Occupational Exposure to Orthopoxviruses Among Laboratory Personnel
Laboratory-acquired exposures to orthopoxviruses and subsequent infections are occasionally reported among laboratory personnel. In the United States, 14 Orthopoxvirus infections were reported during 2004–2014 among personnel working in diagnostic and research facilities. However, the true number of infections might be higher as not all Orthopoxvirus infections are reported.
Diagnostic and research facilities that handle Orthopoxviruses should therefore have established procedures instructing their staff in how to prevent and respond to occupational exposures.
Case Reports
- Laboratory-Acquired Vaccinia Virus Infection in a Recently Immunized Person — Massachusetts, 2013 Source: MMWR Rep 2015;64:435–438
- Laboratory-Acquired Vaccinia Virus Infection — Virginia, 2008 Source: MMWR Rep 2009 58:797–800
- Laboratory-Acquired Vaccinia Exposures and Infections — United States, 2005–2007 Source: MMWR Rep 2008 57:401–404
- Lewis F, Chernak E, Goldman E, Li Y, Karem K, Damon IK, et al. Ocular Vaccinia Infection in Laboratory Worker, Philadelphia, 2004. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12(1):134-137.
- MacNeil A, Reynolds MG, Damon IK. Risks associated with vaccinia virus in the laboratory. 2009:385(1), 1-4
- McCollum AM, Austin C, Nawrocki J, Howland J, Pryde J, Vaid A, Holmes D, Weil MR, Li Y, Wilkins K, Zhao H, Smith SK, Karem K, Reynolds MG, Damon IK; Investigation of the First Laboratory-Acquired Human Cowpox Virus Infection in the United States. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, Volume 206, Issue 1, 1 July 2012, Pages 63–68
- Moussatché N, Tuyama M, Kato SE, et al. Accidental Infection of Laboratory Worker with Vaccinia. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2003;9(6):724-726.
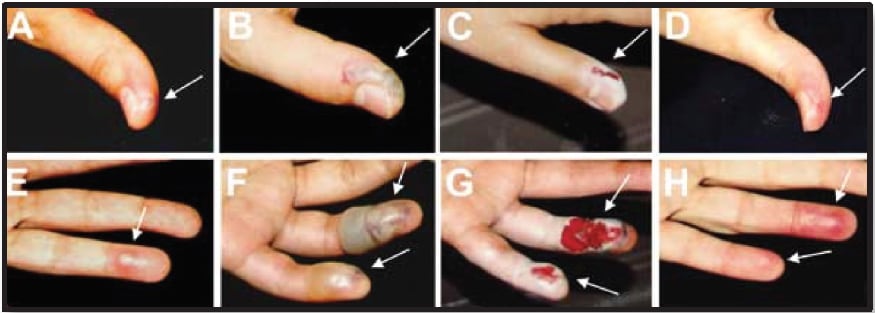
Progression of infection following an accidental needle stick inoculation with Vaccinia virus. From Moussatché et al, 2003.