Estimates of New HIV Infections in the United States, 2006-2009
Images and graphics highlighting major findings of the report are available for download. These high-resolution, public domain images are ready to print in your publication.
These images are in the public domain and are thus free of any copyright restrictions. As a matter of courtesy, we request that the content provider be credited and notified of any public or private usage of an image.
This bar chart shows in 2009 an estimated: 11,400 new HIV infections occurred among white men who have sex with men; 10,800 were among black men who have sex with men; 6,000 were among Hispanic men who have sex with men; 5,400 were among black heterosexual women; 2,400 were among black heterosexual men; 1,700 were among Hispanic heterosexual women; 1,700 were among white heterosexual women; 1,200 were among black, male injection drug users; and 940 were among black, female injection drug users.
This chart shows in the U.S. in 2009, 61 percent of new HIV infections were among men who have sex with men; 27 percent among heterosexuals; 9 percent among injection drug users; and 3 percent among men who reported both having sex with men & using injection drugs.
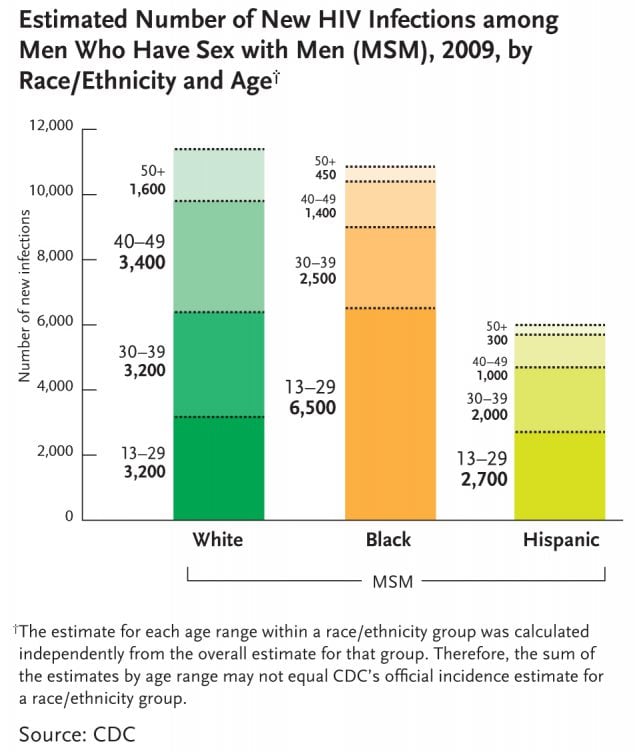
This chart breaks down the number of new HIV infections among men who have sex with men in the U.S. in 2009 by race/ethnicity and age, showing: among white men who have sex with men, most new infections occurred among those aged 40-49 (3,400 new infections), followed by those aged 13-29 and 30-29 (3,200 each). 1,600 infections occurred among white men who have sex with men aged 50+. Among black men who have sex with men, most new infections occurred among those aged 13-29 (6,500), followed by those aged 30-39 (2,500), then those aged 40-49 (1,400). 450 new infections occurred among black men who have sex with men aged 50+. Among Hispanic men who have sex with men, most new infections occurred among those aged 13-29 (2,700), followed by those aged 30-39 (2,000) and those aged 40-49 (1,000). 300 new infections occurred among Hispanic men who have sex with men aged 50+. (Note: The estimate for each age range within a race/ethnicity group was calculated independently from the overall estimate for that group. Therefore, the sum of the estimates by age range may not equal CDC’s official incidence estimate for a race/ethnicity group.)
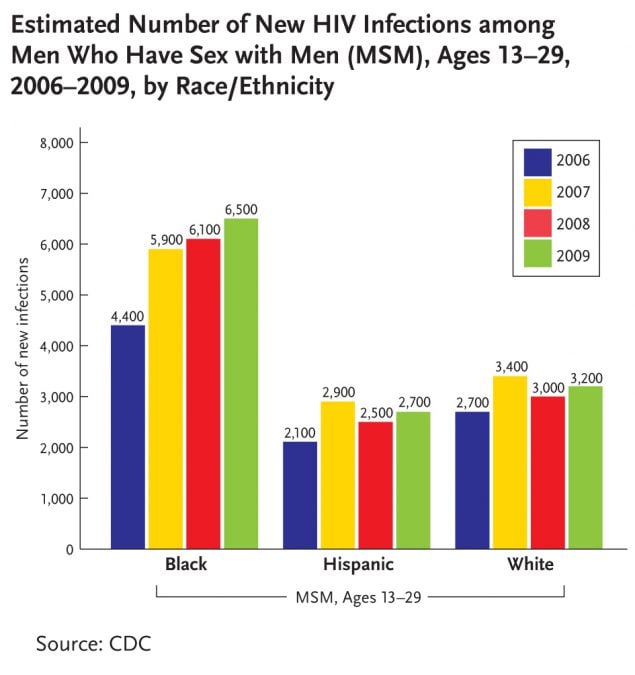
This bar chart shows the number of new infections among men who have sex with men aged 13-29 in the U.S. broken down by age and by year of infection between 2006 and 2009. In 2006, 4,400 new infections occurred among black men who have sex with men in this age group, 5,900 in 2007, 6,100 in 2008, and 6,500 in 2009. In 2006, 2,100 new infections occurred among Hispanic men who have sex with men in this age group, 2,900 in 2007, 2,500 in 2008, and 2,700 in 2009. In 2006, 2,700 new infections occurred among white men who have sex with men in this age group, 3,400 in 2007, 3,000 in 2008, and 3,200 in 2009.
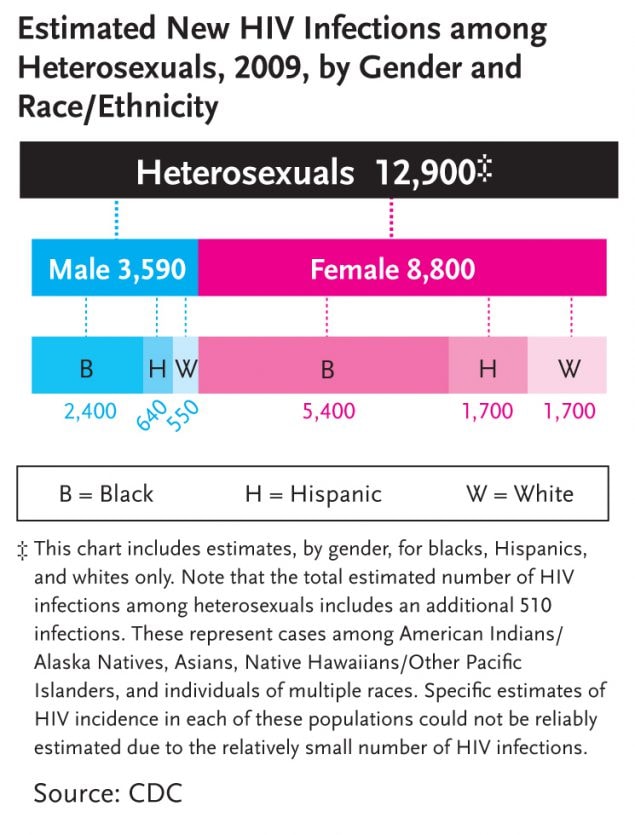
This graph shows that in the US in 2009, an estimated 12,900 new HIV infections occurred among heterosexuals. 3,590 of those were among males and 8,800 among females. Among males by race/ethnicity, 2,400 were among blacks, 640 were among Hispanics and 550 were among whites. Among females by race/ethnicity, 5,400 were among blacks, 1,700 were among Hispanics and 1,700 were among whites. (Note: This chart includes estimates, by gender, for blacks, Hispanics and whites only. Note that the total estimated numbers of HIV infections among heterosexuals includes an additional 510 infections. These represent cases among American Indians/Alaska Natives, Asians, Native Hawaiians/Other Pacific Islanders, and individuals of multiple races. Specific estimates of HIV incidence in each of these populations could not be reliably estimated due to the relatively small number of HIV infections.)
This graph shows that in the US in 2009, an estimated 4,500 new HIV infections occurred among injection drug users. 2,400 of those were among males and 1,960 among females. Among males by race/ethnicity, 1,200 were among blacks, 560 were among Hispanics and 640 were among whites. Among females by race/ethnicity, 940 were among blacks, 370 were among Hispanics and 650 were among whites. (Note: This chart includes estimates, by gender, for blacks, Hispanics and whites only. (Note that the total estimated numbers of HIV infections among heterosexuals includes an additional 140 infections. These represent cases among American Indians/Alaska Natives, Asians, Native Hawaiians/Other Pacific Islanders, and individuals of multiple races. Specific estimates of HIV incidence in each of these populations could not be reliably estimated due to the relatively small number of HIV infections.)
This graph shows that in the US in 2009 the rate of new HIV infections among black males was 103.9 cases per 100,000 population, the rate for Hispanic males was 39.9 cases per 100,000 population, and the rate for white males was 15.9 cases per 100,000 population. The rate among black females was 39.7 cases per 100,000 population, the rate for Hispanic females was 11.8 cases per 100,000 population, and the rate among white women was 2.6 cases per 100,000 population.