What is the Global Health Security Agenda?
The Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA) – GHSA is a global effort to strengthen the world’s ability to prevent, detect, and respond to infectious disease threats. More than 70 countries have signed onto the GHSA framework, including the United States, which made a strong commitment to the initial five-year period of GHSA and continues to support its strategic priorities through GHSA 2024. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a leading role in supporting progress towards the GHSA 2024 target for the United States by working directly with partner country governments to strengthen public health systems and reduce the risk of infectious disease outbreaks.
GHSA 2024 – In 2018, all member countries committed to the next phase of the GHSA strategic framework, termed “GHSA 2024”. GHSA 2024 positions member countries to develop the leadership, technical knowledge, and collaborative foundation to sustain health security in the long term:
- Develop sustainable financing mechanisms for global health security
- Promote multi-sector collaboration to improve GHS capacities
- Improve information sharing across member countries
- Strengthen accountability to member country commitments
GHSA 2024’s target is for countries to take greater ownership of global health security efforts, and for more than 100 countries to improve health-security-related technical areas within five years. The 100 countries need to complete the Joint External Evaluation (JEE) and reach the level of “Demonstrated Capacity” in at least five technical areas. The JEE defines “Demonstrated Capacity” as a score of ‘4’ on a 1 to 5 scale where one is the lowest and five is the highest.
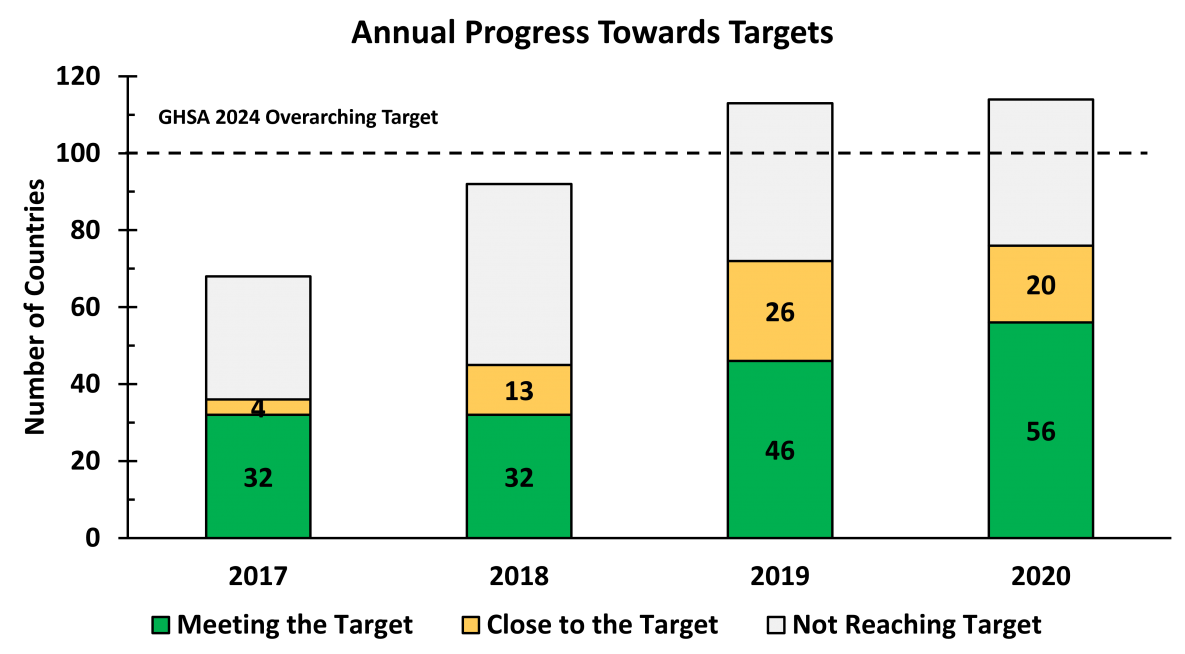
The graph depicts the Global Health Security Agenda’s annual progress towards the target from 2017 – 2020. In 2017, 32 countries met the target with four countries close to the target; in 2018, additional 8 countries were close to the target; in 2019, 46 countries met the target, and 26 countries were close to the target; in 2020, 56 countries met the target, and 20 countries were close to the target.