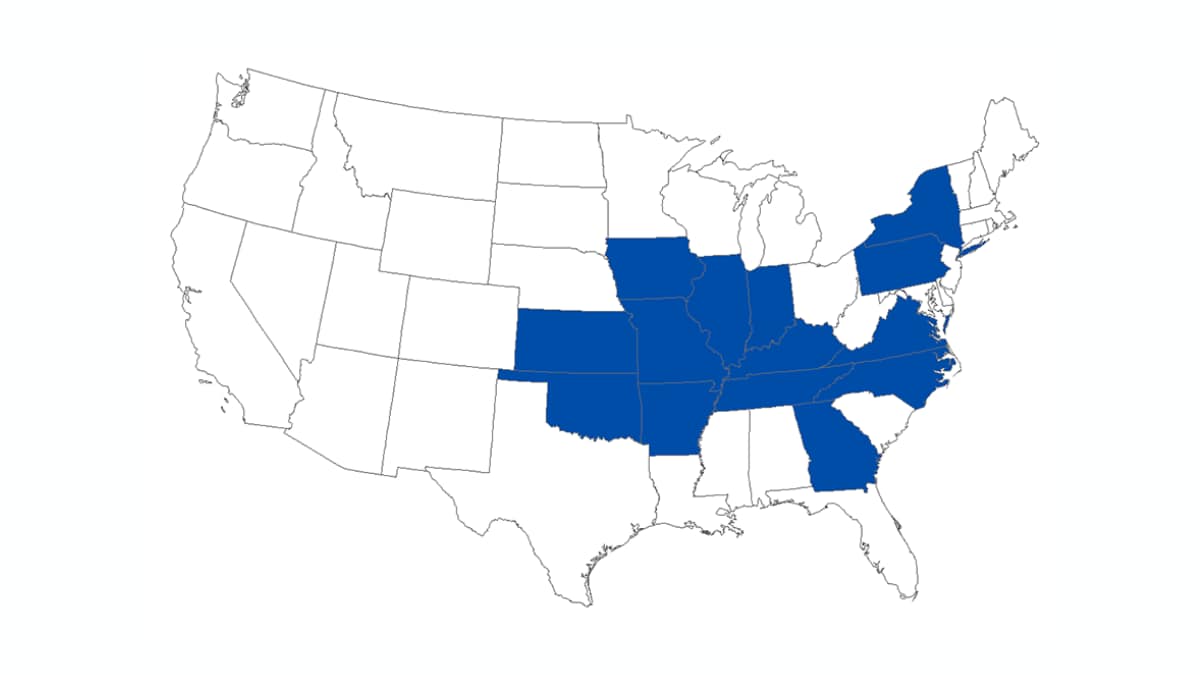
As of November 2022, Heartland virus disease cases have been identified in residents from the following states: Arkansas, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Missouri, New York, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, and Virginia.