Participating States and Success Stories
Participating States
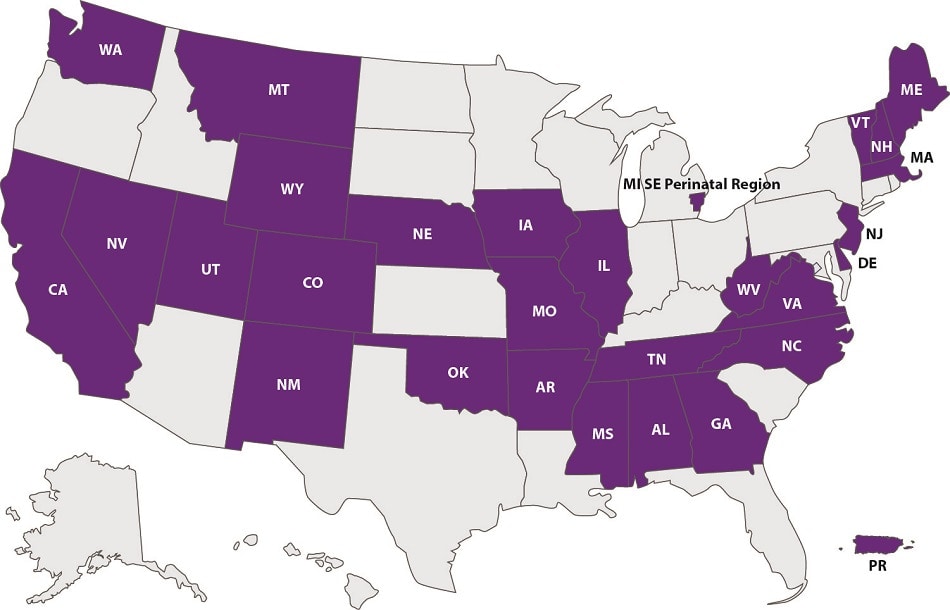
As of April 2023, a total of 27 states (Alabama, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Iowa, Maine, Massachusetts, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, Nevada, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, and Wyoming), the southeast perinatal region of Michigan, and Puerto Rico have successfully implemented CDC LOCATeSM.
Success Stories
The rate of severe maternal morbidity in Massachusetts has increased over time, with notable racial and ethnic disparities. Levels of Maternal Care is one strategy to reduce morbidity by ensuring pregnant and birthing people have equitable access to delivery centers that appropriately address their level of risk. The Perinatal-Neonatal Quality Improvement Network of Massachusetts (PNQIN) assembled a task force to implement CDC LOCATeSM to understand available resources by hospital and region across Massachusetts.
The Betsy Lehman Center for Patient Safety, a nonregulatory state agency focusing on safety and quality, administered CDC LOCATeSM to the 40 hospitals providing obstetric services in Massachusetts. In addition to the standard CDC LOCATeSM questions, the assessment included questions about hospital training and quality improvement practices relevant to health equity and patient safety. All 40 hospitals participated on a voluntary basis. As a result of their involvement with CDC LOCATeSM, each hospital received a detailed report of their results and were invited to discuss quality improvement opportunities offered by PNQIN, including a discussion of discrepancies between hospital self-reported Level of Maternal Care and CDC LOCATeSM-assessed Level of Maternal Care when applicable. These efforts help optimize equitable risk-appropriate obstetric care for patients and families.
Montana implemented CDC LOCATeSM to assess levels of maternal and neonatal care and collect data about facility capacity and service delivery in the state. The Montana Obstetrics and Maternal Support (MOMS) program was initiated by a 5-year grant awarded to the Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services from the Health Resources and Services Administration to reduce maternal morbidity and mortality in the state.
Because of the unique geographic landscape of Montana, addressing challenges associated with rural obstetric care requires statewide coordination of all available perinatal care. MOMS facilitates quality improvement in maternal care through the Montana Perinatal Quality Collaborative and the Alliance for Innovation in Maternal Health initiative.
MOMS also established Montana’s Maternal Mortality Review Committee and implemented the CDC LOCATeSM assessment as part of a broader effort to identify areas for improvement. CDC LOCATeSM contributes to these initiatives by providing Montana’s maternal health partners and facilities with important information related to health care preparedness and risk-appropriate care. Montana added a module to the end of the CDC LOCATeSM assessment to gather additional information on provider training, transport, medical products, and accessibility.
As a result of participating in CDC LOCATeSM, Montana launched an emergency obstetric services assessment to assess capacity and preparedness in critical access hospitals without an obstetric unit (i.e., facilities that do not participate in CDC LOCATeSM). Paired with CDC LOCATeSM, this assessment will contribute to statewide conversations on perinatal regionalization. Moving forward, Montana will focus on linking CDC LOCATeSM data to maternal hospital discharge data, birth certificate data, and infant death certificate data to identify opportunities for improving risk-appropriate care in the state.