Control of Wood Dust From Horizontal Belt Sanders
1996
DHHS (NIOSH) Publication Number 96-121
Hazard
The use of horizontal belt sanders in woodworking creates significant amounts of wood dust. Workers exposed to wood dusts have experienced a variety of adverse health effects such as eye and skin irritation, allergy, reduced lung function, asthma, and nasal cancer. Therefore, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health* (NIOSH) recommends limiting wood dust exposures to prevent these health problems.
Controls
Surveys by NIOSH researchers indicated that wood dust from the horizontal belt sanders used in woodworking was not effectively controlled. As a result, researchers developed an inexpensive auxiliary ventilation system for the horizontal belt sanders that significantly reduced wood dust emissions into the workroom.
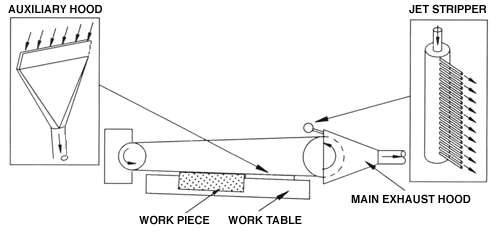
Auxiliary Ventilation System
Typically, belt sander emissions are controlled only by an exhaust hood covering the drive pulley. The new ventilation system reduced wood dust emitted into the workroom by more than 75% and can easily be built into new belt sanders or added to existing ones. The system consists of two devices: a narrow Auxiliary Hood and an Air Jet Stripper. (See ILLUSTRATION) The Auxiliary Hood is located between the belt surface and the worktable downstream from the sanding operation. The Air Jet Stripper is located inside the main exhaust hood. These two devices, in combination with the main exhaust hood, decrease wood dust in the workroom without affecting the sanding operations. In addition, the Jet Stripper cleans the belt, reducing the frequency of belt changes. This dust control device is not currently commercially available. Call NIOSH for more information.
*NIOSH is the Federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for preventing work-related illness and injuries. HAZARD CONTROLS are based on research studies that show reduced worker exposure to hazardous agents or activities.
Illustration: Top View of Belt Sander with Auxiliary Ventilation System
A technical report Control of Wood Dust from Horizontal Belt Sanding, Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 46(10):567 577(1985), has been published on this subject. Also, a videotape on this topic Innovations in Belt Sander Ventilation, Tape #180, 8 minutes, may be borrowed free of charge.
This document is one in a series of seven HAZARD CONTROLS concerning wood dust control techniques listed below that are available free upon request from NIOSH:
- HC4 Control of Wood Dust from Horizontal Belt Sanders
- HC5 Control of Wood Dust from Shapers
- HC6 Control of Wood Dust from Automated Routers
- HC7 Control of Wood Dust from Large Diameter Disc Sanders
- HC8 Control of Wood Dust from Random Orbital Hand Sanders
- HC9 Control of Wood Dust from Orbital Hand Sanders
- HC10 Control of Wood Dust from Table Saws
Acknowledgments
The principal contributors to this HAZARD CONTROLS are Jennifer L. Topmiller, Division of Physical Sciences and Engineering, and Jerome P. Flesch, Education and Information Division, NIOSH.
This document is in the public domain and may be freely copied or reprinted. NIOSH encourages all readers of this HAZARD CONTROLS to make it available to all interested employers and workers.
Control of Wood Dust From Horizontal Belt Sanders pdf icon[PDF – 177 KB]
