AMD Activities: 2022
CDC announced a new contract opportunity through the 2023 Broad Agency Announcement (BAA): 75D301-23-R-72545 on December 28, 2022. Topic 12 of this solicitation will provide funding to businesses, universities, and healthcare partners for genomic sequencing and other advanced laboratory and bioinformatic methods for the detection, assessment, prediction and tracking of pathogens of public health importance. Please refer to the frequently asked question document.
Informational Conference Call: Tuesday, Jan 10, from 12:30-1:30 EST on BAA Topic 12.
- Dial by your location
+1 669 254 5252 US (San Jose)
+1 646 828 7666 US (New York)
+1 669 216 1590 US (San Jose)
+1 551 285 1373 US - Meeting ID: 160 4311 5031
- Passcode: 775334378
Application Deadline: Feb 03, 2023, 03:00 pm EST
From 2020 through 2022, more than $63 million was awarded through 39 BAA projects to fill knowledge gaps, develop bioinformatic and other tools, and promote innovation in the COVID-19 response. Funding awarded is determined through a competitive selection process based on scientific needs and funds available, and the awardees are typically announced each fall. These projects complement other AMD investments in bioinformatics, genomic epidemiology, and the latest next-generation genomic sequencing technologies.
Posted on Friday, November 9, 2022
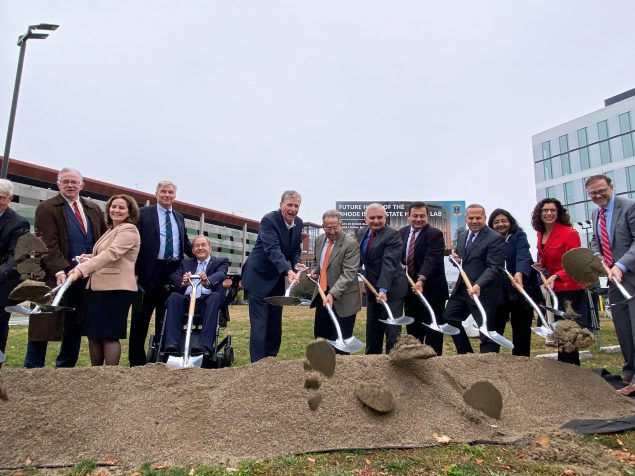
In late October, Rhode Island state leaders gathered to celebrate the new construction of the state’s public health laboratory. The facility is planned to be more energy efficient and provide a more optimized workspace with capacity to handle surges in response activity. The $81.7 million award comes from CDC’s Office of AMD as part of the agency’s efforts to integrate the latest next-generation genomic sequencing technologies across the nation.
Posted on Monday, November 28, 2022
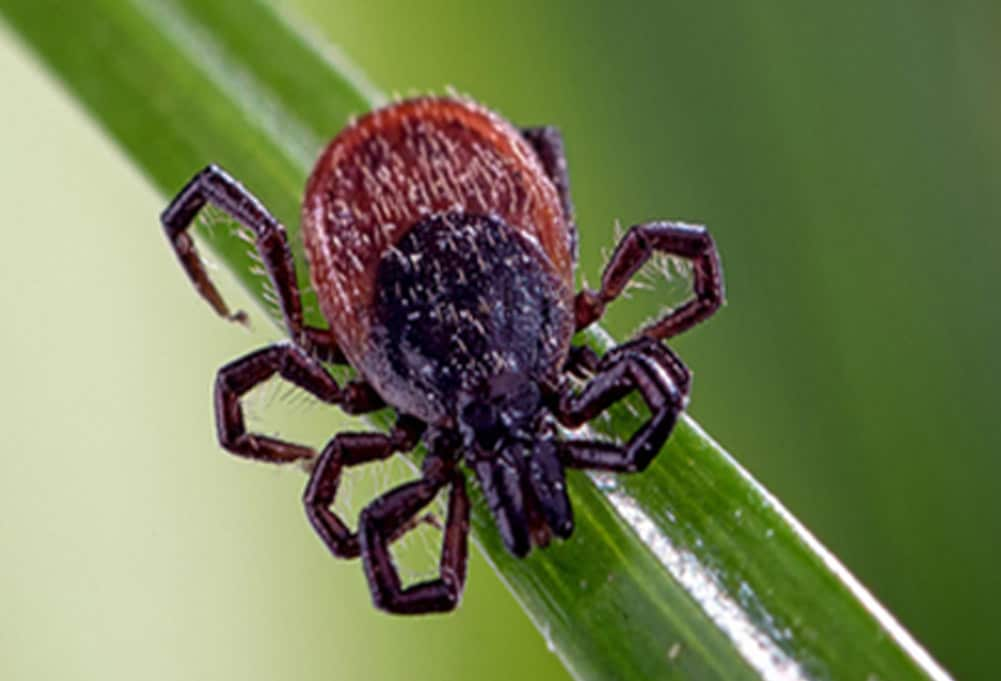
Anaplasmosis is a disease caused by the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum, spread to people by the bite of an infected tick. In the United States, A. phagocytophilm is carried primarily by the blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis) in the Northeast and Midwestern United States and the western blacklegged tick (Ixodes pacificus) along the West Coast. The need to monitor changes in the risk of human infection is important, but surveillance data that don’t separate human and non-human variants inflate estimates of risk for humans acquiring anaplasmosis. In a recent study, CDC scientists used next-generation sequencing (NGS) with novel targets to identify A. phagocytophilum in ticks and differentiate variants that are known to cause disease in humans from those that have not been shown to make people sick. They used NGS to increase variant testing efficiency and increase specificity compared with traditional PCR analysis. The assay also identifies unique clades, or groups of variants that come from the same ancestor, within both human and non-human variants. Researchers also developed a PCR assay for laboratories without access to NGS technology. Learn more: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877959X22001431?via%3Dihub
Posted on Tuesday, September 20, 2022
Today, CDC announced 5-year awards to five state public health departments. The awards will establish the Pathogen Genomics Centers of Excellence (PGCoE) network. The PGCoE network is intended to foster and improve innovation and technical capacity in pathogen genomics, molecular epidemiology, and bioinformatics to better prevent, control, and respond to microbial threats of public health importance.
Posted on Friday, August 25, 2022
The Office of Advanced Molecular Detection (OAMD) within CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases is recruiting for a director. Since its establishment in 2014, OAMD has fostered innovation in the application of pathogen genomics to public health. In this time, it has overseen the establishment of cutting-edge genomics technologies throughout the US public health system and is now seeking a director to lead OAMD into a new era where epidemiologists and laboratory scientists routinely use genomics to monitor, investigate, and respond to all infectious diseases of public health importance.
The OAMD Director will lead a growing office of approximately 30 employees and contractors and provide leadership and expertise in the development and execution of research projects across four centers and at least 13 divisions. The office manages an annual budget of $35M and oversees a $1.7B appropriation in the American Rescue Plan Act to accelerate the use of pathogen genomics in the public health system. The office also partners with state and local health departments, other federal agencies such as NIH, and a variety of non-governmental organizations. In addition, OAMD manages a growing portfolio of international activities.
Interested candidates should apply by 09/23/2022.
0602 Medical Officer: https://www.usajobs.gov/job/672556400
0601 General Health Science: https://www.usajobs.gov/job/672556200
Specifics on This Position:
- The senior scientist level compensation package is commensurate with qualifications and experience and may result in a higher salary than what is reflected in the USAjobs vacancy announcement.
- This position may be eligible for workplace flexibilities which may include remote work or telework options, and/or flexible work scheduling. These flexibilities may be requested in accordance with the HHS Workplace Flexibilities policy.
For more information, contact Beth Weekley.
Posted on Monday, June 15, 2022
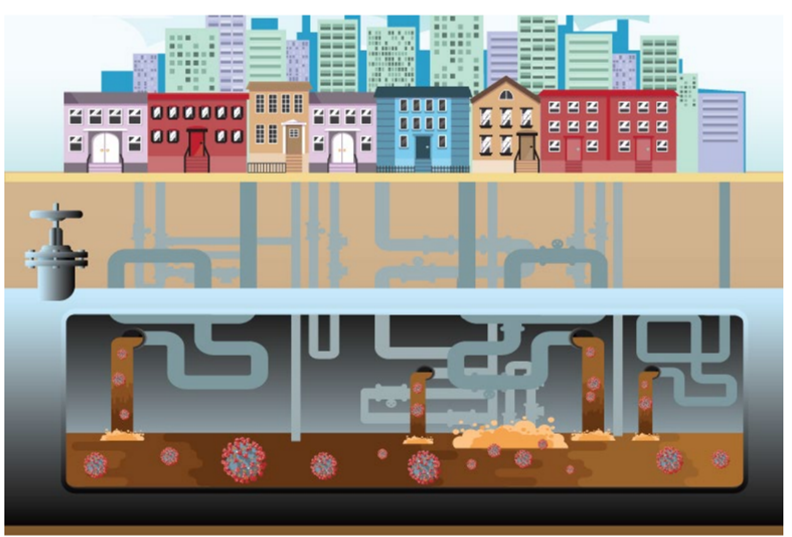
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, CDC launched the National Wastewater Surveillance System (NWSS) in September 2020 to coordinate and support the nation’s capacity to monitor SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. Wastewater testing is a novel approach for monitoring the virus, providing timely information about the changing prevalence of COVID-19 in different communities. This information can be a critical early warning for authorities of new outbreaks and inform local decision-making, such as where to have mobile testing and vaccination sites.
Posted on Monday, May 27, 2022
US airports serve more than 1 billion travelers each year. Public health professionals at these locations are on the front lines to detect new lineages of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, that enter the United States through arriving travelers. An innovative new program, CDC’s Traveler-based SARS-CoV-2 Genomic Surveillance Program, leverages multiple strategies, including pooled sample collection from arriving passengers, to detect new and rare SARS-CoV-2 lineages early.
Posted on Monday, March 28, 2022
Just five days after the World Health Organization (WHO) classified B.1.1.529 as a variant of concern (VOC), scientists in San Francisco identified the first case of Omicron in the United States. The Infectious Disease Division at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), received funding from CDC to track the evolution and spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the state. Supplemental support to state, local, and territorial public health laboratories and strategic investments in academic research projects have expanded the reach of genomic sequencing.
Posted on Friday, March 18, 2022
CDC announced a new competitive cooperative agreement on March 18, 2022, that will provide funding to establish the US Pathogen Genomics Centers of Excellence (PGCoE) network. This cooperative agreement will establish several centers of excellence, each consisting of a health department and one or more academic institutions.
Posted on Friday, March 11, 2022
In a recent episode of the Emerging Infectious Diseases podcast, host Sarah Gregory spoke with Dr. Jorge Muñoz-Jordan, Lead for NCEZID’s Dengue Diagnostics and Research Laboratory Team. They discussed the origin, spread, and evolution of the Zika virus in Puerto Rico from 2016 through 2017 and how the availability of next-generation sequencing helped them learn more about this virus. Dr. Muñoz also spoke about how the team was able to build on their existing work with vector-borne diseases to develop a molecular diagnostic test for Zika.
Posted on Wednesday, January 26, 2022

The Advanced Molecular Detection (AMD) program is helping build and integrate laboratory, bioinformatics, and epidemiology technologies across CDC and nationwide. The new AMD Investments section features a set of three national maps that detail how the AMD program supports state and local jurisdictions to build genomic sequencing capacity and provide workforce training. The maps represent funding from annual AMD appropriations and other supplemental sources, including multi-year funding from the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021. This support is distributed through the ELC and other funding mechanisms.