Vulnerable Counties and Jurisdictions Experiencing or At-Risk of Outbreaks
A 2014-2015 outbreak of HIV infection among a rural network of persons who inject drugs (PWID) underscored the intersection of the expanding crises of opioid misuse, injection drug use, and associated increases in bloodborne infectious diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) conducted a national assessment to identify U.S. communities potentially vulnerable to rapid spread of HIV, if introduced, and new or continuing high rates of hepatitis C virus infections among PWID. Jurisdictions also consulted with CDC and provided evidence that their jurisdiction is experiencing or at risk for significant increases in hepatitis infections or an HIV outbreak due to injection drug use.
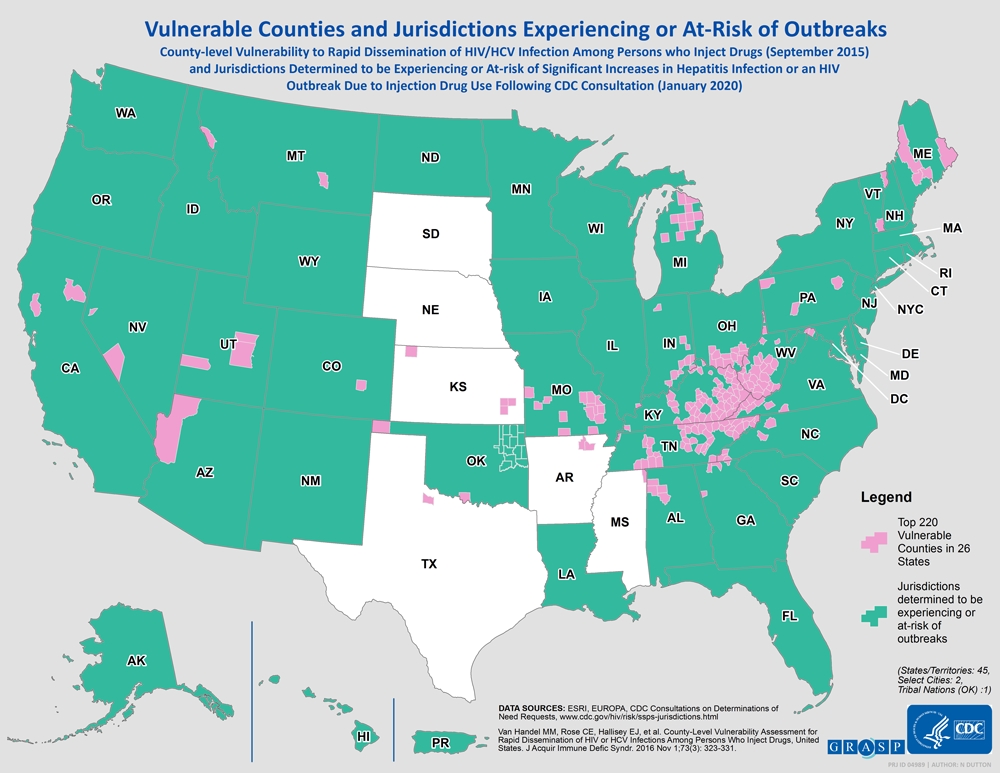
Map includes top 220 vulnerable counties determined to be at-risk of outbreaks from the 2016 national assessment (in pink), jurisdictions determined to be experiencing or at-risk of significant increases in viral hepatitis infection or HIV outbreak due to injection drug use following CDC consultation (in teal), and states that did not request a CDC consultation for experiencing or at-risk of significant increases in hepatitis infections or an HIV outbreak due to injection drug use (in white).
Data Sources: ESRI, EUROPA, CDC Consultations on Determinations of Need Requests
| State | County | Rank (of 220) |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Walker | 37 |
| Franklin | 206 | |
| Marion | 100 | |
| Winston | 109 | |
| Arizona | Mohave | 208 |
| Arkansas | Sharp | 157 |
| Lawrence | 201 | |
| California | Lake | 199 |
| Plumas | 152 | |
| Colorado | Crowley | 220 |
| Georgia | Murray | 159 |
| Towns | 120 | |
| Fannin | 82 | |
| Haralson | 200 | |
| Illinois | Hardin | 68 |
| Indiana | Crawford | 112 |
| Starke | 70 | |
| Switzerland | 94 | |
| Scott | 32 | |
| Washington | 57 | |
| Ripley | 195 | |
| Dearborn | 213 | |
| Jennings | 158 | |
| Fayette | 81 | |
| Henry | 128 | |
| Kansas | Rawlins | 218 |
| Woodson | 144 | |
| Allen | 171 | |
| Wilson | 181 | |
| Kentucky | Hickman | 191 |
| Menifee | 31 | |
| Breckinridge | 202 | |
| Lincoln | 97 | |
| Grayson | 126 | |
| Knott | 17 | |
| Perry | 4 | |
| Clay | 5 | |
| Laurel | 65 | |
| Leslie | 8 | |
| Adair | 93 | |
| Russell | 54 | |
| Wayne | 99 | |
| Cumberland | 101 | |
| Allen | 180 | |
| Clinton | 11 | |
| Monroe | 163 | |
| Green | 132 | |
| Edmonson | 179 | |
| Mercer | 214 | |
| Boyle | 35 | |
| Casey | 153 | |
| Taylor | 75 | |
| Powell | 15 | |
| Magoffin | 23 | |
| Garrard | 167 | |
| Lee | 30 | |
| Breathitt | 3 | |
| Owsley | 12 | |
| Rockcastle | 40 | |
| Estill | 25 | |
| Wolfe | 1 | |
| Knox | 9 | |
| Harlan | 45 | |
| Whitley | 14 | |
| McCreary | 48 | |
| Bell | 6 | |
| Letcher | 50 | |
| Johnson | 53 | |
| Martin | 34 | |
| Floyd | 10 | |
| Pike | 21 | |
| Gallatin | 108 | |
| Greenup | 129 | |
| Carroll | 67 | |
| Campbell | 212 | |
| Grant | 77 | |
| Lewis | 178 | |
| Carter | 154 | |
| Bath | 125 | |
| Robertson | 175 | |
| Elliott | 56 | |
| Lawrence | 39 | |
| Boyd | 187 | |
| Maine | Somerset | 145 |
| Washington | 170 | |
| Kennebec | 193 | |
| Waldo | 135 | |
| Michigan | Kalkaska | 207 |
| Alcona | 184 | |
| Crawford | 197 | |
| Oscoda | 88 | |
| Cheboygan | 215 | |
| Presque Isle | 174 | |
| Montmorency | 91 | |
| Roscommon | 192 | |
| Lake | 137 | |
| Clare | 87 | |
| Ogemaw | 86 | |
| Mississippi | Tishomingo | 164 |
| Missouri | Bates | 177 |
| Cedar | 107 | |
| St. Francois | 69 | |
| Hickory | 156 | |
| Wayne | 119 | |
| Ozark | 185 | |
| Wright | 194 | |
| Iron | 117 | |
| Madison | 58 | |
| Reynolds | 55 | |
| Ripley | 183 | |
| Crawford | 148 | |
| Washington | 130 | |
| Montana | Mineral | 161 |
| Treasure | 211 | |
| Nevada | Esmeralda | 118 |
| Storey | 52 | |
| North Carolina | Wilkes | 104 |
| Graham | 124 | |
| Cherokee | 189 | |
| Clay | 63 | |
| Burke | 176 | |
| Ohio | Brown | 127 |
| Adams | 51 | |
| Scioto | 136 | |
| Clinton | 190 | |
| Highland | 196 | |
| Pike | 72 | |
| Gallia | 155 | |
| Athens | 173 | |
| Vinton | 146 | |
| Jackson | 111 | |
| Meigs | 123 | |
| Oklahoma | Cimarron | 217 |
| Jefferson | 89 | |
| Pennsylvania | Crawford | 188 |
| Luzerne | 38 | |
| Cambria | 131 | |
| Tennessee | Lake | 216 |
| Benton | 24 | |
| Hardin | 36 | |
| McNairy | 141 | |
| Humphreys | 83 | |
| Perry | 33 | |
| Lewis | 168 | |
| Wayne | 160 | |
| Lawrence | 172 | |
| Hawkins | 71 | |
| Fentress | 115 | |
| Overton | 95 | |
| Carter | 59 | |
| Washington | 198 | |
| Smith | 140 | |
| Grainger | 66 | |
| Greene | 79 | |
| Morgan | 106 | |
| Hamblen | 138 | |
| Bledsoe | 139 | |
| Meigs | 105 | |
| DeKalb | 102 | |
| Cannon | 42 | |
| Warren | 203 | |
| Rhea | 103 | |
| White | 134 | |
| Jefferson | 149 | |
| Cocke | 41 | |
| Roane | 92 | |
| Polk | 142 | |
| Scott | 26 | |
| Campbell | 46 | |
| Union | 74 | |
| Pickett | 43 | |
| Clay | 64 | |
| Jackson | 19 | |
| Macon | 116 | |
| Claiborne | 80 | |
| Hancock | 13 | |
| Sullivan | 151 | |
| Johnson | 169 | |
| Texas | Foard | 204 |
| Utah | Carbon | 84 |
| Beaver | 114 | |
| Emery | 186 | |
| Vermont | Essex | 143 |
| Windham | 219 | |
| Virginia | Lee | 73 |
| Buchanan | 28 | |
| Tazewell | 96 | |
| Dickenson | 29 | |
| Wise | 78 | |
| Wythe | 210 | |
| Russell | 61 | |
| Patrick | 166 | |
| West Virginia | Logan | 20 |
| Raleigh | 18 | |
| Mercer | 147 | |
| Mingo | 7 | |
| Wyoming | 16 | |
| McDowell | 2 | |
| Summers | 110 | |
| Monroe | 47 | |
| Fayette | 27 | |
| Boone | 22 | |
| Hancock | 49 | |
| Brooke | 76 | |
| Marshall | 182 | |
| Calhoun | 90 | |
| Mason | 85 | |
| Roane | 165 | |
| Braxton | 150 | |
| Clay | 60 | |
| Wayne | 62 | |
| Kanawha | 209 | |
| Cabell | 122 | |
| Lincoln | 121 | |
| Tyler | 162 | |
| Taylor | 133 | |
| Webster | 113 | |
| Nicholas | 98 | |
| Morgan | 44 | |
| Berkeley | 205 |
508 ACCESSIBILITY of these resources: Section 508 requires Federal agencies to ensure that individuals with disabilities who are members of the public or Federal employees have access to and use of electronic and information technology that is comparable to that provided to individuals without disabilities, unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency. If you need assistance with the resources on this page, please contact NCHHSTPPolicy@cdc.gov and include “508 Accommodation” without quotes in the subject line of your email. In the body of the email, please specify the resources and the URL that you would like to access.