Key points
- Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) include fever, mouth sores, and a skin rash on the hands and feet.
- HFMD is common in infants and children younger than 5 years old.
- Most children have mild symptoms for 7 to 10 days.

Signs and symptoms
HFMD symptoms usually include fever, mouth sores, and skin rash.
Fever and flu-like symptoms
Children often get a fever and other flu-like symptoms 3 to 5 days after they catch the virus. These can include:
- Fever
- Eating or drinking less
- Sore throat
- Feeling unwell
Mouth sores
Your child can get painful mouth sores. These sores usually start as small red spots, often on the tongue and insides of the mouth. The spots blister and can become painful.
Signs that swallowing might be painful for your child:
- Not eating or drinking
- Drooling more than usual
- Only wanting to drink cold fluids

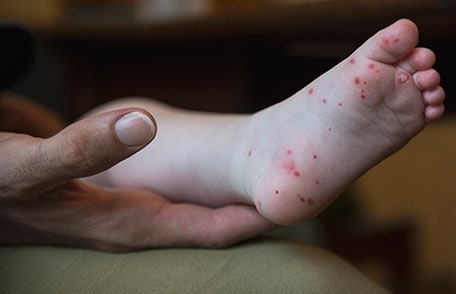
Skin rash
Your child can get a rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It can also show up on the buttocks, legs, and arms.
The rash usually is not itchy and looks like flat or slightly raised red spots; sometimes with blisters that have an area of redness at their base. Fluid in the blister can contain the virus that causes HFMD.
Keep blisters clean and avoid touching them.
Complications
HFMD is usually not serious and complications from it are rare. Nearly all people get better in 7 to 10 days with minimal or no medical treatment.
Dehydration
Some people, especially young children, can get dehydrated (lose bodily fluids). This can happen if they are not able to swallow enough liquids because of painful mouth sores. Parents can prevent dehydration by making sure their child drinks enough liquids.
Fingernail and toenail loss
Although very rare, people may lose a fingernail or toenail after having HFMD. Most reports of fingernail and toenail loss have been in children. In these reported cases, the person usually lost the nail within a few weeks after being sick. The nail usually grew back on its own. However, there is no evidence that HFMD was the cause of the nail loss.
Viral (aseptic) meningitis
Although very rare, a small number of people with HFMD get viral meningitis. This causes fever, headache, stiff neck, or back pain. The infected person may require to be hospitalized for a few days.
Encephalitis or paralysis
While extremely rare, a small number of people. with HFMD get encephalitis (swelling of the brain) or paralysis (can’t move parts of the body).
When to see a healthcare provider
See a healthcare provider if your child:
- Cannot drink well and you are worried they are dehydrated.
- Has a fever that lasts longer than 3 days.
- Has a weakened immune system (body's ability to fight germs and sickness).
- Is having severe symptoms.
- Has symptoms that do not improve after 10 days.
- Is very young, especially younger than 6 months.
Healthcare providers can usually identify HFMD by examining the rash appearance while considering the child's age and other symptoms. Sometimes, they might collect samples from the child's throat or poop. Then they will send them to a laboratory to test for the virus.
